|
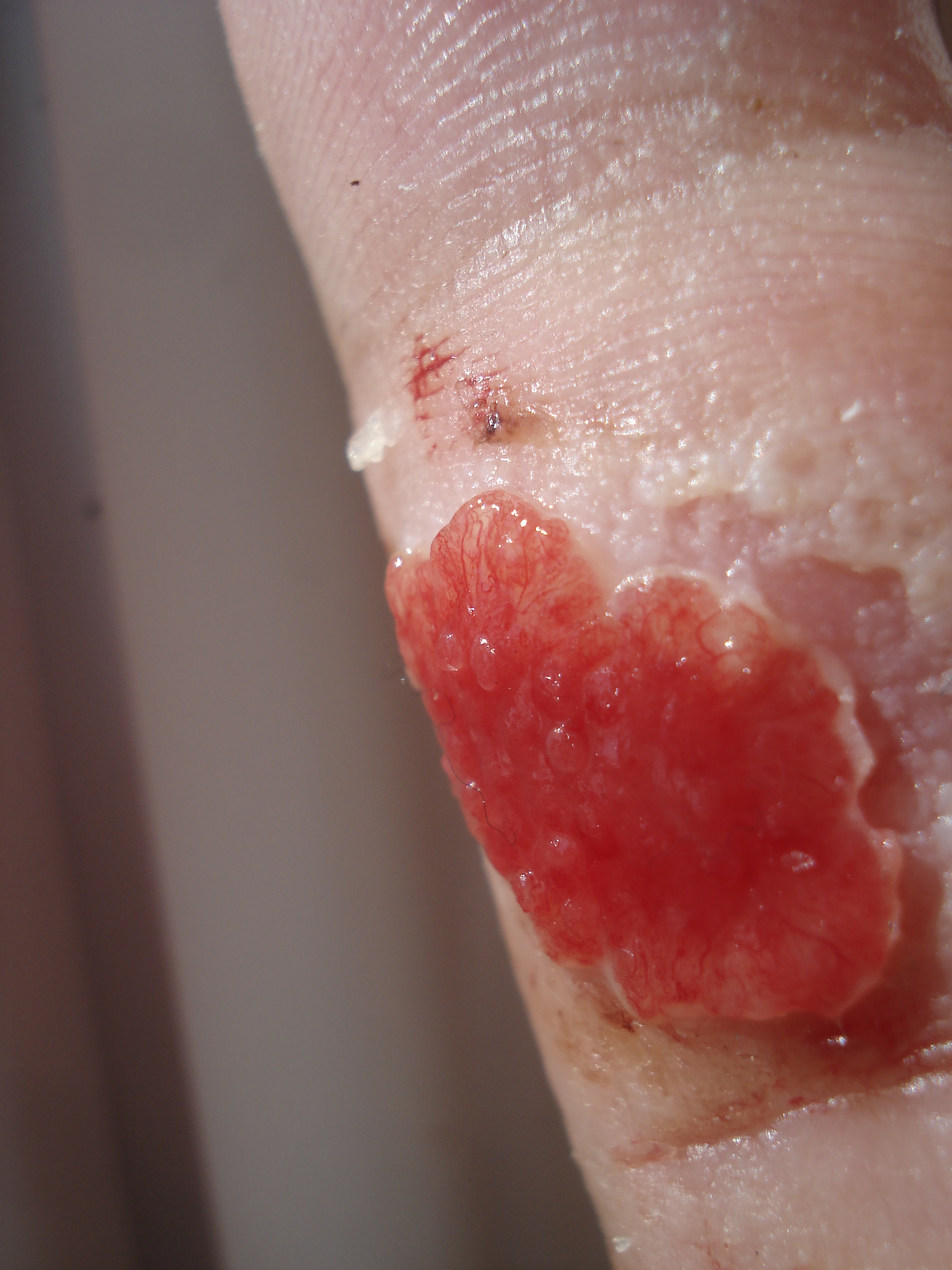
Pulp Polyp
A pulp polyp, also known as chronic hyperplastic pulpitis, is a "productive" (i.e., growing) inflammation of Pulp (tooth), dental pulp in which the development of granulation tissue is seen in response to persistent, low-grade mechanical irritation and bacterial invasion of the pulp. Pathogenesis Pulp polyps develop as overgrowth of the pulpal tissue resulting in the hyperplastic mass. Factors which may contribute to the development of a pulp polyp includes: * Persistence of balance between the irritant and tissue resistance * Continuous low-grade inflammation * Well vascularised pulpal tissue with good tissue reactivity * An open carious cavity * Young patients with a good immune system * Wide apical foramen of the affected tooth to prevent the occurrence of pulpal strangulation and necrosis in response to inflammation Characteristics Pulp polyps are characterised by overgrowth of the pulp tissue outside the boundary of a tooth's pulp chamber. A pulp polyp may be found in an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulp (tooth)
The pulp is the connective tissue, nerves, blood vessels, and odontoblasts that comprise the innermost layer of a tooth. The pulp's activity and signalling processes regulate its behaviour. Anatomy The pulp is the neurovascular bundle central to each tooth, permanent or primary. It is composed of a central pulp chamber, pulp horns, and radicular canals. The large mass of the pulp is contained within the pulp chamber, which is contained in and mimics the overall shape of the crown of the tooth.Illustrated Dental Embryology, Histology, and Anatomy, Bath-Balogh and Fehrenbach, Elsevier, 2011, page 164. Because of the continuous deposition of the dentine, the pulp chamber becomes smaller with the age. This is not uniform throughout the coronal pulp but progresses faster on the floor than on the roof or sidewalls. Radicular pulp canals extend down from the cervical region of the crown to the root apex. They are not always straight but vary in shape, size, and number. They are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Granulation Tissue
Granulation tissue is new connective tissue and microscopic blood vessels that form on the surfaces of a wound during the healing process. Granulation tissue typically grows from the base of a wound and is able to fill wounds of almost any size. Examples of granulation tissue can be seen in pyogenic granulomas and pulp polyps. Its histological appearance is characterized by proliferation of fibroblasts and new thin-walled, delicate capillaries (angiogenesis), infiltrated inflammatory cells in a loose extracellular matrix. Appearance During the migratory phase of wound healing, granulation tissue is: * light red or dark pink, being perfused with new capillary loops or "buds"; * soft to the touch; * moist; * bumpy (granular) in appearance, due to punctate hemorrhages; * pulsatile on palpation; * painless when healthy; Structure Granulation tissue is composed of tissue matrix supporting a variety of cell types, most of which can be associated with one of the following functions: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dental Caries
Tooth decay, also known as cavities or caries, is the breakdown of teeth due to acids produced by bacteria. The cavities may be a number of different colors from yellow to black. Symptoms may include pain and difficulty with eating. Complications may include inflammation of the tissue around the tooth, tooth loss and infection or abscess formation. The cause of cavities is acid from bacteria dissolving the hard tissues of the teeth ( enamel, dentin and cementum). The acid is produced by the bacteria when they break down food debris or sugar on the tooth surface. Simple sugars in food are these bacteria's primary energy source and thus a diet high in simple sugar is a risk factor. If mineral breakdown is greater than build up from sources such as saliva, caries results. Risk factors include conditions that result in less saliva such as: diabetes mellitus, Sjögren syndrome and some medications. Medications that decrease saliva production include antihistamines and antide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tooth
A tooth ( : teeth) is a hard, calcified structure found in the jaws (or mouths) of many vertebrates and used to break down food. Some animals, particularly carnivores and omnivores, also use teeth to help with capturing or wounding prey, tearing food, for defensive purposes, to intimidate other animals often including their own, or to carry prey or their young. The roots of teeth are covered by gums. Teeth are not made of bone, but rather of multiple tissues of varying density and hardness that originate from the embryonic germ layer, the ectoderm. The general structure of teeth is similar across the vertebrates, although there is considerable variation in their form and position. The teeth of mammals have deep roots, and this pattern is also found in some fish, and in crocodilians. In most teleost fish, however, the teeth are attached to the outer surface of the bone, while in lizards they are attached to the inner surface of the jaw by one side. In cartilaginous fish, s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dental Restoration
Dental restoration, dental fillings, or simply fillings are treatments used to restore the function, integrity, and morphology of missing tooth structure resulting from caries or external trauma as well as to the replacement of such structure supported by dental implants. They are of two broad types—''direct'' and ''indirect''—and are further classified by location and size. A root canal filling, for example, is a restorative technique used to fill the space where the dental pulp normally resides. Tooth preparation Restoring a tooth to good form and function requires two steps: # preparing the tooth for placement of restorative material or materials, and # placement of these materials. The process of preparation usually involves cutting the tooth with a rotary dental handpiece and dental burrs, a dental laser, or though air abrasion to make space for the planned restorative materials and to remove any dental decay or portions of the tooth that are structurally unsound. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Necrosis
Necrosis () is a form of cell injury which results in the premature death of cells in living tissue by autolysis. Necrosis is caused by factors external to the cell or tissue, such as infection, or trauma which result in the unregulated digestion of cell components. In contrast, apoptosis is a naturally occurring programmed and targeted cause of cellular death. While apoptosis often provides beneficial effects to the organism, necrosis is almost always detrimental and can be fatal. Cellular death due to necrosis does not follow the apoptotic signal transduction pathway, but rather various receptors are activated and result in the loss of cell membrane integrity and an uncontrolled release of products of cell death into the extracellular space. This initiates in the surrounding tissue an inflammatory response, which attracts leukocytes and nearby phagocytes which eliminate the dead cells by phagocytosis. However, microbial damaging substances released by leukocytes would crea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |