|
Pak1
Serine/threonine-protein kinase PAK 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''PAK1'' gene. PAK1 is one of six members of the PAK family of serine/threonine kinases which are broadly divided into group I (PAK1, PAK2 and PAK3) and group II (PAK4, PAK6 and PAK5/7). The PAKs are evolutionarily conserved. PAK1 localizes in distinct sub-cellular domains in the cytoplasm and nucleus. PAK1 regulates cytoskeleton remodeling, phenotypic signaling and gene expression, and affects a wide variety of cellular processes such as directional motility, invasion, metastasis, growth, cell cycle progression, angiogenesis. PAK1-signaling dependent cellular functions regulate both physiologic and disease processes, including cancer, as PAK1 is widely overexpressed and hyperstimulated in human cancer, at-large. Discovery PAK1 was first discovered as an effector of the Rho GTPases in rat brain by Manser and colleagues in 1994. The human PAK1 was identified as a GTP-dependent interacting partner ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
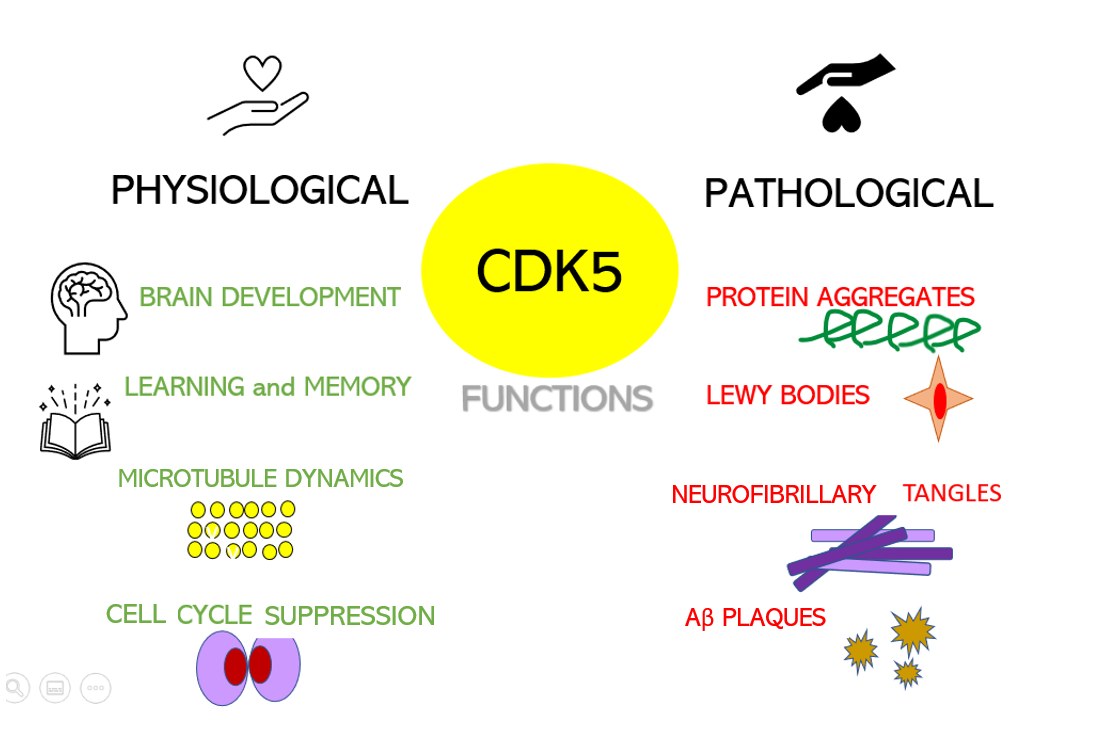
Cyclin-dependent Kinase 5
Cyclin-dependent kinase 5 is a protein, and more specifically an enzyme, that is encoded by the Cdk5 gene. It was discovered 15 years ago, and it is saliently expressed in post-mitotic central nervous system neurons (CNS). The molecule belongs to the cyclin-dependent kinase family. Kinases are enzymes that catalyze reactions of phosphorylation. This process allows the substrate to gain a phosphate group donated by an organic compound known as ATP. Phosphorylations are of vital importance during glycolysis, therefore, making kinases an essential part of the cell due to their role in the metabolism, cell signaling, and many other processes. Structure Cdk5 is a proline-directed serine/threonine kinase, which was first identified as a CDK family member due to its similar structure to CDC2/CDK1 in humans, a protein that plays a crucial role in the regulation of the cell cycle. The gene Cdk5 contains 12 exons in a region that contains around 5000 nucleotides (5kb), as it was det ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C-Raf
RAF proto-oncogene serine/threonine-protein kinase, also known as proto-oncogene c-RAF or simply c-Raf or even Raf-1, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''RAF1'' gene. The c-Raf protein is part of the ERK1/2 pathway as a MAP kinase (MAP3K) that functions downstream of the Ras subfamily of membrane associated GTPases. C-Raf is a member of the Raf kinase family of serine/threonine-specific protein kinases, from the TKL (Tyrosine-kinase-like) group of kinases. Discovery The first Raf gene, v-Raf was found in 1983. It was isolated from the murine retrovirus bearing the number 3611. It was soon demonstrated to be capable to transform rodent fibroblasts to cancerous cell lines, so this gene was given the name Virus-induced Rapidly Accelerated Fibrosarcoma (V-RAF). A year later, another transforming gene was found in the avian retrovirus MH2, named v-Mil - that turned out to be highly similar to v-Raf. Researchers were able to demonstrate that these genes encode enzymes th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BMX (gene)
Cytoplasmic tyrosine-protein kinase BMX is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''BMX'' gene. Function Tyrosine kinases are either receptor molecules, which contain transmembrane and extracellular domains, or nonreceptor proteins, which are located intracellularly. One family of nonreceptor TKs includes the genes TEC (gene), TEC, TXK (gene), TXK, ITK (gene), ITK, and BTK (gene), BTK. All of these proteins are homologs of the ''Drosophila'' Src28 TK and contain an SH3 domain, SH3 and SH2 domain, SH2 domain upstream of the TK domain. Interactions BMX has been shown to Protein-protein interaction, interact with: * PAK1, * PTK2, * PTPN21 and * RUFY1. References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * External links * Tyrosine kinases {{gene-X-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PAK2
Serine/threonine-protein kinase PAK 2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''PAK2'' gene. PAK2 is one of three members of Group I PAK family of serine/threonine kinases. The PAKs are evolutionary conserved. PAK2 and its cleaved fragment localize in both the cytoplasmic or nuclear compartments. PAK2 signaling modulates apoptosis, endothelial lumen formation, viral pathogenesis, and cancer including, breast, hepatocarcinoma, and gastric and cancer, at-large. Discovery The human PAK2 was identified as a downstream effector of Rac or Cdc42. Gene and spliced variants The PAK2 gene is about 92.7-kb long. The gene contains 15 exons and generates three alternatively spliced transcripts - two of which code proteins of 524 amino acids and 221 amino acids, while the third one is a 371-bp non-coding RNA transcript(Gene from review) There are two transcripts generated from the murine PAK2 gene, a 5.7-kb transcript coding a 524 amino acids long polypeptide and a 1.2-kb long non ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. Almost all metabolic processes in the cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts are catalytic RNA molecules, called ribozymes. Enzymes' specificity comes from their unique three-dimensional structures. Like all catalysts, enzymes increase the reaction ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GTPase
GTPases are a large family of hydrolase enzymes that bind to the nucleotide guanosine triphosphate (GTP) and hydrolyze it to guanosine diphosphate (GDP). The GTP binding and hydrolysis takes place in the highly conserved P-loop "G domain", a protein domain common to many GTPases. Functions GTPases function as molecular switches or timers in many fundamental cellular processes. Examples of these roles include: * Signal transduction in response to activation of cell surface receptors, including transmembrane receptors such as those mediating taste, smell and vision. * Protein biosynthesis (a.k.a. translation) at the ribosome. * Regulation of cell differentiation, proliferation, division and movement. * Translocation of proteins through membranes. * Transport of vesicles within the cell, and vesicle-mediated secretion and uptake, through GTPase control of vesicle coat assembly. GTPases are active when bound to GTP and inactive when bound to GDP. In the generalized recepto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ARPC1B
Actin-related protein 2/3 complex subunit 1B is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''ARPC1B'' gene. Function This gene encodes one of seven subunits of the human Arp2/3 protein complex. This subunit is a member of the SOP2 family of proteins and is most similar to the protein encoded by gene ARPC1A. The similarity between these two proteins suggests that they both may function as p41 subunit of the human Arp2/3 complex that facilitates branching of actin filaments in cells. Isoforms of the p41 subunit may adapt the functions of the complex to different cell types or developmental stages. Indeed, it has recently been shown that variants of the Arp2/3 complex differ in their ability to promote actin assembly, with complexes containing ARPC1B and ARPC5L being better at this than those containing ARPC1A and ARPC5. The differing functions of ARPC1A and ARPC1B are also evident in the recent discovery of patients with severe or total ARPC1B deficiency, who have platelet and i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ARHGEF2
Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''ARHGEF2'' gene. Function Rho GTPases play a fundamental role in numerous cellular processes that are initiated by extracellular stimuli that work through G protein-coupled receptors. The encoded protein may form complex with G proteins and stimulate rho-dependent signals. Interactions ARHGEF2 has been shown to interact with PAK1 Serine/threonine-protein kinase PAK 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''PAK1'' gene. PAK1 is one of six members of the PAK family of serine/threonine kinases which are broadly divided into group I (PAK1, PAK2 and PAK3) and group II .... References External links * Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * {{gene-1-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moiety (chemistry)
In organic chemistry, a moiety ( ) is a part of a molecule that is given a name because it is identified as a part of other molecules as well. Typically, the term is used to describe the larger and characteristic parts of organic molecules, and it should not be used to describe or name smaller functional groups of atoms that chemically react in similar ways in most molecules that contain them. Occasionally, a moiety may contain smaller moieties and functional groups. A moiety that acts as a branch extending from the backbone of a hydrocarbon molecule is called a substituent or side chain, which typically can be removed from the molecule and substituted with others. Active moiety In pharmacology, an active moiety is the part of a molecule or ion – excluding appended inactive portions – that is responsible for the physiological or pharmacological action of a drug substance. Inactive appended portions of the drug substance may include either the alcohol or acid moiety of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thiol
In organic chemistry, a thiol (; ), or thiol derivative, is any organosulfur compound of the form , where R represents an alkyl or other organic substituent. The functional group itself is referred to as either a thiol group or a sulfhydryl group, or a sulfanyl group. Thiols are the sulfur analogue of alcohols (that is, sulfur takes the place of oxygen in the hydroxyl () group of an alcohol), and the word is a blend of "''thio-''" with "alcohol". Many thiols have strong odors resembling that of garlic or rotten eggs. Thiols are used as odorants to assist in the detection of natural gas (which in pure form is odorless), and the "smell of natural gas" is due to the smell of the thiol used as the odorant. Thiols are sometimes referred to as mercaptans () or mercapto compounds, a term introduced in 1832 by William Christopher Zeise and is derived from the Latin ('capturing mercury')''Oxford American Dictionaries'' (Mac OS X Leopard). because the thiolate group () bonds very strong ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Redox
Redox (reduction–oxidation, , ) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of substrate (chemistry), substrate change. Oxidation is the loss of Electron, electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is the gain of electrons or a decrease in the oxidation state. There are two classes of redox reactions: * ''Electron-transfer'' – Only one (usually) electron flows from the reducing agent to the oxidant. This type of redox reaction is often discussed in terms of redox couples and electrode potentials. * ''Atom transfer'' – An atom transfers from one substrate to another. For example, in the rusting of iron, the oxidation state of iron atoms increases as the iron converts to an oxide, and simultaneously the oxidation state of oxygen decreases as it accepts electrons released by the iron. Although oxidation reactions are commonly associated with the formation of oxides, other chemical species can serve the same function. In hydrogen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |