|
PTPRU
Receptor-type tyrosine-protein phosphatase PCP-2 (also known as PTP-pi, PTP lambda, hPTP-J, PTPRO and PTP psi), is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''PTPRU'' gene. Function The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the protein tyrosine phosphatase (PTP) family. PTPs are known to be signaling molecules that regulate a variety of cellular processes including cell growth, differentiation, mitotic cycle, and oncogenic transformation. This PTP possesses an extracellular region, a single transmembrane region, and two tandem intracellular catalytic tyrosine phosphatase domains, and thus represents a receptor-type PTP (RPTP). The extracellular region contains a meprin-A5 antigen-PTPmu (MAM) domain, one Ig-like domain and four fibronectin type III-like repeats, and thus is a member of the type R2B RPTP family. It was cloned by many groups and given different names, including PCP-2, PTP pi, PTP lambda, hPTP-J, PTPRO, and PTP psi. Other type R2B RPTPs include PTPRM, PTPRK, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
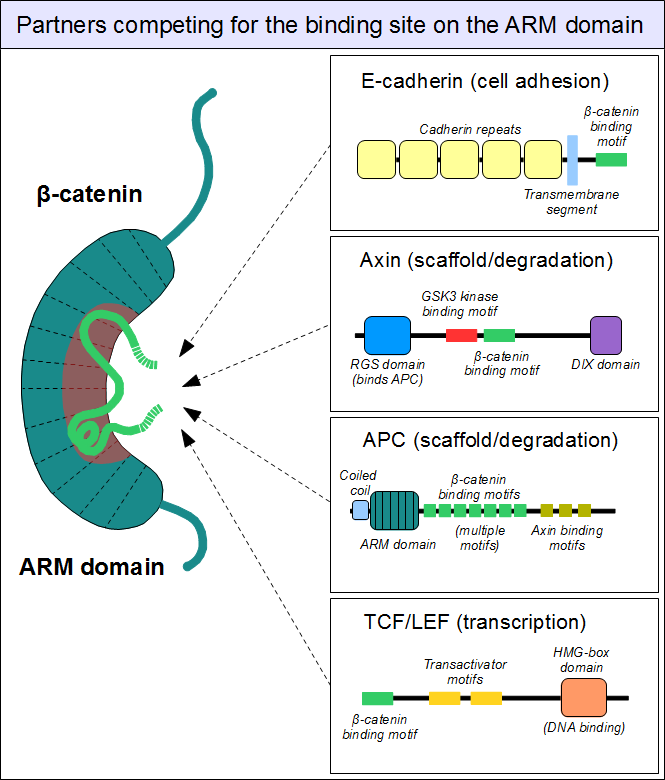
B-catenin
Catenin beta-1, also known as beta-catenin (β-catenin), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CTNNB1'' gene. Beta-catenin is a dual function protein, involved in regulation and coordination of cell–cell adhesion and gene transcription. In humans, the CTNNB1 protein is encoded by the ''CTNNB1'' gene. In ''Drosophila'', the homologous protein is called ''armadillo''. β-catenin is a subunit of the cadherin protein complex and acts as an intracellular signal transducer in the Wnt signaling pathway. It is a member of the catenin protein family and homologous to γ-catenin, also known as plakoglobin. Beta-catenin is widely expressed in many tissues. In cardiac muscle, beta-catenin localizes to adherens junctions in intercalated disc structures, which are critical for electrical and mechanical coupling between adjacent cardiomyocytes. Mutations and overexpression of β-catenin are associated with many cancers, including hepatocellular carcinoma, colorectal carcinoma, lung c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PTPRT
Receptor-type tyrosine-protein phosphatase T is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''PTPRT'' gene. PTPRT is also known as PTPrho, PTPρ and human accelerated region 9. The human accelerated regions are 49 regions of the human genome that are conserved among vertebrates, but in humans show significant distinction from other vertebrates. This region may, therefore, have played a key role in differentiating humans from apes. Function The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the protein tyrosine phosphatase (PTP) family. PTPs are known to be signaling molecules that regulate a variety of cellular processes including cell growth, differentiation, mitotic cycle, and oncogenic transformation. PTPrho has been proposed to function during development of the nervous system and as a tumor suppressor in cancer. Structure This PTP possesses an extracellular region, a single transmembrane region, and two tandem intracellular catalytic domains, and thus represents a recept ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
β-catenin
Catenin beta-1, also known as beta-catenin (β-catenin), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CTNNB1'' gene. Beta-catenin is a dual function protein, involved in regulation and coordination of cell–cell adhesion and gene transcription. In humans, the CTNNB1 protein is encoded by the ''CTNNB1'' gene. In ''Drosophila'', the homologous protein is called ''armadillo''. β-catenin is a subunit of the cadherin protein complex and acts as an intracellular signal transducer in the Wnt signaling pathway. It is a member of the catenin protein family and homologous to γ-catenin, also known as plakoglobin. Beta-catenin is widely expressed in many tissues. In cardiac muscle, beta-catenin localizes to adherens junctions in intercalated disc structures, which are critical for electrical and mechanical coupling between adjacent cardiomyocytes. Mutations and overexpression of β-catenin are associated with many cancers, including hepatocellular carcinoma, colorectal carcinoma, lung c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. Almost all metabolic processes in the cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts are catalytic RNA molecules, called ribozymes. Enzymes' specificity comes from their unique three-dimensional structures. Like all catalysts, enzymes increase the reaction ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melanoma
Melanoma, also redundantly known as malignant melanoma, is a type of skin cancer that develops from the pigment-producing cells known as melanocytes. Melanomas typically occur in the skin, but may rarely occur in the mouth, intestines, or eye (uveal melanoma). In women, they most commonly occur on the legs, while in men, they most commonly occur on the back. About 25% of melanomas develop from moles. Changes in a mole that can indicate melanoma include an increase in size, irregular edges, change in color, itchiness, or skin breakdown. The primary cause of melanoma is ultraviolet light (UV) exposure in those with low levels of the skin pigment melanin. The UV light may be from the sun or other sources, such as tanning devices. Those with many moles, a history of affected family members, and poor immune function are at greater risk. A number of rare genetic conditions, such as xeroderma pigmentosum, also increase the risk. Diagnosis is by biopsy and analysis of any skin lesion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AP3S2
AP-3 complex subunit sigma-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''AP3S2'' gene. Interactions AP3S2 has been shown to interact with AP3B1 AP-3 complex subunit beta-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''AP3B1'' gene. Function This gene encodes a protein that may play a role in organelle biogenesis associated with melanosomes, platelet dense granules, and lysosomes. Th .... References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * External links * * {{protein-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AP3S1
AP-3 complex subunit sigma-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''AP3S1'' gene In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a ba .... References External links * Further reading * * * * * * {{protein-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AP3M1
AP-3 complex subunit mu-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''AP3M1'' gene. The protein encoded by this gene is the medium subunit of AP-3, which is an adaptor-related protein complex associated with the Golgi region as well as more peripheral intracellular structures. AP-3 facilitates the budding of vesicles from the Golgi membrane and may be directly involved in protein sorting to the endosomal/lysosomal system. AP-3 is a heterotetrameric protein complex composed of two large subunits (delta and beta3), a medium subunit ( mu3), and a small subunit ( sigma 3). Mutations in one of the large subunits of AP-3 have been associated with the Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome, a genetic disorder characterized by defective lysosome-related organelles In cell biology, an organelle is a specialized subunit, usually within a cell, that has a specific function. The name ''organelle'' comes from the idea that these structures are parts of cells, as organs are to the body, hence ''or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AP3D1
AP-3 complex subunit delta-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''AP3D1'' gene. Function AP3D1 is a subunit of the AP3 adaptor-like complex, which is not associated with clathrin. The AP3D1 subunit is implicated in intracellular biogenesis and trafficking of pigment granules and possibly platelet dense granules and neurotransmitter vesicles. upplied by OMIMref name="entrez" /> Interactions AP3D1 has been shown to interact with SYBL1 Synaptobrevin-like protein 1 (SYBL1), also known as vesicle-associated membrane protein 7 (VAMP7), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''VAMP7'', or ''SYBL1'', gene. Function SYBL1 is a transmembrane protein that is a member of the s .... References External links * Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * {{gene-19-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AP3B2
AP-3 complex subunit beta-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''AP3B2'' gene In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a ba .... References External links * Further reading * * * * * * * * * {{protein-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AP3B1
AP-3 complex subunit beta-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''AP3B1'' gene. Function This gene encodes a protein that may play a role in organelle biogenesis associated with melanosomes, platelet dense granules, and lysosomes. The encoded protein is part of the heterotetrameric AP-3 protein complex which interacts with the scaffolding protein clathrin. Mutations in this gene are associated with Hermansky–Pudlak syndrome type 2. Interactions AP3B1 has been shown to interact with AP3S2 AP-3 complex subunit sigma-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''AP3S2'' gene. Interactions AP3S2 has been shown to interact Advocates for Informed Choice, doing business as, dba interACT or interACT Advocates for Intersex Youth, .... References External links GeneReviews/NCBI/NIH/UW entry on Hermansky-Pudlak Syndrome* Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * {{gene-5-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |