|
Pulsus Paradoxus
Pulsus paradoxus, also paradoxic pulse or paradoxical pulse, is an abnormally large decrease in stroke volume, systolic blood pressure and pulse wave amplitude during inspiration. The normal fall in pressure is less than 10 mmHg. When the drop is more than 10 mmHg, it is referred to as pulsus paradoxus. Pulsus paradoxus is not related to pulse rate or heart rate, and it is not a paradoxical rise in systolic pressure. The normal variation of blood pressure during breathing/respiration is a decline in blood pressure during inhalation and an increase during exhalation. Pulsus paradoxus is a sign that is indicative of several conditions, including cardiac tamponade, chronic sleep apnea, croup, and obstructive lung disease (e.g. asthma, COPD). The ''paradox'' in ''pulsus paradoxus'' is that, on physical examination, one can detect beats on cardiac auscultation during inspiration that cannot be palpated at the radial pulse. It results from an accentuated decrease of the blood pres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Systolic Blood Pressure
Blood pressure (BP) is the pressure of circulating blood against the walls of blood vessels. Most of this pressure results from the heart pumping blood through the circulatory system. When used without qualification, the term "blood pressure" refers to the pressure in the large arteries. Blood pressure is usually expressed in terms of the systolic pressure (maximum pressure during one heartbeat) over diastolic pressure (minimum pressure between two heartbeats) in the cardiac cycle. It is measured in millimeters of mercury ( mmHg) above the surrounding atmospheric pressure. Blood pressure is one of the vital signs—together with respiratory rate, heart rate, oxygen saturation, and body temperature—that healthcare professionals use in evaluating a patient's health. Normal resting blood pressure, in an adult is approximately systolic over diastolic, denoted as "120/80 mmHg". Globally, the average blood pressure, age standardized, has remained about the same since 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heart Rate
Heart rate (or pulse rate) is the frequency of the heartbeat measured by the number of contractions (beats) of the heart per minute (bpm). The heart rate can vary according to the body's physical needs, including the need to absorb oxygen and excrete carbon dioxide, but is also modulated by numerous factors, including, but not limited to, genetics, physical fitness, stress or psychological status, diet, drugs, hormonal status, environment, and disease/illness as well as the interaction between and among these factors. It is usually equal or close to the pulse measured at any peripheral point. The American Heart Association states the normal resting adult human heart rate is 60–100 bpm. Tachycardia is a high heart rate, defined as above 100 bpm at rest. Bradycardia is a low heart rate, defined as below 60 bpm at rest. When a human sleeps, a heartbeat with rates around 40–50 bpm is common and is considered normal. When the heart is not beating in a regular pattern, this is ref ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulmonary Embolism
Pulmonary embolism (PE) is a blockage of an pulmonary artery, artery in the lungs by a substance that has moved from elsewhere in the body through the bloodstream (embolism). Symptoms of a PE may include dyspnea, shortness of breath, chest pain particularly upon breathing in, and coughing up blood. Symptoms of a deep vein thrombosis, blood clot in the leg may also be present, such as a erythema, red, warm, swollen, and painful leg. Signs of a PE include low blood oxygen saturation, oxygen levels, tachypnea, rapid breathing, tachycardia, rapid heart rate, and sometimes a mild fever. Severe cases can lead to Syncope (medicine), passing out, shock (circulatory), abnormally low blood pressure, obstructive shock, and cardiac arrest, sudden death. PE usually results from a blood clot in the leg that travels to the lung. The risk of blood clots is increased by advanced age, cancer, prolonged bed rest and immobilization, smoking, stroke, long-haul travel over 4 hours, certain genetics, g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiogenic Shock
Cardiogenic shock (CS) is a medical emergency resulting from inadequate blood flow due to the dysfunction of the ventricles of the heart.Textbooks of Internal MedicinHarrison's Principles of Internal Medicine 16th Edition, The McGraw-Hill CompaniesCecil Textbook of Medicine by Lee Goldman, Dennis Ausiello, 22nd Edition (2003), W. B. Saunders CompanyThe Oxford Textbook of Medicine Edited by David A. Warrell, Timothy M. Cox and John D. Firth with Edward J. Benz, Fourth Edition (2003), Oxford University Press, Shock: An Overview PDF by Michael L. Cheatham, MD, Ernest F.J. Block, MD, Howard G. Smith, MD, John T. Promes, MD, Surgical Critical Care Service, Department of Surgical Education, |
Pericardial Effusion
A pericardial effusion is an abnormal accumulation of fluid in the pericardial cavity. The pericardium is a two-part membrane surrounding the heart: the outer fibrous connective membrane and an inner two-layered serous membrane. The two layers of the serous membrane enclose the pericardial cavity (the potential space) between them.Phelan, D., Collier, P., Grimm, R. Pericardial Disease'. Cleveland Clinic. July 2015. Retrieved Nov 2020. This pericardial space contains a small amount of pericardial fluid. The fluid is normally 15-50 mL in volume. The pericardium, specifically the pericardial fluid provides lubrication, maintains the anatomic position of the heart in the chest, and also serves as a barrier to protect the heart from infection and inflammation in adjacent tissues and organs.Vogiatzidis, Konstantinos et al.Physiology of pericardial fluid production and drainage" ''Frontiers in physiology'' vol. 6 62. 18 Mar. 2015, doi:10.3389/fphys.2015.00062 By definition, a pericardial e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constrictive Pericarditis
Constrictive pericarditis is a medical condition characterized by a thickened, fibrotic pericardium, limiting the heart's ability to function normally. In many cases, the condition continues to be difficult to diagnose and therefore benefits from a good understanding of the underlying cause. Signs and symptoms Signs and symptoms of constrictive pericarditis are consistent with the following: fatigue, swollen abdomen, difficulty breathing (dyspnea), swelling of legs and general weakness. Related conditions are bacterial pericarditis, pericarditis and pericarditis after a heart attack. Causes The cause of constrictive pericarditis in the developing world are idiopathic in origin, though likely infectious in nature. In regions where tuberculosis is common, it is the cause in a large portion of cases. Causes of constrictive pericarditis include: * Tuberculosis * Incomplete drainage of purulent pericarditis * Fungal and parasitic infections * Chronic pericarditis * Postviral pericard ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myocardial Infarction
A myocardial infarction (MI), commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when blood flow decreases or stops to the coronary artery of the heart, causing damage to the heart muscle. The most common symptom is chest pain or discomfort which may travel into the shoulder, arm, back, neck or jaw. Often it occurs in the center or left side of the chest and lasts for more than a few minutes. The discomfort may occasionally feel like heartburn. Other symptoms may include shortness of breath, nausea, feeling faint, a cold sweat or feeling tired. About 30% of people have atypical symptoms. Women more often present without chest pain and instead have neck pain, arm pain or feel tired. Among those over 75 years old, about 5% have had an MI with little or no history of symptoms. An MI may cause heart failure, an irregular heartbeat, cardiogenic shock or cardiac arrest. Most MIs occur due to coronary artery disease. Risk factors include high blood pressure, smoking, diabetes, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
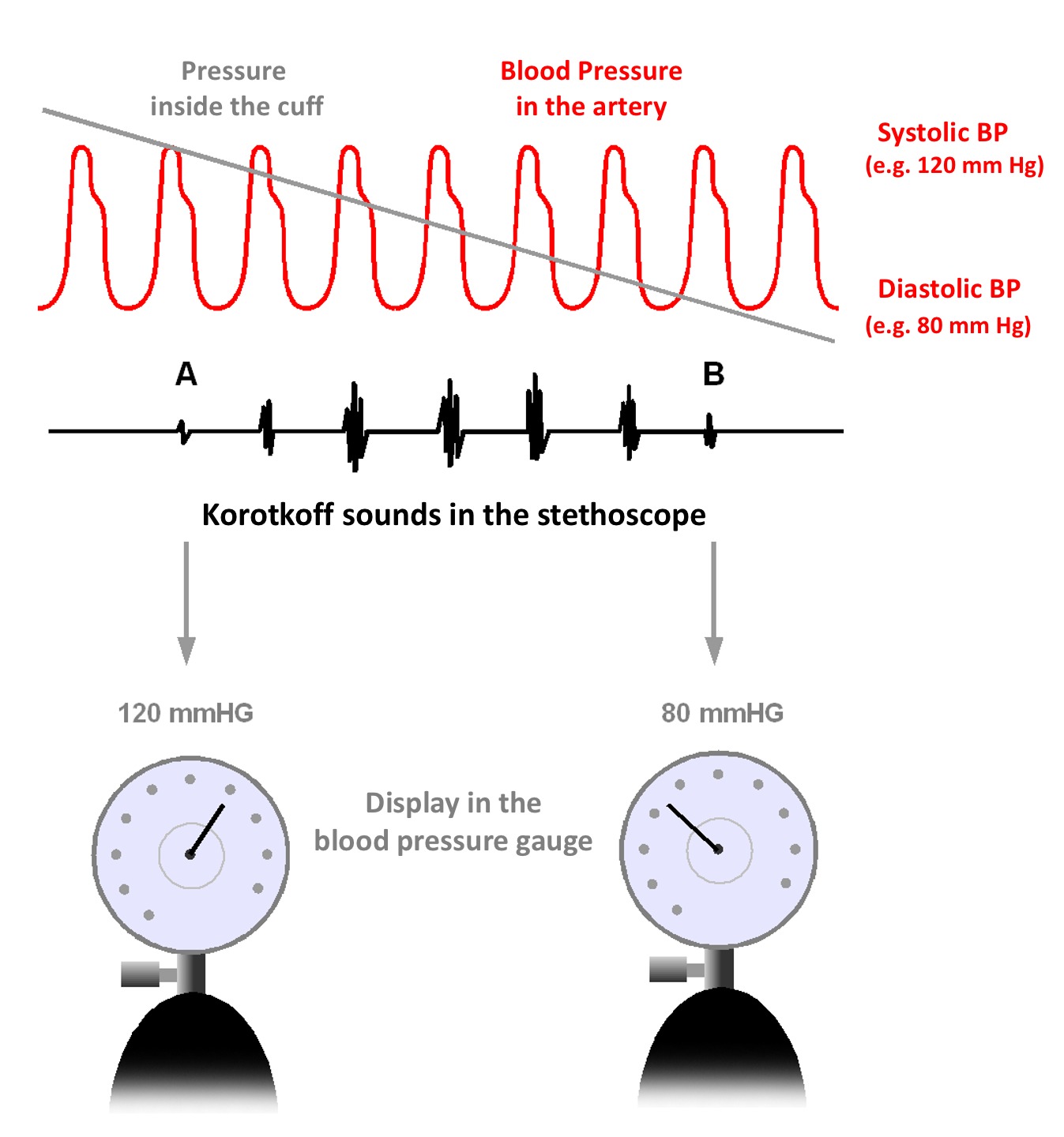
Korotkoff Sounds
Korotkoff sounds are the sounds that medical personnel listen for when they are taking blood pressure using a non-invasive procedure. They are named after Nikolai Korotkov, a Russian physician who discovered them in 1905, when he was working at the Imperial Medical Academy in St. Petersburg, the Russian Empire. Description The sounds heard during the measurement of blood pressure are not the same as the heart sounds heard during chest auscultation that are due to vibrations inside the ventricles associated with the snapping shut of the valves. If a stethoscope is placed over the brachial artery in the antecubital fossa in a normal person (without arterial disease), no sound should be audible. As the heart beats, these pulses are transmitted smoothly via laminar (non-turbulent) blood flow throughout the arteries, and no sound is produced. Similarly, if the cuff of a sphygmomanometer is placed around a patient's upper arm and inflated to a pressure above the patient's systol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blood Pressure Cuff
A sphygmomanometer ( ), a blood pressure monitor, or blood pressure gauge, is a device used to measure blood pressure, composed of an inflatable cuff to collapse and then release the artery under the cuff in a controlled manner, and a mercury or aneroid manometer to measure the pressure. Manual sphygmomanometers are used with a stethoscope when using the auscultatory technique. A sphygmomanometer consists of an inflatable cuff, a measuring unit (the mercury manometer, or aneroid gauge), and a mechanism for inflation which may be a manually operated bulb and valve or a pump operated electrically. Types Both manual and digital meters are currently employed, with different trade-offs in accuracy versus convenience. Manual A stethoscope is required for auscultation ( see below). Manual meters are best used by trained practitioners, and, while it is possible to obtain a basic reading through palpation alone, this yields only the systolic pressure. * Mercury sphygmomanomet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulse Pressure
Pulse pressure is the difference between systolic and diastolic blood pressure. It is measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg). It represents the force that the heart generates each time it contracts. Resting blood pressure is normally approximately 120/80 mmHg, which yields a pulse pressure of approximately 40 mm Hg. Causes High High sodium intake may cause high pulse pressure. Calculation Pulse pressure is the (higher) systolic blood pressure minus the (lower) diastolic blood pressure. The systemic pulse pressure is approximately proportional to stroke volume, or the amount of blood ejected from the left ventricle during systole (pump action) and inversely proportional to the compliance (similar to Elasticity) of the aorta. The aorta has the highest compliance in the arterial system due in part to a relatively greater proportion of elastin fibers versus smooth muscle and collagen. This serves the important function of damping the pulsatile ( max pump pressure) ou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stroke Volume
In cardiovascular physiology, stroke volume (SV) is the volume of blood pumped from the left ventricle per beat. Stroke volume is calculated using measurements of ventricle volumes from an echocardiogram and subtracting the volume of the blood in the ventricle at the end of a beat (called end-systolic volume) from the volume of blood just prior to the beat (called end-diastolic volume). The term ''stroke volume'' can apply to each of the two ventricles of the heart, although it usually refers to the left ventricle. The stroke volumes for each ventricle are generally equal, both being approximately 70 mL in a healthy 70-kg man. Stroke volume is an important determinant of cardiac output, which is the product of stroke volume and heart rate, and is also used to calculate ejection fraction, which is stroke volume divided by end-diastolic volume. Because stroke volume decreases in certain conditions and disease states, stroke volume itself correlates with cardiac function. Calculati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Afterload
Afterload is the pressure that the heart must work against to eject blood during systole (ventricular contraction). Afterload is proportional to the average arterial pressure. As aortic and pulmonary pressures increase, the afterload increases on the left and right ventricles respectively. Afterload changes to adapt to the continually changing demands on an animal's cardiovascular system. Afterload is proportional to mean systolic blood pressure and is measured in millimeters of mercury (mm Hg). Hemodynamics Afterload is a determinant of cardiac output. Cardiac output is the product of stroke volume and heart rate. Afterload is a determinant of stroke volume (in addition to preload, and strength of myocardial contraction). Following Laplace's law, the tension upon the muscle fibers in the heart wall is the pressure within the ventricle multiplied by the volume within the ventricle divided by the wall thickness (this ratio is the other factor in setting the afterload). The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |