|
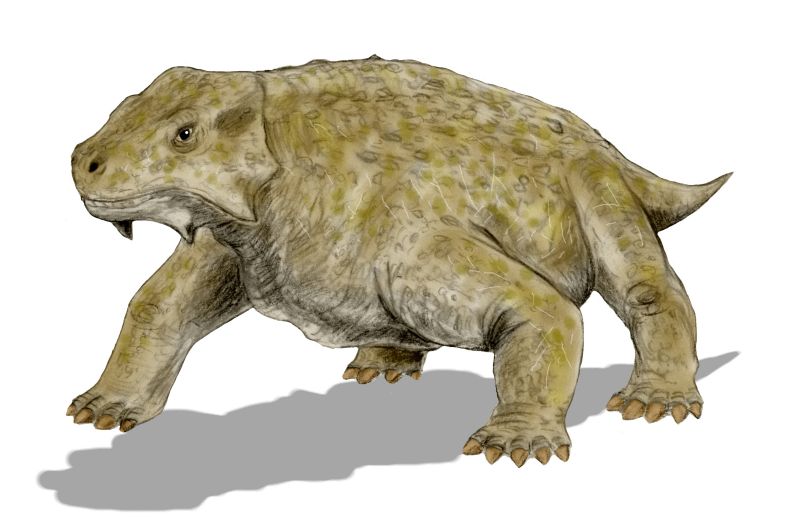
Pumiliopareia
''Pumiliopareia'' is an extinct genus of pareiasauridae, pareiasaurid parareptile from the Permian period of South Africa. It is known from a complete skeleton with osteoderms. Description ''Pumiliopareia'' was about 50 cm in length with a 12 cm skull. It is the smallest known member of the pareiasaurs, measuring only a fifth as long as some of its larger relatives. Like ''Anthodon (reptile), Anthodon'', its body was entirely covered with osteoderms. In analyses that support a pareiasaur origin of turtles, the sister taxon of the testudines. However it specifically shares with turtles a single trait only: Ribs greatly expanded anteroposteriorly (i.e. wide). Classification Originally included under the genus ''Nanoparia'', it was given its own name by Lee 1997 who found it did not form a clade with ''Nanoparia luckhoffi'', the type species of that genus, and preferred to have monophyletic genera. ''Nanoparia'' may still be a paraphyletic genus, which is allowed in Linan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pumiliopareiasauria
Velosauria is a group of Pareiasauria, pareiasaur Sauropsida, reptiles that existed in the late Permian period. They ranged in size from the 50-centimeter-long ''Pumiliopareia'' to the 3-meter-long ''Scutosaurus''. Velosaurs were some of the largest reptiles of their time. Description Velosaurs were large reptiles that were characterized by their short tails, small heads, broad feet, and their legs, which were directly in between sprawling and semi-erect. Velosaurs' bodies were covered in osteoderms and smaller scales all over. Their heads came in all sorts of different shapes; from the cheek-frilled ''Scutosaurus'' to the spiky-headed ''Elginia'' to the nose-horned ''Arganaceras''. They were herbivorous, and it is believed that their large bodies housed a complex gut. Classification Some paleontologists believe velosaurs to be the direct ancestors to turtles. They argue that the smaller Pumiliopareiasauria, pumiliopareiasaurs evolved large, plate-like scutes that laid flat on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pumiliopareiasauria
Velosauria is a group of Pareiasauria, pareiasaur Sauropsida, reptiles that existed in the late Permian period. They ranged in size from the 50-centimeter-long ''Pumiliopareia'' to the 3-meter-long ''Scutosaurus''. Velosaurs were some of the largest reptiles of their time. Description Velosaurs were large reptiles that were characterized by their short tails, small heads, broad feet, and their legs, which were directly in between sprawling and semi-erect. Velosaurs' bodies were covered in osteoderms and smaller scales all over. Their heads came in all sorts of different shapes; from the cheek-frilled ''Scutosaurus'' to the spiky-headed ''Elginia'' to the nose-horned ''Arganaceras''. They were herbivorous, and it is believed that their large bodies housed a complex gut. Classification Some paleontologists believe velosaurs to be the direct ancestors to turtles. They argue that the smaller Pumiliopareiasauria, pumiliopareiasaurs evolved large, plate-like scutes that laid flat on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pareiasaurs
Pareiasaurs (meaning "cheek lizards") are an extinct clade of large, herbivorous parareptiles. Members of the group were armoured with scutes which covered large areas of the body. They first appeared in southern Pangea during the Middle Permian, before becoming globally distributed during the Late Permian. Pareiasaurs were the largest reptiles of the Permian, reaching sizes equivalent to those of contemporary therapsids. Pareiasaurs became extinct at the end of the Permian during the Permian-Triassic extinction event. Description Pareiasaurs ranged in size from long, and may have weighed up to . They were stocky, with short tails, small heads, robust limbs, and broad feet. The cow-sized species ''Bunostegos'', which lived 260 million years ago, is the earliest known example of a tetrapod with a fully erect posture as its legs were positioned directly under its body. Pareiasaurs were protected by bony scutes called osteoderms that were set into the skin. Their heavy skulls were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanoparia
''Nanoparia'' is an extinct genus of pareiasaur that lived in the Permian. Description It was about 60 cm in length, and weighed around 8 to 10 kilograms. Classification This is an unusual small, spiny specialised form. The skull is very similar to that of Pareiasaurus and Romer considered it a synonym of the latter. Orlov however (in Osnovy Paleontology, the monumental multi-volume Russian textbook of Paleontology) placed it in the Elginiinae. Kuhn (1969) however argues that while resembling Elginia in the ossifications at the rear of the skull, it differs completely in proportions and would not seem to be related. Lee (1997) considers it a basal member of the dwarf pareiasaurs. ''Nanoparia'' is believed to be among the pareiasaur genera most closely related to turtles Turtles are an order (biology), order of reptiles known as Testudines, characterized by a special turtle shell, shell developed mainly from their ribs. Modern turtles are divided into two major gro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anthodon (reptile)
''Anthodon'' (meaning "flower tooth") is an extinct genus of pareiasaurid parareptile from the Permian period of South Africa and Tanzania. History Richard Owen, who described ''Anthodon'', thought it was a dinosaur because dinosaurian skull material from the Early Cretaceous had become associated with the Permian material. The dinosaur material was later separated out by Robert Broom in 1912 and was renamed as the stegosaurid ''Paranthodon'' by Franz Nopcsa in 1929. Description This small form combines the primitive feature of interpterygoid fenestrae with an advanced feature of turtle-like armor. It was about in length, and weighed around . Small dermal ossicles covered the body, while the pattern of armor plates on the back reminiscent of a turtle shell. The tail was further shortened relative to less derived forms. Some other forms are characterized by having smooth skulls and armor on the dorsal midline. Skull The skull was small, and the cheekbones unornamented as in oth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Changhsingian
In the geologic time scale, the Changhsingian or Changxingian is the latest age or uppermost stage of the Permian. It is also the upper or latest of two subdivisions of the Lopingian Epoch or Series. The Changhsingian lasted from to 251.902 million years ago (Ma). It was preceded by the Wuchiapingian and followed by the Induan. The greatest mass extinction in the Phanerozoic eon, the Permian–Triassic extinction event, occurred during this age. The extinction rate peaked about a million years before the end of this stage. Stratigraphic definitions The Changhsingian is named after Changxing () in northern Zhejiang, China. The stage was named for the Changhsing Limestone. The name was first used for a stage in 1970; 1973: ''Permian stages names'', in: : ''The Permian and Triassic systems and their mutual boundary'', Canadian Society of Petroleum Geologists Memoir 2, pp 522–548. and was anchored in the international timescale in 1981.; 2006: ''The Global Boundary Stratotype Sect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Permian Reptiles Of Africa
The Permian ( ) is a geologic period and stratigraphic system which spans 47 million years from the end of the Carboniferous Period million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Triassic Period 251.9 Mya. It is the last period of the Paleozoic Era; the following Triassic Period belongs to the Mesozoic Era. The concept of the Permian was introduced in 1841 by geologist Sir Roderick Murchison, who named it after the region of Perm in Russia. The Permian witnessed the diversification of the two groups of amniotes, the synapsids and the sauropsids (reptiles). The world at the time was dominated by the supercontinent Pangaea, which had formed due to the collision of Euramerica and Gondwana during the Carboniferous. Pangaea was surrounded by the superocean Panthalassa. The Carboniferous rainforest collapse left behind vast regions of desert within the continental interior. Amniotes, which could better cope with these drier conditions, rose to dominance in place of their amphibian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paraphyletic
In taxonomy (general), taxonomy, a group is paraphyletic if it consists of the group's most recent common ancestor, last common ancestor and most of its descendants, excluding a few Monophyly, monophyletic subgroups. The group is said to be paraphyletic ''with respect to'' the excluded subgroups. In contrast, a monophyletic group (a clade) includes a common ancestor and ''all'' of its descendants. The terms are commonly used in phylogenetics (a subfield of biology) and in the tree model of historical linguistics. Paraphyletic groups are identified by a combination of Synapomorphy and apomorphy, synapomorphies and symplesiomorphy, symplesiomorphies. If many subgroups are missing from the named group, it is said to be polyparaphyletic. The term was coined by Willi Hennig to apply to well-known taxa like Reptilia (reptiles) which, as commonly named and traditionally defined, is paraphyletic with respect to mammals and birds. Reptilia contains the last common ancestor of reptiles a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Testudines
Turtles are an order (biology), order of reptiles known as Testudines, characterized by a special turtle shell, shell developed mainly from their ribs. Modern turtles are divided into two major groups, the Pleurodira (side necked turtles) and Cryptodira (hidden necked turtles), which differ in the way the head retracts. There are 360 living and recently extinct species of turtles, including land-dwelling tortoises and freshwater terrapins. They are found on most continents, some islands and, in the case of sea turtles, much of the ocean. Like other Amniote, amniotes (reptiles, birds, and mammals) they breathe air and do not lay eggs underwater, although many species live in or around water. Turtle shells are made mostly of bone; the upper part is the domed Turtle shell#Carapace, carapace, while the underside is the flatter plastron or belly-plate. Its outer surface is covered in scale (anatomy), scales made of keratin, the material of hair, horns, and claws. The carapace bon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Permian
The Permian ( ) is a geologic period and stratigraphic system which spans 47 million years from the end of the Carboniferous Period million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Triassic Period 251.9 Mya. It is the last period of the Paleozoic Era; the following Triassic Period belongs to the Mesozoic Era. The concept of the Permian was introduced in 1841 by geologist Sir Roderick Murchison, who named it after the region of Perm in Russia. The Permian witnessed the diversification of the two groups of amniotes, the synapsids and the sauropsids ( reptiles). The world at the time was dominated by the supercontinent Pangaea, which had formed due to the collision of Euramerica and Gondwana during the Carboniferous. Pangaea was surrounded by the superocean Panthalassa. The Carboniferous rainforest collapse left behind vast regions of desert within the continental interior. Amniotes, which could better cope with these drier conditions, rose to dominance in place of their am ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osteoderms
Osteoderms are bony deposits forming scales, plates, or other structures based in the dermis. Osteoderms are found in many groups of extant and extinct reptiles and amphibians, including lizards, crocodilians, frogs, temnospondyls (extinct amphibians), various groups of dinosaurs (most notably ankylosaurs and stegosaurians), phytosaurs, aetosaurs, placodonts, and hupehsuchians (marine reptiles with possible ichthyosaur affinities). Osteoderms are uncommon in mammals, although they have occurred in many xenarthrans ( armadillos and the extinct glyptodonts and mylodontid and scelidotheriid ground sloths). The heavy, bony osteoderms have evolved independently in many different lineages. The armadillo osteoderm is believed to develop in subcutaneous dermal tissues. These varied structures should be thought of as anatomical analogues, not homologues, and do not necessarily indicate monophyly. The structures are however derived from scutes, common to all classes of amnio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Kingdom (biology), biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals Heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, are Motility, able to move, can Sexual reproduction, reproduce sexually, and go through an ontogenetic stage in which their body consists of a hollow sphere of Cell (biology), cells, the blastula, during Embryogenesis, embryonic development. Over 1.5 million Extant taxon, living animal species have been Species description, described—of which around 1 million are Insecta, insects—but it has been estimated there are over 7 million animal species in total. Animals range in length from to . They have Ecology, complex interactions with each other and their environments, forming intricate food webs. The scientific study of animals is known as zoology. Most living animal species are in Bilateria, a clade whose members have a Symmetry in biology#Bilate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |