|
Puccinia Hordei
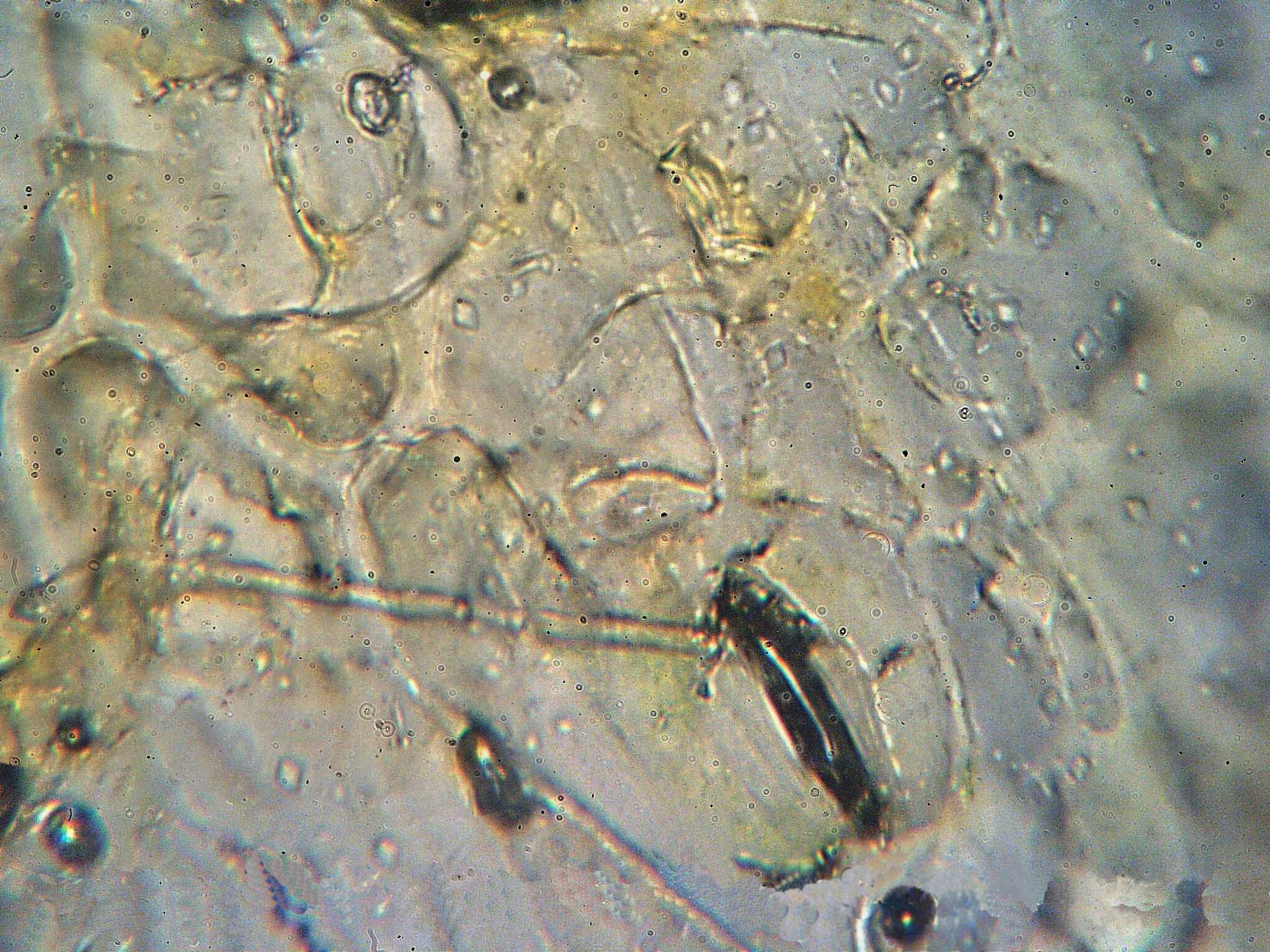
''Puccinia hordei'' is a species of rust fungus Rusts are plant diseases caused by pathogenic fungi of the order Pucciniales (previously known as Uredinales). An estimated 168 rust genera and approximately 7,000 species, more than half of which belong to the genus ''Puccinia'', are currently .... A plant pathogen, it can cause leaf rust of barley, also known as brown rust of barley. At the time of Johnston ''et al.'', 2013's discovery of severe susceptibility in Golden Promise, this was considered to be the most susceptible variety in the world. Soon thereafter however, Yeo ''et al.'', 2014 found SusPtrit was slightly worse. These results alter the meaning of such a basic term as "fully susceptible" to brown rust. See also * List of ''Puccinia'' species References Fungal plant pathogens and diseases Barley diseases Leaf diseases hordei Fungi described in 1871 {{fungus-plant-disease-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rust Fungus
Rusts are plant diseases caused by pathogenic fungi of the order Pucciniales (previously known as Uredinales). An estimated 168 rust genera and approximately 7,000 species, more than half of which belong to the genus ''Puccinia'', are currently accepted. Rust fungi are highly specialized plant pathogens with several unique features. Taken as a group, rust fungi are diverse and affect many kinds of plants. However, each species has a very narrow range of hosts and cannot be transmitted to non-host plants. In addition, most rust fungi cannot be grown easily in pure culture. A single species of rust fungi may be able to infect two different plant hosts in different stages of its life cycle, and may produce up to five morphologically and cytologically distinct spore-producing structures viz., spermogonia, aecia, uredinia, telia, and basidia in successive stages of reproduction. Each spore type is very host specific, and can typically infect only one kind of plant. Rust fungi are o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plant Pathogen
Plant pathology (also phytopathology) is the scientific study of diseases in plants caused by pathogens (infectious organisms) and environmental conditions (physiological factors). Organisms that cause infectious disease include fungi, oomycetes, bacteria, viruses, viroids, virus-like organisms, phytoplasmas, protozoa, nematodes and parasitic plants. Not included are ectoparasites like insects, mites, vertebrate, or other pests that affect plant health by eating plant tissues. Plant pathology also involves the study of pathogen identification, disease etiology, disease cycles, economic impact, plant disease epidemiology, plant disease resistance, how plant diseases affect humans and animals, pathosystem genetics, and management of plant diseases. Overview Control of plant diseases is crucial to the reliable production of food, and it provides significant problems in agricultural use of land, water, fuel and other inputs. Plants in both natural and cultivated populat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leaf Rust (barley)
Leaf rust is a fungal disease of barley caused by ''Puccinia hordei''. It is also known as brown rust and it is the most important rust disease on barley. Symptoms Pustules of leaf rust are small and circular, producing a mass of orange-brown powdery spores. They appear on the leaf sheaths and predominantly on the upper leaf surfaces. Heavily infected leaves die prematurely. Disease cycle Crop losses Leaf rust of barley is considered a relatively minor disease in the United States. However, sporadic outbreaks have occurred in the southeastern and Midwestern regions of the country. Pathotypes and host resistance Most of the barley cultivars grown in the United States are susceptible to ''Puccinia hordei''. Nineteen seedling resistance genes (i.e. ''Rph''1 to ''Rph''19) have been identified, but only three (''Rph''3, 7 and 9) have been deployed in commercial cutlivars worldwide. In the United States, the ''Rph''7 gene effectively controlled the disease for over ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crop Disease Susceptibility
Plant disease resistance protects plants from pathogens in two ways: by pre-formed structures and chemicals, and by infection-induced responses of the immune system. Relative to a susceptible plant, disease resistance is the reduction of pathogen growth on or in the plant (and hence a reduction of disease), while the term disease tolerance describes plants that exhibit little disease damage despite substantial pathogen levels. Disease outcome is determined by the three-way interaction of the pathogen, the plant and the environmental conditions (an interaction known as the disease triangle). Defense-activating compounds can move cell-to-cell and systematically through the plant's vascular system. However, plants do not have circulating immune cells, so most cell types exhibit a broad suite of antimicrobial defenses. Although obvious ''qualitative'' differences in disease resistance can be observed when multiple specimens are compared (allowing classification as “resistant” or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Golden Promise
Barley (''Hordeum vulgare''), a member of the grass family, is a major cereal grain grown in temperate climates globally. It was one of the first cultivated grains, particularly in Eurasia as early as 10,000 years ago. Globally 70% of barley production is used as animal fodder, while 30% as a source of fermentable material for beer and certain distilled beverages, and as a component of various foods. It is used in soups and stews, and in barley bread of various cultures. Barley grains are commonly made into malt in a traditional and ancient method of preparation. In 2017, barley was ranked fourth among grains in quantity produced () behind maize, rice and wheat. Etymology The Old English word for barley was ', which traces back to Proto-Indo-European and is cognate to the Latin word ' "flour" (''see corresponding entries''). The direct ancestor of modern English ''barley'' in Old English was the derived adjective ''bærlic'', meaning "of barley". The first citation of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annual Reviews (publisher)
Annual Reviews is an independent, non-profit academic publishing company based in San Mateo, California. As of 2021, it publishes 51 journals of review articles and ''Knowable Magazine'', covering the fields of life, biomedical, physical, and social sciences. Review articles are usually “peer-invited” solicited submissions, often planned one to two years in advance, which go through a peer-review process. The organizational structure has three levels: a volunteer board of directors, editorial committees of experts for each journal, and paid employees. Annual Reviews' stated mission is to synthesize and integrate knowledge "for the progress of science and the benefit of society". The first Annual Reviews journal, the ''Annual Review of Biochemistry'', was published in 1932 under the editorship of Stanford University chemist J. Murray Luck, who wanted to create a resource that provided critical reviews on contemporary research. The second journal was added in 1939. By ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annual Review Of Phytopathology
The ''Annual Review of Phytopathology'' is a peer-reviewed academic journal that publishes review articles about phytopathology, the study of diseases that affect plants. It was first published in 1963 as the result of a collaboration between the American Phytopathological Society and the nonprofit publisher Annual Reviews. As of 2022, ''Journal Citation Reports'' lists the journal's 2021 impact factor as 10.850, ranking it seventh of 238 journal titles in the category "Plant Sciences". Its current editors are Jan E. Leach and Steven E. Lindow. History In the 1950s, the American Phytopathological Society had intended to publish its own journal to cover significant developments in the field of phytopathology, or plant diseases. However, the nonprofit publisher Annual Reviews offered to publish the journal for them, and they agreed due to their publishing experience. In 1961, the American Phytopathological Society compiled the editorial board of the journal at their annual meeting. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Puccinia Species
This is an incomplete list of species in the fungal genus ''Puccinia''. Members of this genus are pathogens on all major cereal crop species except rice, and some cause large economic losses. According to the ''Dictionary of the Fungi'' (10th edition, 2008), the widespread genus contains about 4000 species. *'' Puccinia abrotani'' *'' Puccinia abrupta'' *'' Puccinia acetosae'' *'' Puccinia achilleae'' *'' Puccinia adjuncta'' *'' Puccinia adoxae'' *'' Puccinia aegopodii'' *'' Puccinia agrophila'' *'' Puccinia akiraho'' *'' Puccinia albescens'' *'' Puccinia alboclava'' *'' Puccinia albulensis'' *'' Puccinia aletridis'' *''Puccinia allii'' *'' Puccinia amphigena'' *'' Puccinia andropogonis'' *'' Puccinia anemones-virginianae'' *''Puccinia angelicae'' *''Puccinia angustata'' *''Puccinia anisotomes'' *''Puccinia annularis'' *''Puccinia antenori'' *''Puccinia anthemidis'' *''Puccinia antirrhini'' *''Puccinia apii'' *''Puccinia arachidis'' *''Puccinia arenariae'' *'' Puccinia areolata' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fungal Plant Pathogens And Diseases
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from the other eukaryotic kingdoms, which by one traditional classification include Plantae, Animalia, Protozoa, and Chromista. A characteristic that places fungi in a different kingdom from plants, bacteria, and some protists is chitin in their cell walls. Fungi, like animals, are heterotrophs; they acquire their food by absorbing dissolved molecules, typically by secreting digestive enzymes into their environment. Fungi do not photosynthesize. Growth is their means of mobility, except for spores (a few of which are flagellated), which may travel through the air or water. Fungi are the principal decomposers in ecological systems. These and other differences place fungi in a single group of related organisms, named the ''Eumycota'' (''true f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barley Diseases ...
This article is a list of diseases of barley (''Hordeum vulgare''). Bacterial and fungal diseases Nematodes, parasitic Virus, viroid and virus-like diseases Phytoplasma diseases Miscellaneous diseases and disorders Sources Barley Diseases, Queensland Government, AustraliaEPPO Standards, Guidelines on good plant protection - Barley, EuropeCommon Names of Diseases, The American Phytopathological Society, USUSDA ARS Fungal Database References Common Names of Diseases, The American Phytopathological Society{{DEFAULTSORT:List Of Barley Diseases * Barley Barley (''Hordeum vulgare''), a member of the grass family, is a major cereal grain grown in temperate climates globally. It was one of the first cultivated grains, particularly in Eurasia as early as 10,000 years ago. Globally 70% of barley pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leaf Diseases
A leaf ( : leaves) is any of the principal appendages of a vascular plant stem, usually borne laterally aboveground and specialized for photosynthesis. Leaves are collectively called foliage, as in "autumn foliage", while the leaves, stem, flower, and fruit collectively form the shoot system. In most leaves, the primary photosynthetic tissue is the palisade mesophyll and is located on the upper side of the blade or lamina of the leaf but in some species, including the mature foliage of ''Eucalyptus'', palisade mesophyll is present on both sides and the leaves are said to be isobilateral. Most leaves are flattened and have distinct upper (adaxial) and lower (abaxial) surfaces that differ in color, hairiness, the number of stomata (pores that intake and output gases), the amount and structure of epicuticular wax and other features. Leaves are mostly green in color due to the presence of a compound called chlorophyll that is essential for photosynthesis as it absorbs light en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.png)