|
Pyotr Akhlyustin
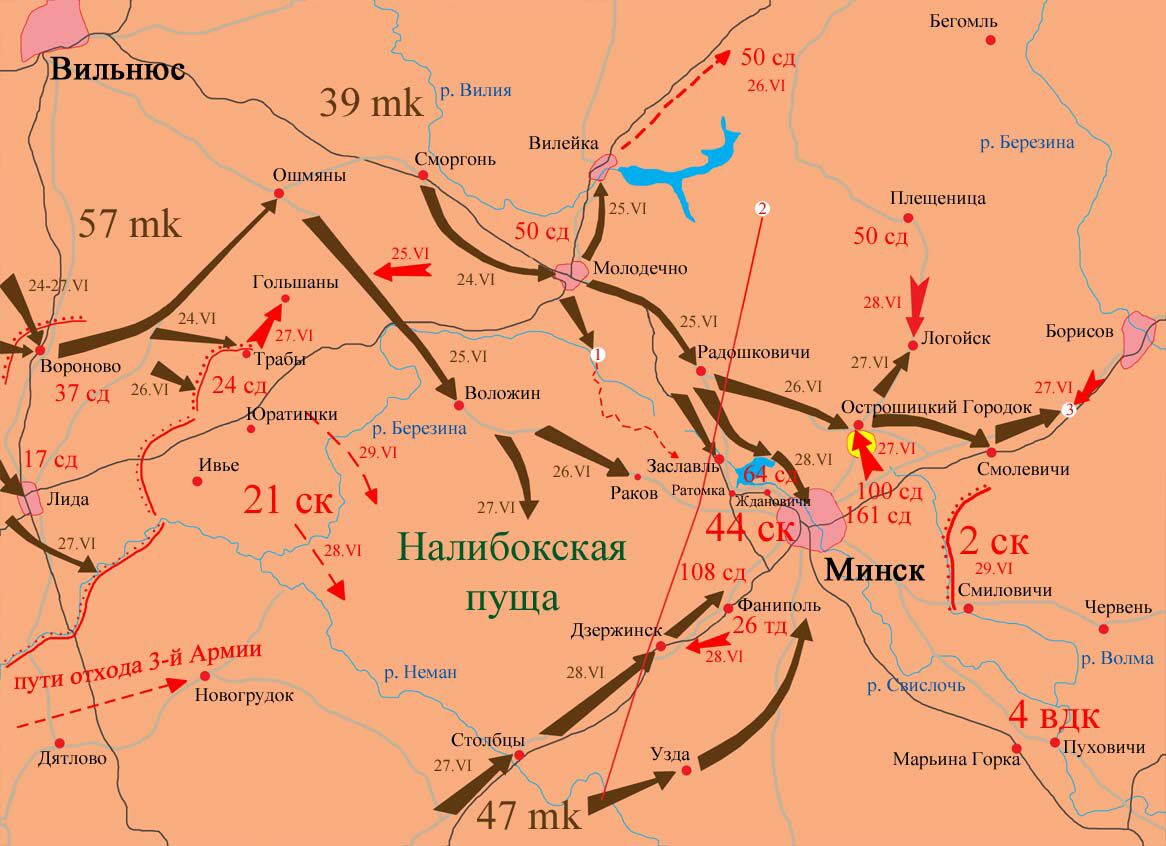
Pyotr Nikolayevich Akhlyustin (; 12 June 1896 – 28 July 1941) was a Red Army major general. Akhlyustin fought in World War I as a cavalryman and joined the Red Army during the Russian Civil War, becoming a junior commander. He held command positions in cavalry units between the wars and commanded a cavalry division in the Soviet invasion of Poland and the Winter War. At the outbreak of Operation Barbarossa, he commanded the 13th Mechanized Corps, destroyed during the Battle of Białystok–Minsk in late June and early July 1941. Akhlyustin escaped, but was killed while trying to reach Soviet lines in late July. Early life, World War I, and Russian Civil War Akhlyustin was born on 12 June 1896 in Kaslinsky Zavod, the son of a worker, and graduated from primary school. During World War I, he was drafted into the Imperial Russian Army in August 1915 and sent to the Western Front, where he fought with the 2nd Pavlograd Life Hussar Regiment as a private, junior '' unter-ofit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kasli
Kasli (russian: Касли́) is a town and the administrative center of Kaslinsky District in Chelyabinsk Oblast, Russia, located among several lakes on the eastern slope of the Middle Urals, northwest of Chelyabinsk, the administrative center of the oblast. Population: History It was founded in 1747 as the settlement of Kaslinsky () around a foundry. Town status was granted to it on July 29, 1942. The Kasli plant became famous for its cast iron castings in the mid-19th century. In 1900, an open-work pavilion was molded from metal for the international exhibition. It is now exhibited in the Yekaterinburg picture gallery. Administrative and municipal status Within the framework of administrative divisions, Kasli serves as the administrative center of Kaslinsky District.Resolution #161 As an administrative division, it is, together with one rural locality (the settlement of Prigorodny), incorporated within Kaslinsky District as the Town of Kasli. As a municipal divisi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Civil War
, date = October Revolution, 7 November 1917 – Yakut revolt, 16 June 1923{{Efn, The main phase ended on 25 October 1922. Revolt against the Bolsheviks continued Basmachi movement, in Central Asia and Tungus Republic, the Far East through the 1920s and 1930s.{{cite book, last=Mawdsley, first=Evan, title=The Russian Civil War, location=New York, publisher=Pegasus Books, year=2007, isbn=9781681770093, url=https://archive.org/details/russiancivilwar00evan, url-access=registration{{rp, 3,230(5 years, 7 months and 9 days) {{Collapsible list , bullets = yes , title = Peace treaties , Treaty of Brest-LitovskSigned 3 March 1918({{Age in years, months, weeks and days, month1=11, day1=7, year1=1917, month2=3, day2=3, year2=1918) , Treaty of Tartu (Russian–Estonian)Signed 2 February 1920({{Age in years, months, weeks and days, month1=11, day1=7, year1=1917, month2=2, day2=2, year2=1920) , Soviet–Lithuanian Peace TreatySigned 12 July 1920({{Age in years, months, weeks and da ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cross Of St
A cross is a geometrical figure consisting of two intersecting lines or bars, usually perpendicular to each other. The lines usually run vertically and horizontally. A cross of oblique lines, in the shape of the Latin letter X, is termed a saltire in heraldic terminology. The cross has been widely recognized as a symbol of Christianity from an early period.''Christianity: an introduction'' by Alister E. McGrath 2006 pages 321-323 However, the use of the cross as a religious symbol predates Christianity; in the ancient times it was a pagan religious symbol throughout Europe and western Asia. The effigy of a man hanging on a cross was set up in the fields to protect the crops. It often appeared in conjunction with the female-genital circle or oval, to signify the sacred marriage, as in Egyptian amulet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ranks And Insignia Of The Russian Armed Forces Until 1917
The Ranks and insignia of the Imperial Russian Armed Forces were the military ranks used by the Imperial Russian Army and the Imperial Russian Navy. Many of the ranks were derived from the Military ranks of the German Empire, German model. The ranks were abolished following the Russian Revolution, with the Red Army adopting an Ranks and insignia of the Red Army and Navy 1918–1935, entirely different system. Army ranks and rank designation The following ranks and their respective insignia were also used by the personnel of the Imperial Russian Air Service from 1912 to 1917. Army ranks 1698-1716 }) ! colspan=3, Field officer, Field officers(russian: Штаб-офицеры, Shtabofitsery, link=no) ! colspan=4, Company-grade officer, Company officers(russian: Обер-офицеры, Oberofitsery, link=no) ! colspan=5, Non-commissioned officer, Non-commissioned officers(russian: Урядники, Uryadniky, link=no) ! colspan=1, Enlisted rank, Enlisted ranks(russian: Нижн� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ryadovoy
(russian: Рядово́й) in the Army, Airborne troops, and Air Force of the Russian Federation is the designation of a member of the rank group of enlisted personnel. The rank is equivalent to ''matros'' ( ru , матрос) in the Russian Navy. In the armed forces of the Soviet Union (and later in those of the Russian Federation) ''yefreytor'' is the second-lowest rank of enlisted personnel. The word relates to the Russian ''ryad'' (russian: ряд), which in a military context means "file" or "rank" (in the sense of "rank and file"). History The Imperial Russian Army used the designation before 1917. The rank re-appeared in the newly named Soviet Army in 1946, replacing the rank of "Red Army man" () used in the Red Army from 1918 to 1946. USSR In the USSR Armed Forces the rank designation ''Ryadovoy'' was introduced in 1946.Ordinance ''Interior Service of the Armed Force of the USSR'', from the year 1946; pertaining to change ''Krasnoarmeets'' and ''Boets'' to ''R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2nd Pavlograd Life Hussar Regiment
The 2nd Pavlograd Life Hussar Regiment () was a cavalry regiment of the Imperial Russian Army. The regiment was originally formed in 1783 as the Pavlograd Light Horse Regiment from the Dnepr and Yekaterinoslav Regiments of Pikemen, although it traced its seniority back to the establishment of both regiments in 1764. It became the Pavlograd Hussar Regiment in 1801, and fought in the Napoleonic Wars, distinguishing itself at the Battle of Schöngrabern during the War of the Third Coalition. The regiment also fought at Austerlitz, Eylau, and Friedland, but served in a secondary theatre during the French invasion of Russia, although it fought in the Battle of Berezina in the latter. Subsequently, it took part in the Russian campaign in Europe, fighting at Leipzig, Craonne and Saint-Dizier. The regiment went on to fight in the Russo-Turkish War of 1828–1829, the November Uprising, the Hungarian Revolution of 1848, the Crimean War, and the January Uprising. Origins The Pavlograd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Front (Russian Empire)
The Western Front (russian: Западный фронт) was an army group in the armed forces of the Russian Empire during the First World War. It was established in August 1915 when the Northwestern Front was split into the Northern Front and Western Front, and was disbanded in 1918. From the time of its formation until the final year of its existence, the Western Front's field headquarters was in Smolensk, but it was later moved to Minsk. Composition * Field Headquarters * 1st Army (August 1915 - April 1916) * 2nd Army (August 1915 - the beginning of 1918) *[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Białystok–Minsk
The Battle of Białystok–Minsk was a German strategic operation conducted by the Wehrmacht's Army Group Centre under Field Marshal Fedor von Bock during the penetration of the Soviet border region in the opening stage of Operation Barbarossa, lasting from 22 June to 9 July 1941. The Army Group's 2nd Panzer Group under Colonel General Heinz Guderian and the 3rd Panzer Group under Colonel General Hermann Hoth decimated the Soviet frontier defenses, defeated all Soviet counter-attacks and encircled four Soviet Armies of the Red Army's Western Front near Białystok and Minsk by 30 June. The majority of the Western Front was enclosed within, and the pockets were liquidated by 9 July. The Red Army lost 420,000 men against Wehrmacht casualties of over 12,157. The Germans destroyed the Soviet Western Front in 18 days and advanced 460 kilometers into the Soviet Union, causing many to believe that the Germans had effectively won the war against the Soviet Union. Prelude Commanded ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operation Barbarossa
Operation Barbarossa (german: link=no, Unternehmen Barbarossa; ) was the invasion of the Soviet Union by Nazi Germany and many of its Axis allies, starting on Sunday, 22 June 1941, during the Second World War. The operation, code-named after Frederick Barbarossa ("red beard"), a 12th-century Holy Roman emperor and German king, put into action Nazi Germany's ideological goal of conquering the western Soviet Union to repopulate it with Germans. The German aimed to use some of the conquered people as forced labour for the Axis war effort while acquiring the oil reserves of the Caucasus as well as the agricultural resources of various Soviet territories. Their ultimate goal was to create more (living space) for Germany, and the eventual extermination of the indigenous Slavic peoples by mass deportation to Siberia, Germanisation, enslavement, and genocide. In the two years leading up to the invasion, Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union signed political and economic pacts for st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Winter War
The Winter War,, sv, Vinterkriget, rus, Зи́мняя война́, r=Zimnyaya voyna. The names Soviet–Finnish War 1939–1940 (russian: link=no, Сове́тско-финская война́ 1939–1940) and Soviet–Finland War 1939–1940 (russian: link=no, Сове́тско-финляндская война́ 1939–1940) are often used in Russian historiographybr>В.Н. Барышников. От прохладного мира к Зимней войне. Восточная политика Финляндии в 1930–е годы. Санкт-Петербург, 1997.; О.Д. Дудорова. Неизвестные страницы Зимней войны. In: Военно-исторический журнал. 1991. №9.; Зимняя война 1939–1940. Книга первая. Политическая история. М., 1998. – ; ttp://www.otvaga2004.narod.ru/photo/winterwar/wwar1.htm М. Коломиец. Танки в Зимней войне 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soviet Invasion Of Poland
The Soviet invasion of Poland was a military operation by the Soviet Union without a formal declaration of war. On 17 September 1939, the Soviet Union invaded Poland from the east, 16 days after Nazi Germany invaded Poland from the west. Subsequent military operations lasted for the following 20 days and ended on 6 October 1939 with the two-way division and annexation of the entire territory of the Second Polish Republic by Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union. This division is sometimes called the Fourth Partition of Poland. The Soviet (as well as German) invasion of Poland was indirectly indicated in the "secret protocol" of the Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact signed on 23 August 1939, which divided Poland into "spheres of influence" of the two powers. German and Soviet cooperation in the invasion of Poland has been described as co-belligerence. The Red Army, which vastly outnumbered the Polish defenders, achieved its targets, encountering only limited resistance. Some 320,000 Poles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Major General
Major general (abbreviated MG, maj. gen. and similar) is a military rank used in many countries. It is derived from the older rank of sergeant major general. The disappearance of the "sergeant" in the title explains the apparent confusion of a lieutenant general outranking a major general, whereas a major outranks a lieutenant. In the Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth and in the United States, when appointed to a field command, a major general is typically in command of a Division (military), division consisting of around 6,000 to 25,000 troops (several regiments or brigades). It is a two-star general, two-star rank that is subordinate to the rank of lieutenant general and senior to the rank of brigadier or brigadier general. In the Commonwealth, major general is equivalent to the navy rank of rear admiral. In air forces with a separate rank structure (Commonwealth), major general is equivalent to air vice-marshal. In some countries including much of Eastern Europe, major ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.png)


.jpg)
