|
Pad Abort Test 2
Pad Abort Test 2 was the follow-on second abort test to Pad Abort Test 1 of the Apollo spacecraft . Objectives Apollo Pad Abort Test 2 was the fifth of six uncrewed Apollo missions that flight tested the capability of the launch escape system (LES) to provide for safe recovery of Apollo crews under critical abort conditions. This flight was the second test of the launch escape system with the abort initiated from the launch pad. The launch escape system included qualified launch escape and pitch motors and was equipped with canards to orient the vehicle aft heat shield forward prior to tower jettison and parachute deployment. A boost protective cover was also provided. The spacecraft was BP-23A, a boilerplate Apollo command module that had been used on mission A-002 A-002 was the third abort test of the Apollo spacecraft. Objectives Mission A-002 was the third in the series of abort tests to demonstrate that the launch system would perform satisfactorily under selected criti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research. NASA was established in 1958, succeeding the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA), to give the U.S. space development effort a distinctly civilian orientation, emphasizing peaceful applications in space science. NASA has since led most American space exploration, including Project Mercury, Project Gemini, the 1968-1972 Apollo Moon landing missions, the Skylab space station, and the Space Shuttle. NASA supports the International Space Station and oversees the development of the Orion spacecraft and the Space Launch System for the crewed lunar Artemis program, Commercial Crew spacecraft, and the planned Lunar Gateway space station. The agency is also responsible for the Launch Services Program, which provides oversight of launch operations and countdown management f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
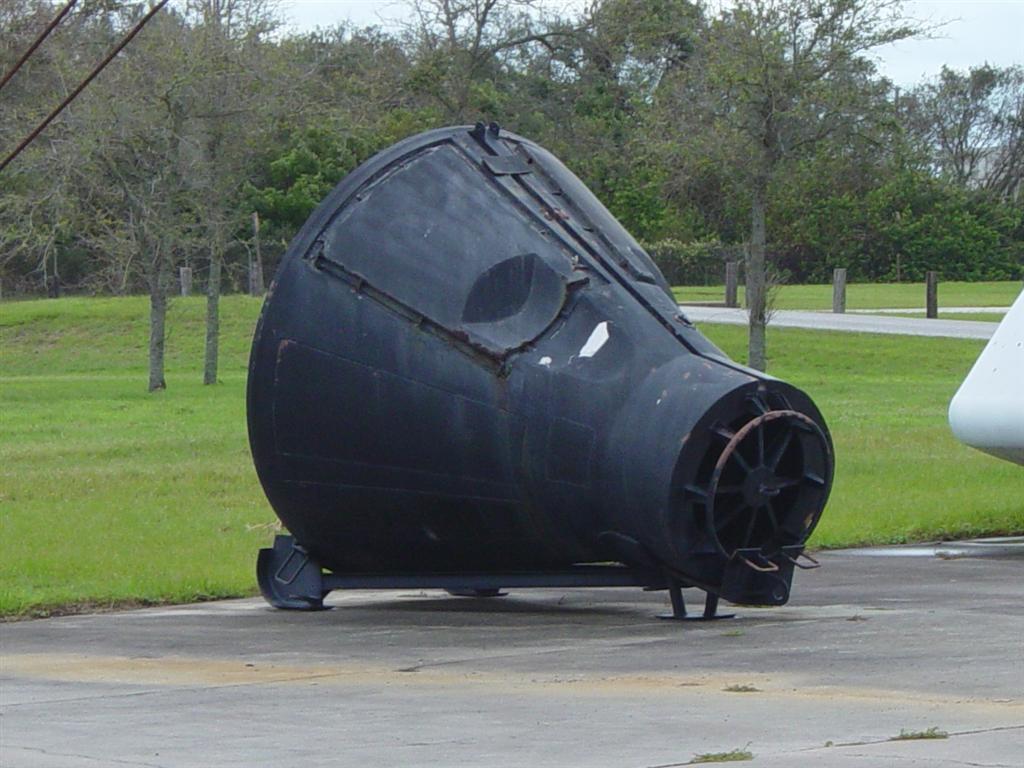
Boilerplate (spaceflight)
A boilerplate spacecraft, also known as a mass simulator, is a nonfunctional craft or payload that is used to test various configurations and basic size, load, and handling characteristics of rocket launch vehicles. It is far less expensive to build multiple, full-scale, non-functional boilerplate spacecraft than it is to develop the full system (design, test, redesign, and launch). In this way, boilerplate spacecraft allow components and aspects of cutting-edge aerospace projects to be tested while detailed contracts for the final project are being negotiated. These tests may be used to develop procedures for mating a spacecraft to its launch vehicle, emergency access and egress, maintenance support activities, and various transportation processes. Boilerplate spacecraft are most commonly used to test crewed spacecraft; for example, in the early 1960s, NASA performed many tests using boilerplate Apollo spacecraft atop Saturn I rockets, and Mercury spacecraft atop Atlas rocke ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1965 In The United States
Events from the year 1965 in the United States. Incumbents Federal Government * President: Lyndon B. Johnson ( D-Texas) * Vice President: ''vacant'' (until January 20), Hubert Humphrey ( D-Minnesota) (starting January 20) * Chief Justice: Earl Warren (California) * Speaker of the House of Representatives: John William McCormack ( D-Massachusetts) * Senate Majority Leader: Mike Mansfield ( D-Montana) * Congress: 88th (until January 3), 89th (starting January 3) Events January * January 1 – The ship '' S.S. Catala'' is driven onto the beach in Ocean Shores, Washington, stranding her. * January 4 – President Lyndon B. Johnson proclaims his "Great Society" during his State of the Union Address. * January 19 – The unmanned ''Gemini 2'' is launched on a suborbital test of various spacecraft systems. * January 20 – President Lyndon B. Johnson begins his full term. Hubert Humphrey is sworn in as Vice President of the United States. February * Februa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A-105
A105 may refer to: Roads * A105 road (England), a road in London connecting Canonbury and Enfield * A105 motorway (France), a road near Combs-la-Ville * A105 is the route number of the Rublevo-Uspenskoe Shosse west of Moscow Other uses * AS-105, a 1965 spaceflight in the Apollo program * Austin A105 A105 may refer to: Roads * A105 road (England), a road in London connecting Canonbury and Enfield * A105 motorway (France), a road near Combs-la-Ville * A105 is the route number of the Rublevo-Uspenskoe Shosse west of Moscow Other uses * AS-105 ..., a 1956 British car, in Austin's ''Westminster'' series * RFA Easedale (A105), a 1941 Royal Fleet Auxiliary fleet tanker ship * ASTM A105, a grade of carbon steel {{Letter-NumberCombDisambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A-104
A104, A.104 or A-104 may refer to: * AS-104, a 1965 spaceflight in the Apollo program * Aero A.104, a 1937 Czechoslovakian biplane light bomber and reconnaissance aircraft * Agusta A.104, a 1960 Italian prototype light helicopter * RFA Eaglesdale (A104), a 1941 Royal Fleet Auxiliary fleet tanker ship Roads * A104 roads, a disambiguation page {{Letter-NumberCombDisambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canard (aeronautics)
In aeronautics, a canard is a wing configuration in which a small forewing or foreplane is placed forward of the main wing of a fixed-wing aircraft or a weapon. The term "canard" may be used to describe the aircraft itself, the wing configuration, or the foreplane.. Canard wings are also extensively used in guided missiles and smart bombs. The term "canard" arose from the appearance of the Santos-Dumont 14-bis of 1906, which was said to be reminiscent of a duck (''canard'' in French) with its neck stretched out in flight. Despite the use of a canard surface on the first powered aeroplane, the Wright Flyer of 1903, canard designs were not built in quantity until the appearance of the Saab Viggen jet fighter in 1967. The aerodynamics of the canard configuration are complex and require careful analysis. Rather than use the conventional tailplane configuration found on most aircraft, an aircraft designer may adopt the canard configuration to reduce the main wing loading, to better ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A-002
A-002 was the third abort test of the Apollo spacecraft. Objectives Mission A-002 was the third in the series of abort tests to demonstrate that the launch system would perform satisfactorily under selected critical abort conditions. The main objective of this mission was to demonstrate the abort capability of the launch escape vehicle in the maximum dynamic pressure region of the Saturn trajectory with conditions approximating the altitude limit at which the Saturn emergency detection system would signal an abort. The launch vehicle was the third in the Little Joe II series. This vehicle differed from the previous two in that flight controls and instrumentation were incorporated, and the vehicle was powered by two Algol and four Recruit rocket motors. The launch escape system was also changed from previous configurations in that canards (forward control surfaces used to orient and stabilize the escape vehicle in the entry attitude) and a command module boost protective cover w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
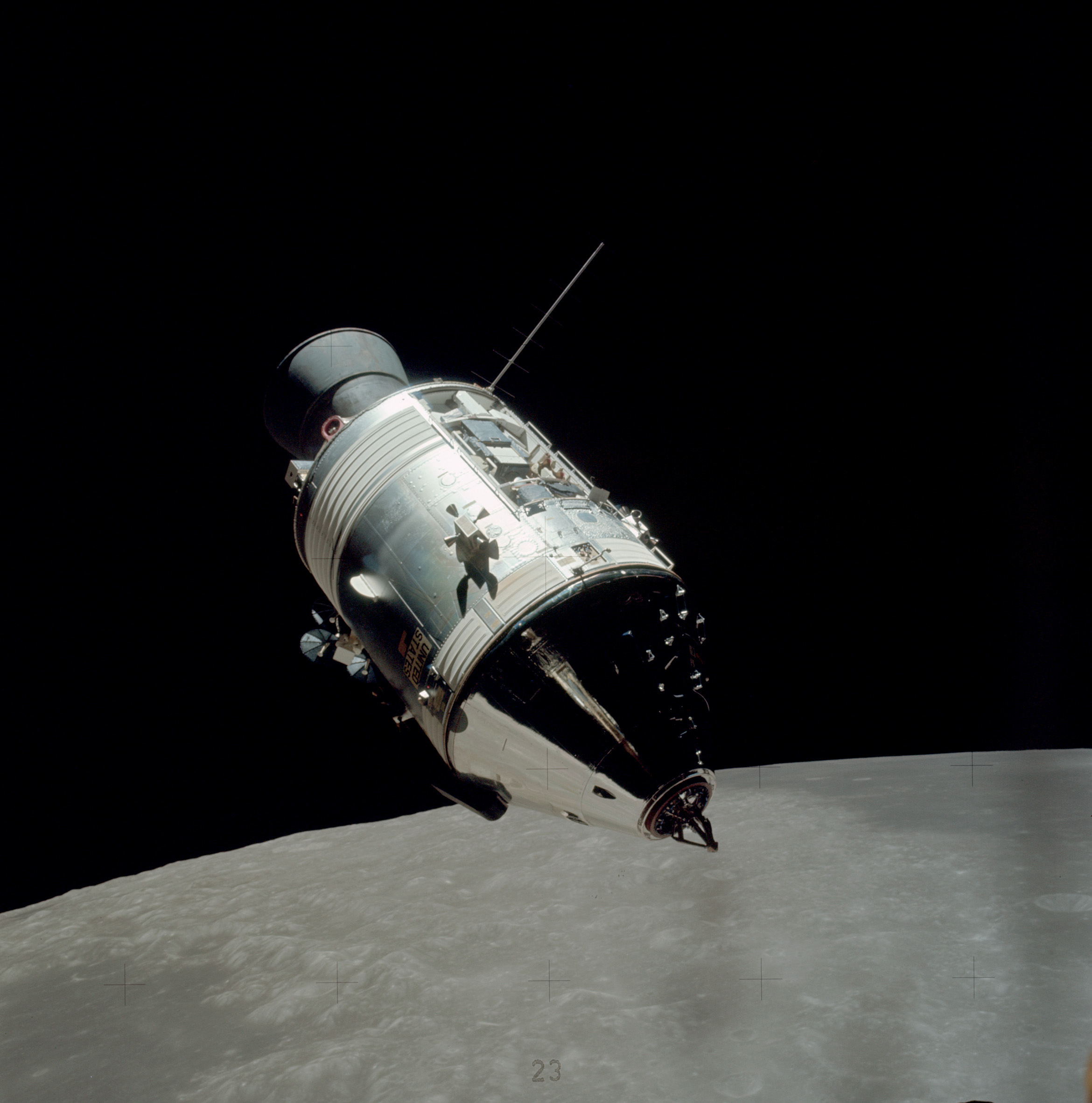
Apollo Command Module
The Apollo command and service module (CSM) was one of two principal components of the United States Apollo spacecraft, used for the Apollo program, which landed astronauts on the Moon between 1969 and 1972. The CSM functioned as a mother ship, which carried a crew of three astronauts and the second Apollo spacecraft, the Apollo Lunar Module, to lunar orbit, and brought the astronauts back to Earth. It consisted of two parts: the conical command module, a cabin that housed the crew and carried equipment needed for atmospheric reentry and splashdown; and the cylindrical service module which provided propulsion, electrical power and storage for various consumables required during a mission. An umbilical connection transferred power and consumables between the two modules. Just before reentry of the command module on the return home, the umbilical connection was severed and the service module was cast off and allowed to burn up in the atmosphere. The CSM was developed and built f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
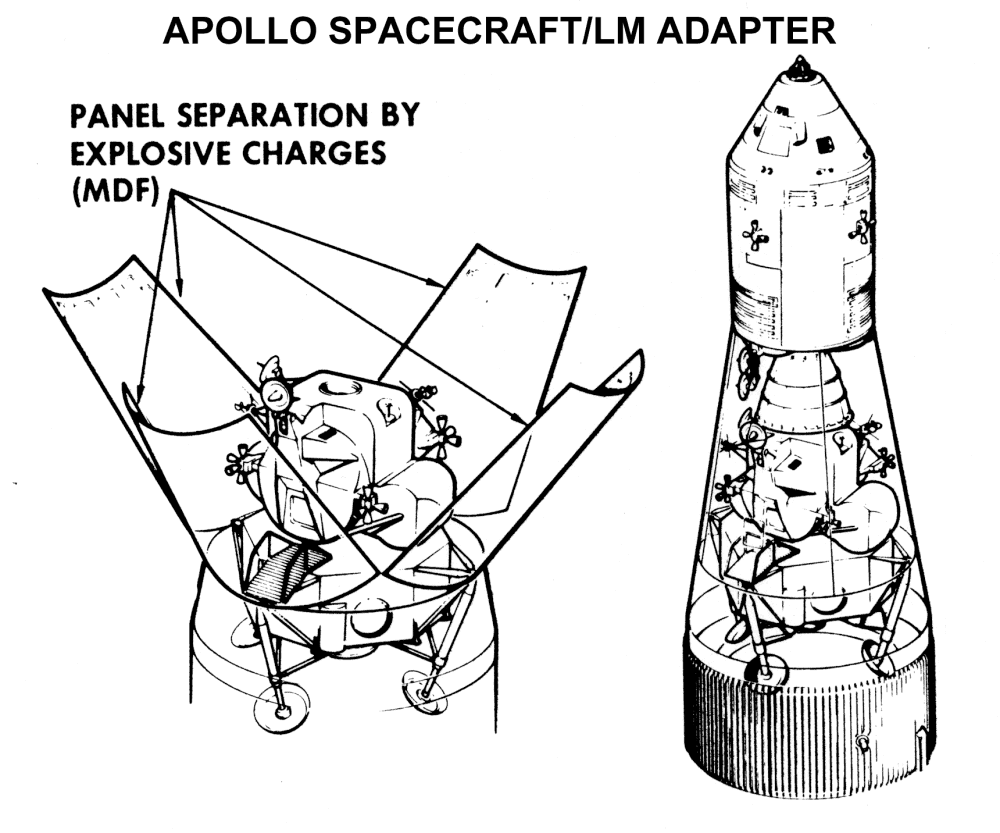
Apollo Spacecraft
The Apollo spacecraft was composed of three parts designed to accomplish the American Apollo program's goal of landing astronauts on the Moon by the end of the 1960s and returning them safely to Earth. The expendable (single-use) spacecraft consisted of a combined command and service module (CSM) and an Apollo Lunar Module (LM). Two additional components complemented the spacecraft stack for space vehicle assembly: a spacecraft–LM adapter (SLA) designed to shield the LM from the aerodynamic stress of launch and to connect the CSM to the Saturn launch vehicle and a launch escape system (LES) to carry the crew in the command module safely away from the launch vehicle in the event of a launch emergency. The design was based on the lunar orbit rendezvous approach: two docked spacecraft were sent to the Moon and went into lunar orbit. While the LM separated and landed, the CSM remained in orbit. After the lunar excursion, the two craft rendezvoused and docked in lunar orbit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apollo (spacecraft)
The Apollo spacecraft was composed of three parts designed to accomplish the American Apollo program's goal of landing astronauts on the Moon by the end of the 1960s and returning them safely to Earth. The expendable (single-use) spacecraft consisted of a combined command and service module (CSM) and an Apollo Lunar Module (LM). Two additional components complemented the spacecraft stack for space vehicle assembly: a spacecraft–LM adapter (SLA) designed to shield the LM from the aerodynamic stress of launch and to connect the CSM to the Saturn launch vehicle and a launch escape system (LES) to carry the crew in the command module safely away from the launch vehicle in the event of a launch emergency. The design was based on the lunar orbit rendezvous approach: two docked spacecraft were sent to the Moon and went into lunar orbit. While the LM separated and landed, the CSM remained in orbit. After the lunar excursion, the two craft rendezvoused and docked in lunar orbit, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pad Abort Test 1
Pad Abort Test 1 was the first abort test of the Apollo spacecraft on November 7, 1963. Objectives Pad Abort Test 1 was a mission to investigate the effects on the Apollo spacecraft during an abort from the pad. The launch escape system (LES) had to be able to pull the spacecraft away from an exploding rocket on the launch pad. The LES then had to gain enough altitude to allow the command module's parachutes to open, preferably with the spacecraft over water and not land. The flight featured a production model LES and a boilerplate (BP-06) Apollo spacecraft, the first mission to feature one. The spacecraft carried no instruments for measuring structural loads as the capsule's boilerplate structure did not represent that of a real spacecraft. Flight On November 7, 1963, an abort signal was sent to the LES at 09:00:01 local time. This began a sequence in which the main solid rockets fired to lift the spacecraft and smaller attitude rockets fired to move it laterally toward the o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pad Abort Test
A pad abort test is a kind of test of a launch escape system which conducted by setting the system along with the spacecraft still on the ground and let the system activate to carry the spacecraft flying away, then separate in the air and make the spacecraft land safely. The purpose of the test is to determine how well the system could get the crew of a spacecraft to safety in an emergency on the launch pad. As the spacecraft is set still on the ground, the test is also called "zero-altitude abort test" in against "high-altitude abort test". Project Mercury ''Section sources.'' The Mercury program included several pad abort tests for the launch escape system with a boilerplate crew module. * 1959 July 22 – First successful pad abort flight test with a functional escape tower attached to a Mercury boilerplate * 1959 July 28 – A Mercury boilerplate with instruments to measure sound pressure levels and vibrations from the Little Joe test rocket and Grand Central abort rocket/ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_(9256079273).jpg)