|
Putyatin (family)
The House of Putyatin (russian: Путятин), also romanized Poutiatine, Putjatin, Putiatin, is a Rurikid family with princely and noble lines. They branched from the dukes of the autonomous principality of Drutsk, sometime in mid-15th century. Notable figures of the princely family * Prince Nikolai Putyatin, Russian philanthropist and philosopher. * Duke Mikiitta Iivananpoika Putjatin settled after mid-15th century to the service of Moscow and received estates from Ivan III * Duke Taavetti Mikiitanpoika Putjatin held in the beginning of the 16th century a remarkable bunch of landed estates in Karelia of Käkisalmi in eastern Finland. He is ancestor of all the presently living members of the princely family of Putjatin. The taxation register of Vatja from the year 1500 lists several of his holdings. * Prince Sergei Putjatin, the second husband of Grand Duchess Maria Pavlovna the younger (1890–1958) Members of other (non-princely) Putiatin families * Yevfimy Putyatin, Russia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
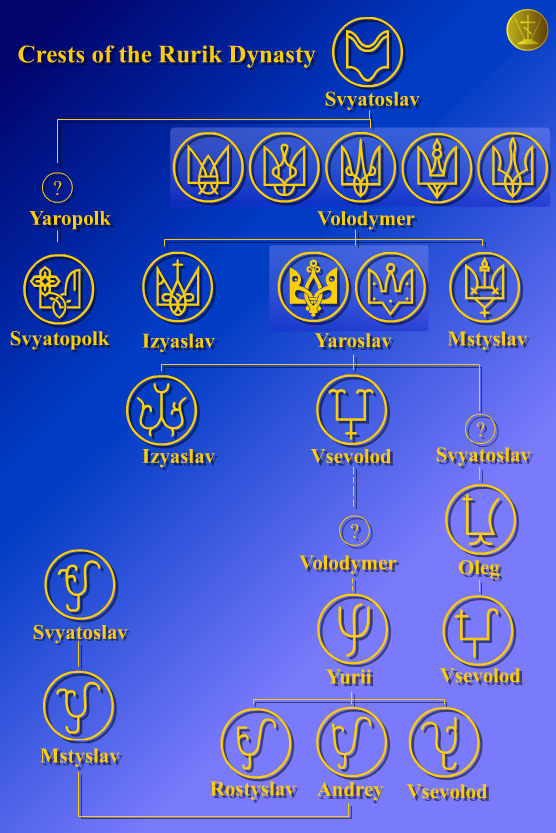
Rurikid
The Rurik dynasty ( be, Ру́рыкавічы, Rúrykavichy; russian: Рю́риковичи, Ryúrikovichi, ; uk, Рю́риковичі, Riúrykovychi, ; literally "sons/scions of Rurik"), also known as the Rurikid dynasty or Rurikids, was a noble lineage founded by the Varangian prince Rurik, who established himself in Novgorod around the year AD 862. The Rurikids were the ruling dynasty of Kievan Rus' (after the conquest of Kiev by Oleg of Novgorod in 882) before it finally disintegrated in the mid-13th century, as well as the successor Rus' principalities and Rus' prince republics of Novgorod, Pskov, Vladimir-Suzdal, Ryazan, Smolensk, Galicia-Volhynia (after 1199), Chernigov, and the Grand Duchy of Moscow (from 1263). Following the disintegration of Kievan Rus', the most powerful state to eventually arise was the Grand Duchy of Moscow, initially a part of Vladimir-Suzdal, which, along with the Novgorod Republic, established the basis of the modern Russian nation.Excer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drutsk
Druck or Drutsk ( be, Друцк, ; pl, Druck, russian: Друцк, also known as ''Дрютескъ'' (''Dryutesk'') or ''Дрюческъ'' (''Druchesk'') in the Middle Ages), is a historical town in Belarus, 40 kilometres (ca. 25 miles) west of Mahilyow. The town was established in 1078 as an outpost of the Principality of Polatsk on the road from Polatsk to Kiev and Chernihov. According to the Drutsk Gospel, the town was built around one of the oldest Christian churches in White Ruthenia erected in 1001. In the 12th century and 13th century it was a centre of the early medieval Principality of Druck, ruled by the dukes of the Polatsk branch of the Rurikid dynasty. Since the 13th century there is only limited information about the town available in the chronicles. In 1524 Drutsk has been burned down by Russians in a war and started to lose its political importance. Exact time and reasons of the town's decline are unknown. Historians estimate the period of decline to between ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nikolai Putyatin
Prince Nikolai Abramovich Putyatin (russian: Николай Абрамович Путятин), also romanized Putiatin, Puttiatin or Poutiatine (16 May 1749 – 13 January 1830) was a philanthropist, philosopher, and eccentric personality from the Rurikid dynasty. Life Born in Kiev, Prince Putyatin joined the Russian army early in his life. After having to oversee a brutal punishment as an officer, he left the service. He learned about architecture and garden arts, and contributed to the Gardens of Tsarskoye Selo. His talent and technical skills earned him a supervising position for public buildings at the court in Saint Petersburg. He was later promoted to Kammerherr and Geheimrat at the imperial court. There he met and fell in love with Elisabeth von Sievers, the daughter of the court's chamberlain Karl von Sievers. Her husband was the influential Russian governor Jacob Johann von Sievers, a relative and protégé of her father. The long-lasting love affair culminated in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grand Duchess Maria Pavlovna Of Russia (1890-1958)
Grand Duchess Maria Pavlovna of Russia may refer to: *Grand Duchess Maria Pavlovna of Russia (1786–1859) Maria Pavlovna (russian: Мария Павловна; 16 February 1786 S 5 February– 23 June 1859) was born a grand duchess of Russia as the daughter of Paul I, Emperor of all the Russias and later became the Grand Duchess of Saxe-Weimar- ..., daughter of Paul I of Russia * Grand Duchess Maria Pavlovna of Russia (1854-1920) or Duchess Marie of Mecklenburg-Schwerin, daughter-in-law of Alexander II of Russia, called "the Elder" * Grand Duchess Maria Pavlovna of Russia (1890–1958), daughter of Grand Duke Paul Alexandrovich of Russia, called "the Younger" {{hndis, name=Maria Pavlovna of Russia, Grand Duchess ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yevfimy Putyatin
Yevfimiy Vasilyevich Putyatin (russian: Евфи́мий Васи́льевич Путя́тин; November 8, 1803 – October 16, 1883), also known as was an admiral in the Imperial Russian Navy. His diplomatic mission to Japan resulted in the signing of the Treaty of Shimoda in 1855, for which he was made a count. His mission to China in 1858 resulted in the Russian Treaty of Tianjin. Early life Putyatin was descended from a noble family in Novgorod. He entered the Naval Cadet Corps, graduating in 1822, and soon afterwards was appointed to the crew of Mikhail Petrovich Lazarev which circumnavigated the globe in a three-year voyage from 1822 to 1825. He subsequently participated in the Battle of Navarino during the Greek War of Independence on October 20, 1827 and was awarded the Order of St. Vladimir, 4th degree. From 1828 to 1832, the participated in numerous missions in the Mediterranean and in the Baltic, and was awarded the Order of St George, 4th class. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Europäische Stammtafeln
''Europäische Stammtafeln'' - German for ''European Family Trees'' - is a series of twenty-nine books which contain sets of genealogical tables of the most influential families of Medieval European history. It is a standard reference work for those researching medieval, imperial, royal and noble families of Europe. A reference to this work is usually to the third series. A fourth series, identified as ''Neue Folge'', was being written by Rev. Detlev Schwennicke who was the sole author who started at volume 17 and is currently being published Frankfurt am Main, by Verlag Vittorio Klostermann. Twenty-nine volumes are available. Detlev Schwennicke died on 24 December 2012.John P. DuLong, Ph.D''Europäische Stammtafeln'' Notes/ref> History The preceding 16 volumes of the third series of the Europäische Stammtafeln (edited by Detlev Schwennicke) was a derivative work which built on the contributions of: * the first series edited by Wilhelm Karl, Prinz zu Isenburg (1903–1956). He pu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rurikids
The Rurik dynasty ( be, Ру́рыкавічы, Rúrykavichy; russian: Рю́риковичи, Ryúrikovichi, ; uk, Рю́риковичі, Riúrykovychi, ; literally "sons/scions of Rurik"), also known as the Rurikid dynasty or Rurikids, was a noble lineage founded by the Varangian prince Rurik, who established himself in Novgorod around the year AD 862. The Rurikids were the ruling dynasty of Kievan Rus' (after the conquest of Kiev by Oleg of Novgorod in 882) before it finally disintegrated in the mid-13th century, as well as the successor Rus' principalities and Rus' prince republics of Novgorod, Pskov, Vladimir-Suzdal, Ryazan, Smolensk, Galicia-Volhynia (after 1199), Chernigov, and the Grand Duchy of Moscow (from 1263). Following the disintegration of Kievan Rus', the most powerful state to eventually arise was the Grand Duchy of Moscow, initially a part of Vladimir-Suzdal, which, along with the Novgorod Republic, established the basis of the modern Russian nation.Excerp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |