|
Pachycheilosuchus
''Pachycheilosuchus'' (meaning "thick lipped crocodile") is an extinct genus of neosuchian from the Early Cretaceous of Texas, United States. Previously known, in part, as the "Glen Rose form", this crocodylomorph is notable for its procoelous vertebrae, otherwise found only in derived eusuchian crocodilians (the vertebrae articulate with a cup on the anterior surface and a rounded posterior surface), a thick margin on the maxillae (the main tooth-bearing bones of the upper jaw; thus "thick lipped crocodile"), and a shield of armor on the neck formed by the fusion of six individual scutes. Description ''Pachycheilosuchus'' is based on SMU 75278, a right maxilla, with the remains of at minimum 13 other individuals also known, representing most of the skeleton except hands, feet, and part of the skull. The remains were recovered near the top of the Glen Rose Formation of Erath County in central Texas, in rocks dating from the early Albian faunal stage. The fossils were found in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
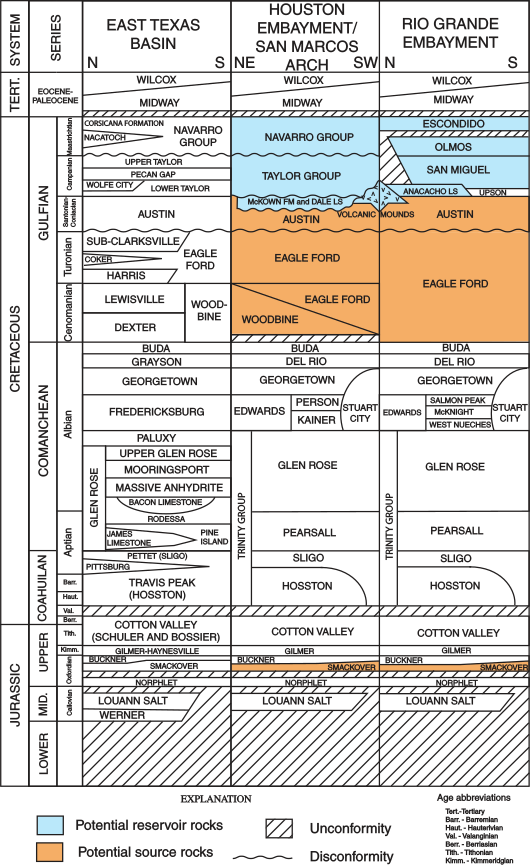
Glen Rose Formation
The Glen Rose Formation is a shallow marine to shoreline geological formation from the lower Cretaceous period exposed over a large area from South Central to North Central Texas. The formation is most widely known for the dinosaur footprints and trackways found in the Dinosaur Valley State Park near the town of Glen Rose, Texas, southwest of Fort Worth and at other localities in Central Texas. Geology The Glen Rose is the uppermost, thickest and most extensively exposed formation of the Trinity Group, a series of shallow-water marine formations deposited on a southeastward flank of the Llano Uplift, through a number of sea regressions and transgressions. Wells drilled in eastern Travis County have encountered over 1,000 feet of the Glen Rose. In the northern part, the Glen Rose is laterally continuous with the Paluxy Formation. The Glen Rose overlies the Hensel Sand and is overlain in turn by formations of the Fredericksburg division. In 1974, Keith Young concluded, b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neosuchia
Neosuchia is a clade within Mesoeucrocodylia that includes all modern extant crocodilians and their closest fossil relatives. It is defined as the most inclusive clade containing all crocodylomorphs more closely related to ''Crocodylus niloticus'' (the Nile Crocodile) than to ''Notosuchus terrestris''. Members of Neosuchia generally share a crocodilian-like bodyform adapted to freshwater aquatic life, as opposed to the terrestrial habits of more basal crocodylomorph groups. The earliest neosuchian is suggested to be the Early Jurassic ''Calsoyasuchus'', which lived during the Sinemurian and Pliensbachian stages in North America. It is often identified as a member of Goniopholididae, though this is disputed, and the taxon may lie outside Neosuchia, which places the earliest records of the group in the Middle Jurassic. Characteristics A tooth notch between the maxilla and premaxilla is a basal characteristic of the Neosuchia, although it is lost in some more derived forms, most nota ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early Cretaceous
The Early Cretaceous ( geochronological name) or the Lower Cretaceous (chronostratigraphic name), is the earlier or lower of the two major divisions of the Cretaceous. It is usually considered to stretch from 145 Ma to 100.5 Ma. Geology Proposals for the exact age of the Barremian-Aptian boundary ranged from 126 to 117 Ma until recently (as of 2019), but based on drillholes in Svalbard the defining early Aptian Oceanic Anoxic Event 1a (OAE1a) was carbon isotope dated to 123.1±0.3 Ma, limiting the possible range for the boundary to c. 122–121 Ma. There is a possible link between this anoxic event and a series of Early Cretaceous large igneous provinces (LIP). The Ontong Java-Manihiki-Hikurangi large igneous province, emplaced in the South Pacific at c. 120 Ma, is by far the largest LIP in Earth's history. The Ontong Java Plateau today covers an area of 1,860,000 km2. In the Indian Ocean another LIP began to form at c. 120 Ma, the Kerguelen P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synapomorphy
In phylogenetics, an apomorphy (or derived trait) is a novel character or character state that has evolved from its ancestral form (or plesiomorphy). A synapomorphy is an apomorphy shared by two or more taxa and is therefore hypothesized to have evolved in their most recent common ancestor. ) In cladistics, synapomorphy implies homology. Examples of apomorphy are the presence of erect gait, fur, the evolution of three middle ear bones, and mammary glands in mammals but not in other vertebrate animals such as amphibians or reptiles, which have retained their ancestral traits of a sprawling gait and lack of fur. Thus, these derived traits are also synapomorphies of mammals in general as they are not shared by other vertebrate animals. Etymology The word —coined by German entomologist Willi Hennig—is derived from the Ancient Greek words (''sún''), meaning "with, together"; (''apó''), meaning "away from"; and (''morphḗ''), meaning "shape, form". Clade analysis T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Body Of Vertebra
Body may refer to: In science * Physical body, an object in physics that represents a large amount, has mass or takes up space * Body (biology), the physical material of an organism * Body plan, the physical features shared by a group of animals * Human body, the entire structure of a human organism ** Dead body, cadaver, or corpse, a dead human body * (living) matter, see: Mind–body problem, the relationship between mind and matter in philosophy * Aggregates within living matter, such as inclusion bodies In arts and entertainment In film and television * ''Body'' (2015 Polish film), a 2015 Polish film * ''Body'' (2015 American film), a 2015 American film * "Body" (''Wonder Showzen'' episode), a 2006 episode of American sketch comedy television series ''Wonder Showzen'' * "Body", an episode of the Adult Swim television series, ''Off the Air'' In literature and publishing * body text, the text forming the main content of any printed matter * body (typography), the size o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Egg (biology)
An egg is an organic vessel grown by an animal to carry a possibly fertilized egg cell (a zygote) and to incubate from it an embryo within the egg until the embryo has become an animal fetus that can survive on its own, at which point the animal hatches. Most arthropods such as insects, vertebrates (excluding live-bearing mammals), and mollusks lay eggs, although some, such as scorpions, do not. Reptile eggs, bird eggs, and monotreme eggs are laid out of water and are surrounded by a protective shell, either flexible or inflexible. Eggs laid on land or in nests are usually kept within a warm and favorable temperature range while the embryo grows. When the embryo is adequately developed it hatches, i.e., breaks out of the egg's shell. Some embryos have a temporary egg tooth they use to crack, pip, or break the eggshell or covering. The largest recorded egg is from a whale shark and was in size. Whale shark eggs typically hatch within the mother. At and up to , the o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Femur
The femur (; ), or thigh bone, is the proximal bone of the hindlimb in tetrapod vertebrates. The head of the femur articulates with the acetabulum in the pelvic bone forming the hip joint, while the distal part of the femur articulates with the tibia (shinbone) and patella (kneecap), forming the knee joint. By most measures the two (left and right) femurs are the strongest bones of the body, and in humans, the largest and thickest. Structure The femur is the only bone in the upper leg. The two femurs converge medially toward the knees, where they articulate with the proximal ends of the tibiae. The angle of convergence of the femora is a major factor in determining the femoral-tibial angle. Human females have thicker pelvic bones, causing their femora to converge more than in males. In the condition ''genu valgum'' (knock knee) the femurs converge so much that the knees touch one another. The opposite extreme is ''genu varum'' (bow-leggedness). In the general populatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Type Species
In zoological nomenclature, a type species (''species typica'') is the species name with which the name of a genus or subgenus is considered to be permanently taxonomically associated, i.e., the species that contains the biological type specimen(s). Article 67.1 A similar concept is used for suprageneric groups and called a type genus. In botanical nomenclature, these terms have no formal standing under the code of nomenclature, but are sometimes borrowed from zoological nomenclature. In botany, the type of a genus name is a specimen (or, rarely, an illustration) which is also the type of a species name. The species name that has that type can also be referred to as the type of the genus name. Names of genus and family ranks, the various subdivisions of those ranks, and some higher-rank names based on genus names, have such types. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brackish Water
Brackish water, sometimes termed brack water, is water occurring in a natural environment that has more salinity than freshwater, but not as much as seawater. It may result from mixing seawater (salt water) and fresh water together, as in estuaries, or it may occur in brackish fossil aquifers. The word comes from the Middle Dutch root '' brak''. Certain human activities can produce brackish water, in particular civil engineering projects such as dikes and the flooding of coastal marshland to produce brackish water pools for freshwater prawn farming. Brackish water is also the primary waste product of the salinity gradient power process. Because brackish water is hostile to the growth of most terrestrial plant species, without appropriate management it is damaging to the environment (see article on shrimp farms). Technically, brackish water contains between 0.5 and 30 grams of salt per litre—more often expressed as 0.5 to 30 parts per thousand (‰), which is a specific gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mudstone
Mudstone, a type of mudrock, is a fine-grained sedimentary rock whose original constituents were clays or muds. Mudstone is distinguished from '' shale'' by its lack of fissility (parallel layering).Blatt, H., and R.J. Tracy, 1996, ''Petrology.'' New York, New York, W. H. Freeman, 2nd ed, 529 pp. The term ''mudstone'' is also used to describe carbonate rocks (limestone or dolomite) that are composed predominantly of carbonate mud. However, in most contexts, the term refers to siliciclastic mudstone, composed mostly of silicate minerals. The NASA Curiosity rover has found deposits of mudstone on Mars that contain organic substances such as propane, benzene and toluene. Definition There is not a single definition of mudstone that has gained general acceptance,Boggs 2006, p.143 though there is wide agreement that mudstones are fine-grained sedimentary rocks, composed mostly of silicate grains with a grain size less than . Individual grains this size are too small to be disting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms when these minerals precipitate out of water containing dissolved calcium. This can take place through both biological and nonbiological processes, though biological processes, such as the accumulation of corals and shells in the sea, have likely been more important for the last 540 million years. Limestone often contains fossils which provide scientists with information on ancient environments and on the evolution of life. About 20% to 25% of sedimentary rock is carbonate rock, and most of this is limestone. The remaining carbonate rock is mostly dolomite, a closely related rock, which contains a high percentage of the mineral dolomite, . ''Magnesian limestone'' is an obsolete and poorly-defined term used variously for dolomite, for limes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bonebed
A bone bed is any geological stratum or deposit that contains bones of whatever kind. Inevitably, such deposits are sedimentary in nature. Not a formal term, it tends to be used more to describe especially dense collections such as Lagerstätte. It is also applied to brecciated and stalagmitic deposits on the floor of caves, which frequently contain osseous remains. In a more restricted sense, the term is used to describe certain thin layers of bony fragments, which occur in well-defined geological strata. One of the best-known of these is the Ludlow Bone Bed, which is found at the base of the Downton Sandstone in the Upper Ludlow series. At Ludlow (England) itself, two such beds are actually known, separated by about . of strata. Although quite thin, the Ludlow Bone Bed can be followed from that town into Gloucestershire, for a distance of . It is almost completely made up of fragments of spines, teeth and scales of ganoid fish. Another well-known bed, formerly known as the B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_(2).jpg)
