|
Public Transportation In Brașov
RATBV S.A., formerly Regia Autonomă de Transport Brașov ( en, Autonomous Transportation Board of Brașov), and commonly referred to as RAT Brașov, is the only public transport operator in the city of Brașov, Romania. It is owned by the Brașov Municipality and it operates on a network of 43 routes inside Brașov, summing up to 664 km, with a fleet of over 225 vehicles. It is also operating 19 routes within the Brașov Metropolitan Area. History The following is a chronological list of events related to road or rail transport in and around Brașov, as well as relevant historical information. The administrative divisions and predominant/official languages consistently change over time; in Saxon cities and villages like Braşov, German was predominant until the late 19th and early 20th centuries, when Romanian and for a few decades, Hungarian, increase in use, ultimately attaining a combined 95.2% in 2011. Except for 'Brașov', the names used are intended to be the on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brașov
Brașov (, , ; german: Kronstadt; hu, Brassó; la, Corona; Transylvanian Saxon: ''Kruhnen'') is a city in Transylvania, Romania and the administrative centre of Brașov County. According to the latest Romanian census (2011), Brașov has a population of 253,200 making it the 7th most populous city in Romania. The metropolitan area is home to 382,896 residents. Brașov is located in the central part of the country, about north of Bucharest and from the Black Sea. It is surrounded by the Southern Carpathians and is part of the historical region of Transylvania. Historically, the city was the center of the Burzenland, once dominated by the Transylvanian Saxons, and a significant commercial hub on the trade roads between Austria (then Archduchy of Austria, within the Habsburg monarchy, and subsequently Austrian Empire) and Turkey (then Ottoman Empire). It is also where the national anthem of Romania was first sung. Names Brassovia, Brassó, Brașov, etc. According to Dragoș Mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Austro-Hungarian Florin
The florin (german: Gulden, hu, forint, hr, forinta/florin, cs, zlatý) was the currency of the lands of the House of Habsburg between 1754 and 1892 (known as the Austrian Empire from 1804 to 1867 and the Austro-Hungarian Monarchy after 1867), when it was replaced by the Austro-Hungarian crown as part of the introduction of the gold standard. In Austria, the florin was initially divided into 60 kreutzers (german: Kreuzer, hu, krajcar, hr, krajczár cs, krejcar). The currency was decimalized in 1857, using the same names for the unit and subunit. Name The name ''Gulden'' was used on the pre-1867 Austrian banknotes and on the German language side of the post-1867 banknotes. In southern Germany, the word Gulden was the standard word for a major currency unit. After 1867 Austrian coins used the name ''Florin''. "Florin" is derived from the city of Florence, Italy where the first florins were minted, from 1252 to 1533. History The florin (German: ''Gulden'') first emerged as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Săcele
Săcele (; German: ''Siebendörfer''; Hungarian: ''Négyfalu'', between 1950 and 2001 ''Szecseleváros'') is a city in Brașov County, Romania, in the Burzenland area of southeastern Transylvania, with a population of 30,798 inhabitants in 2011. It is adjacent to the city of Brașov, its city centre being situated away from downtown Brașov. History The city since 1950 is composed of former villages which now form the main sectors: Baciu (Bácsfalu, Batschendorf), Turcheș (Türkös, Türkeschdorf), Cernatu (Csernátfalu, Zerndorf), and Satulung (Hosszúfalu, Langendorf). After the second half of the 11th century the villages are mentioned as "''septem villae valacheles''" (seven Vlach villages). The first official mention is an act issued on May 16, 1366, by the Hungarian King Ludovic I de Anjou in which he offers the area between the Timiș and Olt rivers to a trusted friend—Count Stanislav. Later it was under the Saxon management of Kronstadt (Brașov). During the Mid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
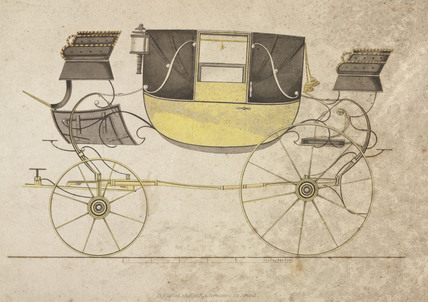
Landau (carriage)
In coachbuilding, a landau is a four-wheeled carriage with a roof that can be let down. It was a luxury carriage. The low shell of the landau provides maximal visibility of the occupants and their clothing, a feature that makes a landau still a popular choice for Lord Mayors in the United Kingdom on ceremonial occasions. History of landau carriages A landau is lightweight and suspended on elliptical springs. It was invented in the 18th century; ''landau'' in this sense is first noted in English in 1743. It was named after the German city of Landau in the Rhenish Palatinate where they were first produced. In the 1830s, Luke Hopkinson, a celebrated coach-maker in Holborn, introduced the Briska Landau, which led with subsequent improvements to the popular landau. Description and development A landau, drawn by a pair or four-in-hand, is one of several kinds of vis-à-vis, a social carriage with facing seats over a dropped footwell (''illustration''), which was perfected by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rupea
Rupea (german: Reps; Transylvanian Saxon: ''Räppes''; hu, Kőhalom, lit=mound of rocks; la, Ripa) is a town in Brașov County in Transylvania, Romania. It administers one village, Fișer (''Schweischer''; ''Sövénység''), which has a fortified church. Older Romanian names for the settlement include ''Cohalm'' and ''Holuma''. At the 2011 census, 71.6% of inhabitants were Romanians, 19.5% Hungarians, 7.1% Roma, and 1.7% Germans (more specifically Transylvanian Saxons). Climate Rupea has a humid continental climate (''Cfb'' in the Köppen climate classification). See also * Battle of Kőhalom A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and force ... * Rupea Citadel References * Populated places in Brașov County Localities in Transylvania Towns in Romania< ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giurgiu
Giurgiu (; bg, Гюргево) is a city in southern Romania. The seat of Giurgiu County, it lies in the historical region of Muntenia. It is situated amongst mud-flats and marshes on the left bank of the Danube facing the Bulgarian city of Ruse on the opposite bank. Three small islands face the city, and a larger one shelters its port, Smarda. The rich grain-growing land to the north is traversed by a railway to Bucharest, the first line opened in Romania, which was built in 1869 and afterwards extended to Smarda. Giurgiu exports timber, grain, salt and petroleum, and imports coal, iron, and textiles. The Giurgiu-Ruse Friendship Bridge, in the shared Bulgarian-Romanian section of the Danube, crosses the river in the outskirts of the city. History The area around Giurgiu was densely populated at the time of the Dacians (1st century BC) as archeological evidence shows, and Burebista's capital was in this area (it is thought to be in Popeşti on the Argeş River). Durin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bucharest
Bucharest ( , ; ro, București ) is the capital and largest city of Romania, as well as its cultural, industrial, and financial centre. It is located in the southeast of the country, on the banks of the Dâmbovița River, less than north of the Danube River and the Bulgarian border. Bucharest was first mentioned in documents in 1459. The city became the capital of Romania in 1862 and is the centre of Romanian media, culture, and art. Its architecture is a mix of historical (mostly Eclectic, but also Neoclassical and Art Nouveau), interbellum ( Bauhaus, Art Deco and Romanian Revival architecture), socialist era, and modern. In the period between the two World Wars, the city's elegant architecture and the sophistication of its elite earned Bucharest the nickname of 'Paris of the East' ( ro, Parisul Estului) or 'Little Paris' ( ro, Micul Paris). Although buildings and districts in the historic city centre were heavily damaged or destroyed by war, earthquakes, and even Nic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carpathian Mountains
The Carpathian Mountains or Carpathians () are a range of mountains forming an arc across Central Europe. Roughly long, it is the third-longest European mountain range after the Urals at and the Scandinavian Mountains at . The range stretches from the far eastern Czech Republic (3%) and Austria (1%) in the northwest through Slovakia (21%), Poland (10%), Ukraine (10%), Romania (50%) to Serbia (5%) in the south. "The Carpathians" European Travel Commission, in The Official Travel Portal of Europe, Retrieved 15 November 2016 The Carpathian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wallachia
Wallachia or Walachia (; ro, Țara Românească, lit=The Romanian Land' or 'The Romanian Country, ; archaic: ', Romanian Cyrillic alphabet: ) is a historical and geographical region of Romania. It is situated north of the Lower Danube and south of the Southern Carpathians. Wallachia is traditionally divided into two sections, Muntenia (Greater Wallachia) and Oltenia (Lesser Wallachia). Dobruja could sometimes be considered a third section due to its proximity and Dobruja#Wallachian rule, brief rule over it. Wallachia as a whole is sometimes referred to as Muntenia through identification with the larger of the two traditional sections. Wallachia was founded as a principality in the early 14th century by Basarab I of Wallachia, Basarab I after a rebellion against Charles I of Hungary, although the first mention of the territory of Wallachia west of the river Olt River, Olt dates to a charter given to the voivode Seneslau in 1246 by Béla IV of Hungary. In 1417, Wallachia was fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)