|
Palestine Grid
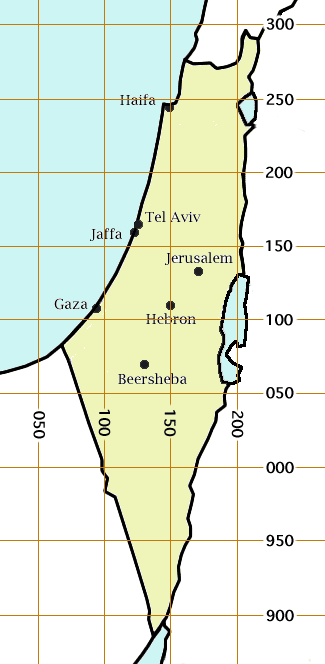
The Palestine grid was the geographic coordinate system used by the Survey Department of Palestine. The system was chosen by the Survey Department of the Government of Palestine in 1922. The projection used was the Cassini-Soldner projection. The central meridian (the line of longitude along which there is no local distortion) was chosen as that passing through a marker on the hill of Mar Elias Monastery south of Jerusalem. The false origin (zero point) of the grid was placed 100 km to the south and west of the Ali el-Muntar hill that overlooks Gaza city. The unit length for the grid was the kilometre; the British units were not even considered. At the time the grid was established, there was no intention of mapping the lower reaches of the Negev Desert, but this did not remain true. Those southern regions having a negative north-south coordinate then became a source of confusion, which was solved by adding 1000 to the northern coordinate in that case. For some military pu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transverse Mercator
The transverse Mercator map projection (TM, TMP) is an adaptation of the standard Mercator projection. The transverse version is widely used in national and international mapping systems around the world, including the Universal Transverse Mercator. When paired with a suitable geodetic datum, the transverse Mercator delivers high accuracy in zones less than a few degrees in east-west extent. Standard and transverse aspects The transverse Mercator projection is the transverse aspect of the standard (or ''Normal'') Mercator projection. They share the same underlying mathematical construction and consequently the transverse Mercator inherits many traits from the normal Mercator: * Both projections are cylindrical: for the Normal Mercator, the axis of the cylinder coincides with the polar axis and the line of tangency with the equator. For the transverse Mercator, the axis of the cylinder lies in the equatorial plane, and the line of tangency is any chosen meridian, thereby designa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geography Of Mandatory Palestine
Geography (from Greek: , ''geographia''. Combination of Greek words ‘Geo’ (The Earth) and ‘Graphien’ (to describe), literally "earth description") is a field of science devoted to the study of the lands, features, inhabitants, and phenomena of Earth. The first recorded use of the word γεωγραφία was as a title of a book by Greek scholar Eratosthenes (276–194 BC). Geography is an all-encompassing discipline that seeks an understanding of Earth and its human and natural complexities—not merely where objects are, but also how they have changed and come to be. While geography is specific to Earth, many concepts can be applied more broadly to other celestial bodies in the field of planetary science. One such concept, the first law of geography, proposed by Waldo Tobler, is "everything is related to everything else, but near things are more related than distant things." Geography has been called "the world discipline" and "the bridge between the human and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geographic Coordinate Systems
The geographic coordinate system (GCS) is a spherical or ellipsoidal coordinate system for measuring and communicating positions directly on the Earth as latitude and longitude. It is the simplest, oldest and most widely used of the various spatial reference systems that are in use, and forms the basis for most others. Although latitude and longitude form a coordinate tuple like a cartesian coordinate system, the geographic coordinate system is not cartesian because the measurements are angles and are not on a planar surface. A full GCS specification, such as those listed in the EPSG and ISO 19111 standards, also includes a choice of geodetic datum (including an Earth ellipsoid), as different datums will yield different latitude and longitude values for the same location. History The invention of a geographic coordinate system is generally credited to Eratosthenes of Cyrene, who composed his now-lost ''Geography'' at the Library of Alexandria in the 3rd century BC. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elyashiv
Elyashiv (, ''lit.'' God will bring back) is a moshav in central Israel. Located in the Sharon plain, it falls under the jurisdiction of Hefer Valley Regional Council. In it had a population of . History The moshav was founded on a site once occupied by the Arab village Khirbet esh Sheikh Mohammed ("The ruin of Sheikh Mohammed").Pringle, 1986, p. 71 Kh. esh Sheikh Muhammed became settled during the rule of Ibrahim Pasha, either by Egyptians or by hamulas (extended families) from mountain villages. In 1882, the PEF's ''Survey of Western Palestine'' found that it consisted of a few adobe huts among ruins. Ancient glazed pottery has been found there. Although Yemenite neighborhoods had been established near many agricultural settlements, it was not until 1930 that independent Yemenite settlements were approved.Sharaby, 1998, p.21 After a prolonged struggle by the Yemenite Workers Federation in Palestine, three moshav ovdim were established: Marmorek in 1930, Tirat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dome Of The Rock
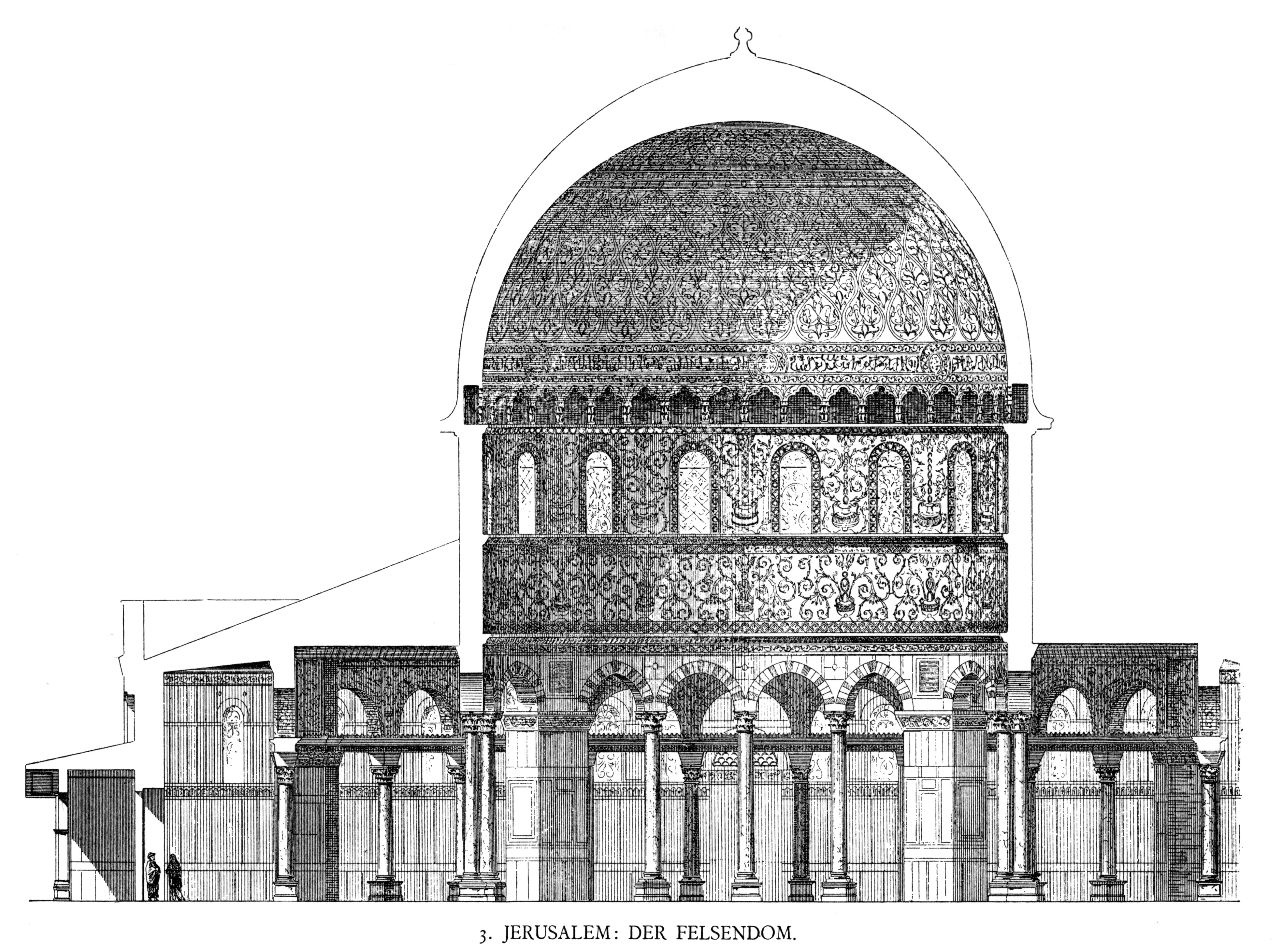
The Dome of the Rock ( ar, قبة الصخرة, Qubbat aṣ-Ṣakhra) is an Islamic shrine located on the Temple Mount in the Old City of Jerusalem, a site also known to Muslims as the ''al-Haram al-Sharif'' or the Al-Aqsa Compound. Its initial construction was undertaken by the Umayyad Caliphate on the orders of Abd al-Malik during the Second Fitna in 691–692 CE, and it has since been situated on top of the site of the Second Jewish Temple (built in to replace the destroyed Solomon's Temple), which was destroyed by the Romans in 70 CE. The original dome collapsed in 1015 and was rebuilt in 1022–23. The Dome of the Rock is the world's oldest surviving work of Islamic architecture. Its architecture and mosaics were patterned after nearby Byzantine churches and palaces, although its outside appearance was significantly changed during the Ottoman period and again in the modern period, notably with the addition of the gold-plated roof, in 1959–61 and again in 1993. The oc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Nations Palestine Map Showing Armistice Agreements Between Israel & Lebanon, Syria, Jordan & Egypt 1949-1950
United may refer to: Places * United, Pennsylvania, an unincorporated community * United, West Virginia, an unincorporated community Arts and entertainment Films * ''United'' (2003 film), a Norwegian film * ''United'' (2011 film), a BBC Two film Literature * ''United!'' (novel), a 1973 children's novel by Michael Hardcastle Music * United (band), Japanese thrash metal band formed in 1981 Albums * ''United'' (Commodores album), 1986 * ''United'' (Dream Evil album), 2006 * ''United'' (Marvin Gaye and Tammi Terrell album), 1967 * ''United'' (Marian Gold album), 1996 * ''United'' (Phoenix album), 2000 * ''United'' (Woody Shaw album), 1981 Songs * "United" (Judas Priest song), 1980 * "United" (Prince Ital Joe and Marky Mark song), 1994 * "United" (Robbie Williams song), 2000 * "United", a song by Danish duo Nik & Jay featuring Lisa Rowe Television * ''United'' (TV series), a 1990 BBC Two documentary series * ''United!'', a soap opera that aired on BBC One from 1965-19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Israeli Transverse Mercator
Israeli Transverse Mercator (ITM), also known as the New Israel Grid (NIG; he, רשת ישראל חדשה, רשת ישראל החדשה ''Reshet Yisra'el Ha-Ḥadasha'') is the new geographic coordinate system for Israel. The name is derived from the transverse Mercator projection it uses and the fact that it is optimized for Israel. ITM has replaced the old coordinate system Israeli Cassini Soldner (ICS), also known as the Old Israel Grid (OIG). It became the official grid for Israel in 1998. The need for a new grid ITM replaced the Old Israel Grid (OIG) ( he, רשת ישראל ישנה), also known as the Israel Cassini Soldner (ICS), which was based on the Cassini-Soldner projection. ICS in turn was a simple modification of the Palestine grid used during the British mandate. The central meridian in the new projection, as in the old one, crosses through Jerusalem. The new grid has two main advantages. One is that the Transverse Mercator projection is better for navigation th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Israeli Cassini Soldner
Israeli Cassini Soldner (ICS), commonly known as the Old Israeli Grid (OIG; he, רשת ישראל הישנה ''Reshet Yisra'el Ha-Yeshana'') is the old geographic coordinate system for Israel. The name is derived from the Cassini Soldner projection it uses and the fact that it is optimized for Israel. ICS has been mostly replaced by the new coordinate system Israeli Transverse Mercator (ITM), also known as the New Israeli Grid (NIG), but still referenced by older books and navigation software. History The Cassini Soldner projection was used by the British Mandate of Palestine, when it was called the Palestine grid. The Palestine grid reached as south as Beer-Sheba. To avoid the existence of negative coordinates in the southern Negev, the False Northing of ICS was increased by 1000000. As a result, coordinates in the south of Israel are higher than 800000. Examples An ICS coordinate is generally given as a pair of two numbers (excluding any digits behind a decimal point which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Israel
Israel (; he, יִשְׂרָאֵל, ; ar, إِسْرَائِيل, ), officially the State of Israel ( he, מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל, label=none, translit=Medīnat Yīsrāʾēl; ), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated on the southeastern shore of the Mediterranean Sea and the northern shore of the Red Sea, and shares borders with Lebanon to the north, Syria to the northeast, Jordan to the east, and Egypt to the southwest. Israel also is bordered by the Palestinian territories of the West Bank and the Gaza Strip to the east and west, respectively. Tel Aviv is the economic and technological center of the country, while its seat of government is in its proclaimed capital of Jerusalem, although Israeli sovereignty over East Jerusalem is unrecognized internationally. The land held by present-day Israel witnessed some of the earliest human occupations outside Africa and was among the earliest known sites of agriculture. It was inhabited by the Canaanites ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis powers. World War II was a total war that directly involved more than 100 million personnel from more than 30 countries. The major participants in the war threw their entire economic, industrial, and scientific capabilities behind the war effort, blurring the distinction between civilian and military resources. Aircraft played a major role in the conflict, enabling the strategic bombing of population centres and deploying the only two nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II was by far the deadliest conflict in human history; it resulted in 70 to 85 million fatalities, mostly among civilians. Tens of millions died due to genocides (including the Holocaust), starvation, ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geographic Coordinate System
The geographic coordinate system (GCS) is a spherical or ellipsoidal coordinate system for measuring and communicating positions directly on the Earth as latitude and longitude. It is the simplest, oldest and most widely used of the various spatial reference systems that are in use, and forms the basis for most others. Although latitude and longitude form a coordinate tuple like a cartesian coordinate system, the geographic coordinate system is not cartesian because the measurements are angles and are not on a planar surface. A full GCS specification, such as those listed in the EPSG and ISO 19111 standards, also includes a choice of geodetic datum (including an Earth ellipsoid), as different datums will yield different latitude and longitude values for the same location. History The invention of a geographic coordinate system is generally credited to Eratosthenes of Cyrene, who composed his now-lost ''Geography'' at the Library of Alexandria in the 3rd century ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |