|
Purple Earth Hypothesis
The Purple Earth hypothesis is an astrobiological hypothesis that photosynthetic life forms of early Earth were based on the simpler molecule retinal rather than the more complex chlorophyll, making Earth appear purple rather than green. An example of retinal-based organisms that exist today are the photosynthetic microbes collectively called Haloarchaea. That time would date somewhere between 2.4 and 3.5 billion years ago, prior to the Great Oxygenation Event. Many Haloarchaea contain the retinal protein, bacteriorhodopsin, in their purple membrane which carries out light-driven proton pumping, generating a proton-motive gradient across the cell membrane and driving ATP synthesis. The haloarchaeal purple membrane constitutes one of the simplest known bioenergetic systems for harvesting light energy. Retinal-containing purple membrane exhibits a single light absorption peak centered in the green-yellow energy-rich region of the solar spectrum, but allows transmission of red and bl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astrobiology
Astrobiology, and the related field of exobiology, is an interdisciplinary scientific field that studies the origins, early evolution, distribution, and future of life in the universe. Astrobiology is the multidisciplinary field that investigates the deterministic conditions and contingent events with which life arises, distributes, and evolves in the universe. Astrobiology makes use of molecular biology, biophysics, biochemistry, chemistry, astronomy, physical cosmology, exoplanetology, geology, paleontology, and ichnology to investigate the possibility of life on other worlds and help recognize biospheres that might be different from that on Earth. The origin and early evolution of life is an inseparable part of the discipline of astrobiology. Astrobiology concerns itself with interpretation of existing scientific data, and although speculation is entertained to give context, astrobiology concerns itself primarily with hypotheses that fit firmly into existing scientific ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Retinal
Retinal (also known as retinaldehyde) is a polyene chromophore. Retinal, bound to proteins called opsins, is the chemical basis of visual phototransduction, the light-detection stage of visual perception (vision). Some microorganisms use retinal to convert light into metabolic energy. In fact, a recent study suggests most living organisms on our planet ~3 billion years ago used retinal to convert sunlight into energy rather than chlorophyll. Since retinal absorbs mostly green light and transmits purple light, this gave rise to the Purple Earth Hypothesis. There are many forms of vitamin A — all of which are converted to retinal, which cannot be made without them. Retinal itself is considered to be a form of vitamin A when eaten by an animal. The number of different molecules that can be converted to retinal varies from species to species. Retinal was originally called retinene, and was renamed after it was discovered to be vitamin A aldehyde. Vertebrate animals ingest reti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chlorophyll
Chlorophyll (also chlorophyl) is any of several related green pigments found in cyanobacteria and in the chloroplasts of algae and plants. Its name is derived from the Greek words , ("pale green") and , ("leaf"). Chlorophyll allow plants to absorb energy from light. Chlorophylls absorb light most strongly in the blue portion of the electromagnetic spectrum as well as the red portion. Conversely, it is a poor absorber of green and near-green portions of the spectrum. Hence chlorophyll-containing tissues appear green because green light, diffusively reflected by structures like cell walls, is less absorbed. Two types of chlorophyll exist in the photosystems of green plants: chlorophyll ''a'' and ''b''. History Chlorophyll was first isolated and named by Joseph Bienaimé Caventou and Pierre Joseph Pelletier in 1817. The presence of magnesium in chlorophyll was discovered in 1906, and was that element's first detection in living tissue. After initial work done by German chemi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Halobacteria
Haloarchaea (halophilic archaea, halophilic archaebacteria, halobacteria) are a class of the Euryarchaeota, found in water saturated or nearly saturated with salt. Halobacteria are now recognized as archaea rather than bacteria and are one of the largest groups. The name 'halobacteria' was assigned to this group of organisms before the existence of the domain Archaea was realized, and while valid according to taxonomic rules, should be updated. Halophilic archaea are generally referred to as haloarchaea to distinguish them from halophilic bacteria. These microorganisms are among the halophile organisms, that they require high salt concentrations to grow, with most species requiring more than 2.0M NaCl for growth and survival. They are a distinct evolutionary branch of the Archaea distinguished by the possession of ether-linked lipids and the absence of murein in their cell walls. Haloarchaea can grow aerobically or anaerobically. Parts of the membranes of haloarchaea are purpl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Oxygenation Event
The Great Oxidation Event (GOE), also called the Great Oxygenation Event, the Oxygen Catastrophe, the Oxygen Revolution, the Oxygen Crisis, or the Oxygen Holocaust, was a time interval during the Paleoproterozoic era when the Earth's atmosphere and the shallow ocean first experienced a rise in the amount of oxygen. This began approximately 2.460–2.426 Ga (billion years) ago, during the Siderian period, and ended approximately 2.060 Ga, during the Rhyacian. Geological, isotopic, and chemical evidence suggests that biologically-produced molecular oxygen (dioxygen, O2) started to accumulate in Earth's atmosphere and changed it from a weakly reducing atmosphere practically free of oxygen into an oxidizing atmosphere containing abundant oxygen, with oxygen levels being as high as 10% of their present atmospheric level by the end of the GOE. The sudden injection of toxic oxygen into an anaerobic biosphere may have caused the extinction of many existing anaerobic species o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
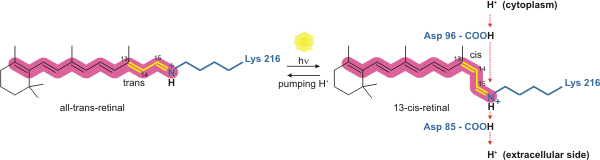
Bacteriorhodopsin
Bacteriorhodopsin is a protein used by Archaea, most notably by haloarchaea, a class of the Euryarchaeota. It acts as a proton pump; that is, it captures light energy and uses it to move protons across the membrane out of the cell. The resulting proton gradient is subsequently converted into chemical energy. Function Bacteriorhodopsin is a light-driven H+ ion transporter found in some haloarchaea, most notably '' Halobacterium salinarum'' (formerly known as syn. ''H. halobium''). The proton-motive force generated by the protein is used by ATP synthase to generate adenosine triphosphate (ATP). By expressing bacteriorhodopsin, the archaea cells are able to synthesise ATP in the absence of a carbon source. Structure Bacteriorhodopsin is a 27 kDa integral membrane protein usually found in two-dimensional crystalline patches known as "purple membrane", which can occupy almost 50% of the surface area of the archaeal cell. The repeating element of the hexagonal lattice is compos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Visible Spectrum
The visible spectrum is the portion of the electromagnetic spectrum that is visual perception, visible to the human eye. Electromagnetic radiation in this range of wavelengths is called ''visible light'' or simply light. A typical human eye will respond to wavelengths from about 380 to about 750 nanometers. In terms of frequency, this corresponds to a band in the vicinity of 400–790 Terahertz (unit), terahertz. These boundaries are not sharply defined and may vary per individual. Under optimal conditions these limits of human perception can extend to 310 nm (ultraviolet) and 1100 nm (near infrared). The optical spectrum is sometimes considered to be the same as the visible spectrum, but some authors define the term more broadly, to include the ultraviolet and infrared parts of the electromagnetic spectrum as well. The spectrum does not contain all the colors that the human visual system can distinguish. ''Excitation purity, Unsaturated colors'' such as pink, or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacteriorhodopsin
Bacteriorhodopsin is a protein used by Archaea, most notably by haloarchaea, a class of the Euryarchaeota. It acts as a proton pump; that is, it captures light energy and uses it to move protons across the membrane out of the cell. The resulting proton gradient is subsequently converted into chemical energy. Function Bacteriorhodopsin is a light-driven H+ ion transporter found in some haloarchaea, most notably '' Halobacterium salinarum'' (formerly known as syn. ''H. halobium''). The proton-motive force generated by the protein is used by ATP synthase to generate adenosine triphosphate (ATP). By expressing bacteriorhodopsin, the archaea cells are able to synthesise ATP in the absence of a carbon source. Structure Bacteriorhodopsin is a 27 kDa integral membrane protein usually found in two-dimensional crystalline patches known as "purple membrane", which can occupy almost 50% of the surface area of the archaeal cell. The repeating element of the hexagonal lattice is compos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haloarchaea
Haloarchaea (halophilic archaea, halophilic archaebacteria, halobacteria) are a class of the Euryarchaeota, found in water saturated or nearly saturated with salt. Halobacteria are now recognized as archaea rather than bacteria and are one of the largest groups. The name 'halobacteria' was assigned to this group of organisms before the existence of the domain Archaea was realized, and while valid according to taxonomic rules, should be updated. Halophilic archaea are generally referred to as haloarchaea to distinguish them from halophilic bacteria. These microorganisms are among the halophile organisms, that they require high salt concentrations to grow, with most species requiring more than 2.0M NaCl for growth and survival. They are a distinct evolutionary branch of the Archaea distinguished by the possession of ether-linked lipids and the absence of murein in their cell walls. Haloarchaea can grow aerobically or anaerobically. Parts of the membranes of haloarchaea are purpli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microbial Rhodopsin
Microbial rhodopsins, also known as bacterial rhodopsins are retinal-binding proteins that provide light-dependent ion transport and sensory functions in halophilic and other bacteria. They are integral membrane proteins with seven transmembrane helices, the last of which contains the attachment point (a conserved lysine) for retinal. This protein family includes light-driven proton pumps, ion pumps and ion channels, as well as light sensors. For example, the proteins from halobacteria include bacteriorhodopsin and archaerhodopsin, which are light-driven proton pumps; halorhodopsin, a light-driven chloride pump; and sensory rhodopsin, which mediates both photoattractant (in the red) and photophobic (in the ultra-violet) responses. Proteins from other bacteria include proteorhodopsin. Contrary to their name, microbial rhodopsins are found not only in Archaea and Bacteria, but also in Eukaryota (such as algae) and viruses; although they are rare in complex multicellular org ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)

.jpg)