|
Pachypleurosaur
left, 220px, '' Pachypleurosaurus'' Pachypleurosauria is an extinct clade of primitive sauropterygian reptiles that vaguely resembled aquatic lizards, and were limited to the Triassic period. They were elongate animals, ranging in size from , with small heads, long necks, paddle-like limbs, and long, deep tails. The limb girdles are greatly reduced, so it is unlikely these animals could move about on land. The widely spaced peg-like teeth project at the front of the jaws, indicating that these animals fed on fish. In the species ''Prosantosaurus'', it was observed that they fed on small fishes and crustaceans which they devoured entirely and that its teeth regrew after they broke off. This was the first observation of tooth replacement in a European pachypleurosaur, the only other discovery of such an event was made in China. Classification Pachypleurosaurs were originally and are often still included within the Nothosauroidea (Carroll 1988, Benton 2004). In some more recent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dactylosaurus
''Dactylosaurus'' is a genus of nothosaur in the family Pachypleurosauridae. Along with '' Anarosaurus'', ''Dactylosaurus'' was one of the earliest known pachypleurosaurs to come from Europe.Lepidosauromorpha: Pachypleurosauridae: Dactylosaurus & Anarosaurus Palaeos.com. Last accessed 2008-07-04. Etymology ''Dactylosaurus'' comes from the ' (), "" and ' (), meaning "" or ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
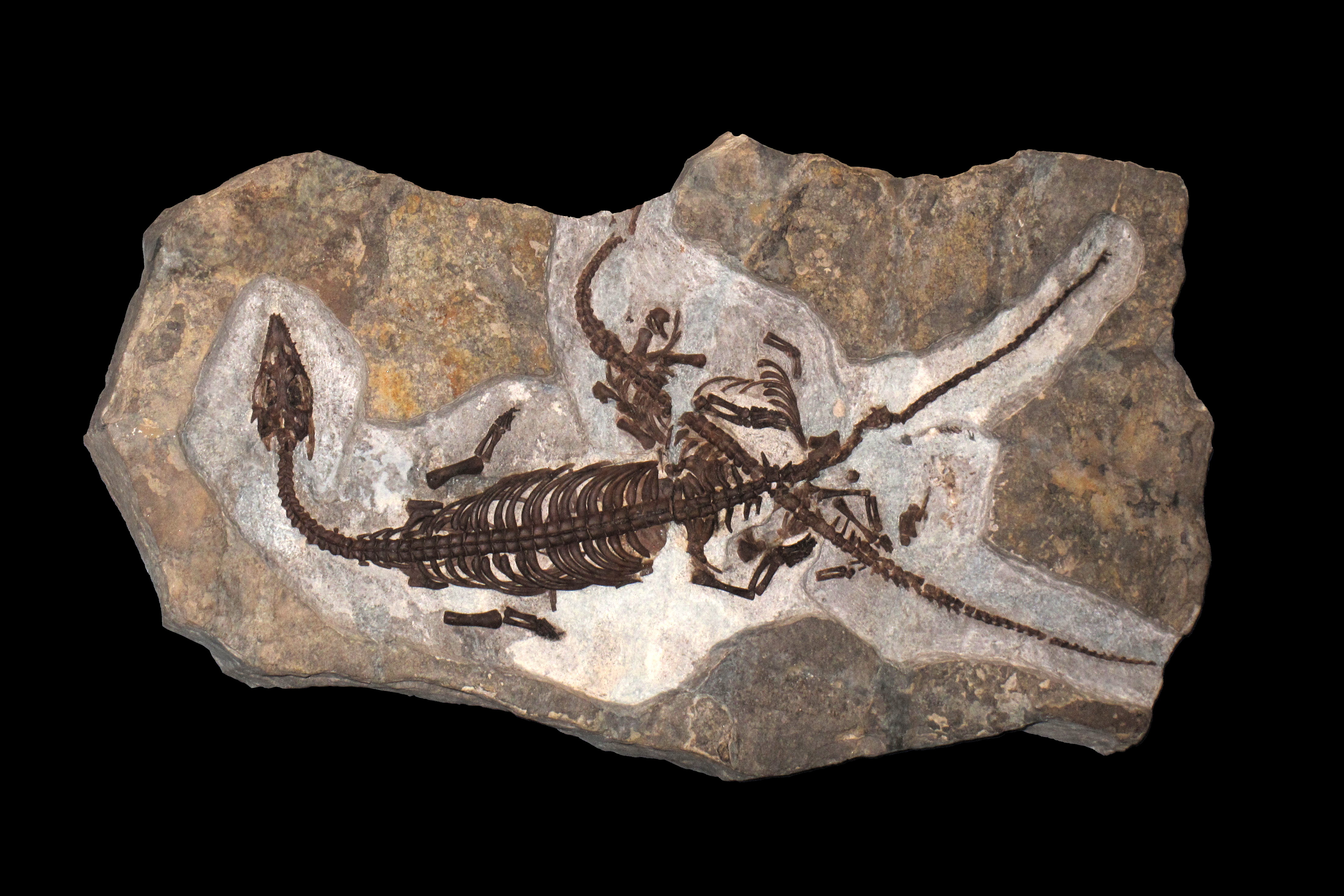
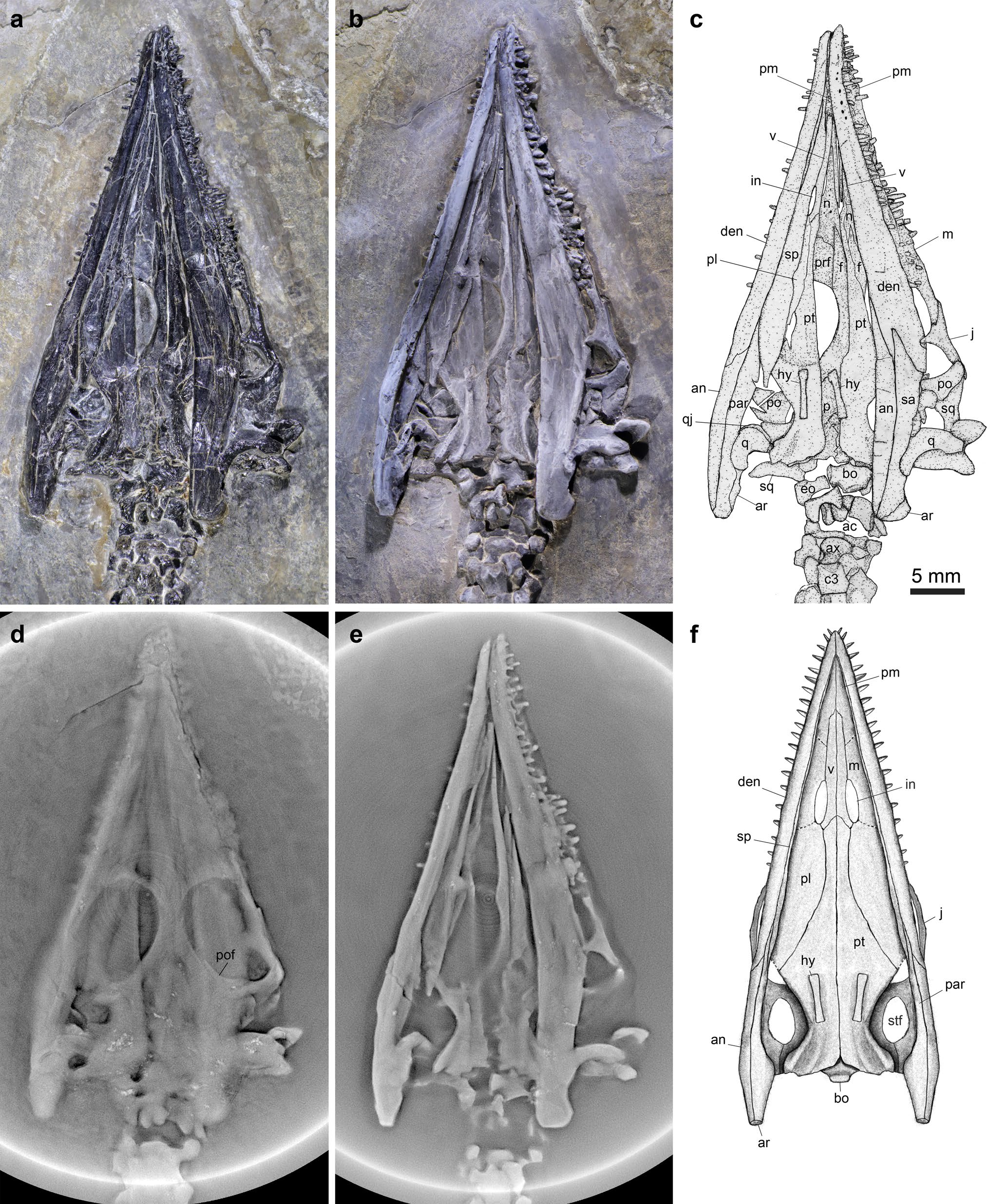
Luopingosaurus
''Luopingosaurus'' (meaning "Luoping lizard") is an extinct genus of pachypleurosaurid sauropterygian from the Middle Triassic Guanling Formation of Yunnan Province, China. The genus contains a single species, ''L. imparilis'', known from a well-preserved, nearly complete skeleton. Discovery and naming The ''Luopingosaurus'' holotype specimen, IVPP V19049, was discovered in sediments of the Guanling Formation, dated to the Anisian age (Pelsonian substage) of the middle Triassic period, in Luoping County, Yunnan Province, China. This specimen consists of a nearly complete, ventrally-exposed, articulated individual, lacking only the end of the tail. The preserved portion of the skeleton measures long. In 2023, Xu ''et al''. described ''Luopingosaurus imparilis'', a new genus and species of pachypleurosaurid, based on these fossil remains. The generic name, "''Luopingosaurus''", combines a reference to the type locality in Luoping County with the Greek word "saurus", meaning ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pachypleurosaurus
''Neusticosaurus'' (sometimes misspelled ''Neuticosaurus'') ("swimming lizard"), is an extinct genus of marine reptile belonging to the pachypleurosaurs, from Italy, Switzerland and Germany. ''Neusticosaurus'' was one of the smallest nothosaurs and probably fed on small fish Fish are aquatic, craniate, gill-bearing animals that lack limbs with digits. Included in this definition are the living hagfish, lampreys, and cartilaginous and bony fish as well as various extinct related groups. Approximately 95% of li .... References *Seeley, H.G. (1882). On ''Neusticosaurus pusillus'' (Fraas), an amphibious reptile having affinities with the terrestrial Nothosauria and with the marine Plesiosauria. Quarterly Journal of the Geological Society of London 38:350–366. Nothosaurs Triassic sauropterygians Middle Triassic reptiles of Europe Taxa named by Harry Seeley Fossil taxa described in 1882 Sauropterygian genera {{triassic-reptile-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nothosaur
Nothosaurs (order Nothosauroidea) were Triassic marine sauropterygian reptiles that may have lived like seals of today, catching food in water but coming ashore on rocks and beaches. They averaged about in length, with a long body and tail.F. v. Huene. 1956. Paläontologie und Phylogenie der Niederen Tetrapoden aleontology and Phylogeny of the Lower Tetrapods ''VEB Gustav Fischer Verlang, Jena'' 1-716 The feet were paddle-like, and are known to have been webbed in life, to help power the animal when swimming. The neck was quite long, and the head was elongated and flattened, and relatively small in relation to the body. The margins of the long jaws were equipped with numerous sharp outward-pointing teeth, indicating a diet of fish and squid. Taxonomy The Nothosauroidea consist of two suborders: * Pachypleurosauria, small primitive forms, and * Nothosauria (including two families Nothosauridae and Simosauridae), which evolved from pachypleurosaurs. The placement of pachypleuros ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serpianosaurus
''Serpianosaurus'' is an extinct genus of pachypleurosaurs known from the Middle Triassic (late Anisian and early Ladinian stages) deposits of Switzerland and Germany. It was a small reptile, with the type specimen of ''S. mirigiolensis'' measuring long. Fossils of the type species, '' S. mirigolensis'', have been found from the middle Grenzbitumenzone, the oldest strata of Monte San Giorgio, Switzerland, an area well known for its abundant pachypleurosaur remains. The locality dates back to sometime around the Anisian/Ladinian boundary of the Middle Triassic, around 242 Ma, with ''Serpianosaurus'' most likely occurring strictly during the latest Anisian. This makes it the one of the oldest sauropterygians from Monte San Giorgio, with only the rare pachypleurosaur ''Odoiporosaurus'' being older. Certain aspects of its morphology also suggest it is one of the most basal forms. Cajus G. Diedrich in 2013 described and named a second species, ''S. germanicus'', based on a postcra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neusticosaurus
''Neusticosaurus'' (sometimes misspelled ''Neuticosaurus'') ("swimming lizard"), is an extinct genus of marine reptile belonging to the pachypleurosaurs, from Italy, Switzerland and Germany. ''Neusticosaurus'' was one of the smallest nothosaurs and probably fed on small fish Fish are aquatic, craniate, gill-bearing animals that lack limbs with digits. Included in this definition are the living hagfish, lampreys, and cartilaginous and bony fish as well as various extinct related groups. Approximately 95% of li .... References *Seeley, H.G. (1882). On ''Neusticosaurus pusillus'' (Fraas), an amphibious reptile having affinities with the terrestrial Nothosauria and with the marine Plesiosauria. Quarterly Journal of the Geological Society of London 38:350–366. Nothosaurs Triassic sauropterygians Middle Triassic reptiles of Europe Taxa named by Harry Seeley Fossil taxa described in 1882 Sauropterygian genera {{triassic-reptile-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anarosaurus
''Anarosaurus'' is an extinct genus of pachypleurosaurs that lived in the Middle Triassic period (Anisian) and has been found in the Jena Formation and the Karlstadt Formation of Germany and the Winterswijk Quarry ( Lower Muschelkalk) of The Netherlands. Two species are known: ''A. pumilio'' (the type species) and ''A. heterodontus''. The holotype of ''A. pumilio'' was originally housed at the Institut und Museum fur Geologie und Palaontologie, Georg-August-Universitat, Gottingen, but can no longer be located today because it was lost or destroyed during World War II. ''Anarosaurus'' was a small reptile with an estimated body length of . See also * List of plesiosaurs This list of plesiosaurs is a comprehensive listing of all genera that have ever been included in the order Plesiosauria, excluding purely vernacular terms. The list includes all commonly accepted genera, but also genera that are now considered inv ... References Triassic plesiosaurs Extinct animals of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keichousaurus
''Keichousaurus'' (key-cho-saurus) is a genus of marine reptile in the pachypleurosaur family which went extinct at the close of the Triassic in the Triassic-Jurassic extinction event. The name derives from Kweichow (now Guizhou Province) in China where the first fossil specimen was discovered in 1957. They are among the most common sauropterygian fossils recovered and are often found as nearly complete, articulated skeletons, making them popular among collectors. ''Keichousaurus'', and the pachypleurosaur family broadly, are sometimes classified within Nothosauroidea, but are otherwise listed as a separate, more primitive lineage within Sauropterygia. Description ''Keichousaurus'', like all sauropterygians, was highly adapted to the aquatic environment. Most specimens had small body, males sexually mature with snout-vent length (SVL), and in females by SVL. Mean SVL for mature males is approximately SVL, and for mature females, at most SVL. It had both long necks and lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eosauropterygia
Sauropterygia (" lizard flippers") is an extinct taxon of diverse, aquatic reptiles that developed from terrestrial ancestors soon after the end-Permian extinction and flourished during the Triassic before all except for the Plesiosauria became extinct at the end of that period. The plesiosaurs would continue to diversify until the end of the Mesozoic. Sauropterygians are united by a radical adaptation of their pectoral girdle, adapted to support powerful flipper strokes. Some later sauropterygians, such as the pliosaurs, developed a similar mechanism in their pelvis. Uniquely among reptiles, sauropterygians moved their tail vertically like modern cetaceans and sirenians. Origins and evolution The earliest sauropterygians appeared about 247 million years ago (Ma), at the start of the Middle Triassic: the first definite sauropterygian with exact stratigraphic datum lies within the Spathian division of the Olenekian era in South China. Early examples were small (around 60&n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sauropterygia
Sauropterygia ("lizard flippers") is an extinct taxon of diverse, aquatic reptiles that developed from terrestrial ancestors soon after the end-Permian extinction and flourished during the Triassic before all except for the Plesiosauria became extinct at the end of that period. The plesiosaurs would continue to diversify until the end of the Mesozoic. Sauropterygians are united by a radical adaptation of their pectoral girdle, adapted to support powerful flipper strokes. Some later sauropterygians, such as the pliosaurs, developed a similar mechanism in their pelvis. Uniquely among reptiles, sauropterygians moved their tail vertically like modern cetaceans and sirenians. Origins and evolution The earliest sauropterygians appeared about 247 million years ago (Ma), at the start of the Middle Triassic: the first definite sauropterygian with exact stratigraphic datum lies within the Spathian division of the Olenekian era in South China. Early examples were small (around 60 c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Honghesaurus
''Honghesaurus'' is an extinct genus of pachypleurosaur from the Anisian-age Guanling Formation of China. The type specimen measures about in total body length. Classification The cladogram below follows Xu and colleagues (2022), when they used ''Youngina'' as a reference point for rooting the tree. Using a selection of placodont Placodonts (" Tablet teeth") are an extinct order of marine reptiles that lived during the Triassic period, becoming extinct at the end of the period. They were part of Sauropterygia, the group that includes plesiosaurs. Placodonts were genera ...s resulted in a less resolved topology. References Triassic sauropterygians Pachypleurosaurs Fossil taxa described in 2022 Anisian life {{triassic-reptile-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wumengosaurus
''Wumengosaurus'' is an extinct aquatic reptile from the Middle Triassic (late Anisian stage) Guanling Formation of Guizhou, southwestern China. It was originally described as a basal eosauropterygian and usually is recovered as such by phylogenetic analyses, although one phylogeny has placed it as the sister taxon to Ichthyosauromorpha while refraining from a formal re-positioning. It was a relatively small reptile, measuring in total body length and weighing . In 2021, Qin ''et al''. described an additional specimen from Guizhou ( Panzhou District) as a new species of ''Wumengosaurus'', ''W. rotundicarpus''. Classification In the 2023 description of ''Luopingosaurus'', Xu ''et al''. recovered ''Wumengosaurus'' as a derived pachypleurosaurid, as the sister taxon to the clade formed by ''Luopingosaurus'' and ''Honghesaurus''. The results of their phylogenetic analyses are shown in the cladogram A cladogram (from Greek ''clados'' "branch" and ''gramma'' "character") is a d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |