|
Public Distribution System (India)
The Public Distribution System (PDS) is an Indian food security system that was established by the Government of India under the Ministry of Consumer Affairs, Food and Public Distribution to distribute food and non-food items to India's poor at subsidised rates. Major commodities distributed include staple food grains, such as wheat, rice, sugar and essential fuels like kerosene, through a network of fair price shops (also known as ration shops) established in several states across the country. Food Corporation of India, a government-owned corporation, procures and maintains the PDS. As of June 2022, India has the largest stock of grain in the world besides China, the government spends billion. Distribution of food grains to poor people throughout the country is managed by state governments. As of 2011 there were 505,879 fair price shops (FPS) across India. Under the PDS scheme, each family below the poverty line is eligible for 35 kg of rice or wheat every month, while ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Minister Of Agriculture, Consumer Affairs Food And Public Distribution Shri Sharad Pawar Meeting All India Fair Price Shop Dealer's Federation On Issues Relating To Functioning Of Fair Price Shops In New Delhi On November 30
''The'' () is a grammatical Article (grammar), article in English language, English, denoting persons or things already mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in English. ''The'' is the Most common words in English, most frequently used word in the English language; studies and analyses of texts have found it to account for seven percent of all printed English-language words. It is derived from gendered articles in Old English which combined in Middle English and now has a single form used with pronouns of any gender. The word can be used with both singular and plural nouns, and with a noun that starts with any letter. This is different from many other languages, which have different forms of the definite article for different genders or numbers. Pronunciation In most dialects, "the" is pronounced as (with the voiced dental fricative followed by a schwa) when followed by a consonant s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urban Bias
Urban bias refers to a political economy argument according to which economic development is hampered by groups who, by their central location in urban areas, are able to pressure governments to protect their interests. It is a structural condition of overurbanization and its growth leads to saturated urban labour market, truncated opportunity structures in rural areas, overburdened public services, distorted sectoral development in world economies, the isolation of large segments of the urban and rural population from the fruits of economic development, and economic growth due to the high costs of urban development.Lipton M. 'Why poor people stay poor: urban bias in world development.'(Cambridge: Harvard UP, 1977) Groups often said to have an 'urban bias' include governments, political parties, labor unions, students, laws, civil servants and manufacturers. These interests are portrayed as often not reflecting the comparative economic advantage of the country, usually a less-indus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Progressive Alliance
United Progressive Alliance (UPA) is a centre-left political alliance of predominantly left-leaning political parties in India. It was formed after the 2004 general election with support from left-leaning political parties when no single party got the majority. UPA ruled India from 2004 till 2014. The largest party in UPA is Indian National Congress (INC). History 2004–2008 UPA was formed soon after the 2004 general elections when no party had won a majority. The then ruling Bharatiya Janata Party-led National Democratic Alliance (NDA) won 181 seats of 544, as opposed to the UPA's tally of 218 seats. The Left Front with 59 MPs (excluding the speaker of the Lok Sabha), the Samajwadi Party with 39 MPs and the Bahujan Samaj Party with 19 MPs were other significant blocks that supported UPA at various times. UPA did not achieve a majority, rather it relied on external support, similar to the formula adopted by the previous minority governments of the United Front, the NDA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Migrant Worker
A migrant worker is a person who Human migration, migrates within a home country or outside it to pursue work. Migrant workers usually do not have the intention to stay permanently in the country or region in which they work. Migrant workers who work outside their home country are also called foreign workers. They may also be called expatriates or guest workers, especially when they have been sent for or invited to work in the host country before leaving the home country. The International Labour Organization estimated in 2019 that there were 169 million international migrants worldwide. Some countries have millions of migrant workers. Some migrant workers are undocumented immigrants or slaves. Worldwide An estimated 14 million foreign workers live in the United States, which draws most of its immigrants from Mexico, including 4 or 5 million illegal aliens, undocumented workers. It is estimated that around 5 million foreign workers live in Northwestern Europe, half-a-millio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
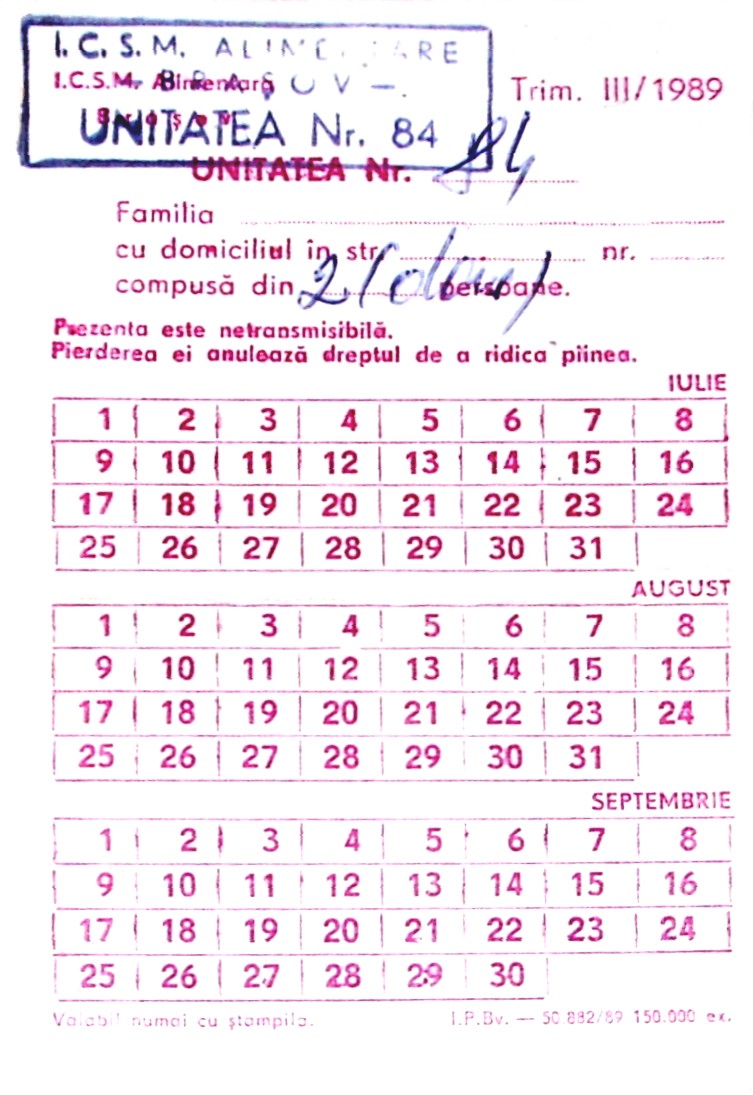
Ration Card
Rationing is the controlled distribution of scarce resources, goods, services, or an artificial restriction of demand. Rationing controls the size of the ration, which is one's allowed portion of the resources being distributed on a particular day or at a particular time. There are many forms of rationing, although rationing by price is most prevalent. Rationing is often done to keep price below the market-clearing price determined by the process of supply and demand in an unfettered market. Thus, rationing can be complementary to price controls. An example of rationing in the face of rising prices took place in the various countries where there was rationing of gasoline during the 1973 energy crisis. A reason for setting the price lower than would clear the market may be that there is a shortage, which would drive the market price very high. High prices, especially in the case of necessities, are undesirable with regard to those who cannot afford them. Traditionalist eco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reseller
A reseller is a company or individual (merchant) that purchases goods or services with the intention of selling them rather than consuming or using them. This is usually done for profit (but can be done at a loss). One example can be found in the industry of telecommunications, where companies buy excess amounts of transmission capacity or call time from other carriers and resell it to smaller carriers. According to the Institute for Partner Education & Development, a reseller's product fulfillment–based business model includes a corporate reseller, retail seller, direct market reseller (DMR), and an internet retailer (eTailer); less than 10 percent of its revenue comes from services. Internet Resellers are known to conduct operations on the Internet through sites on the web. For example, this occurs where individuals or companies act as agents for ICANN accredited registrars. They either sell on commission or for profit and in most cases, but not all, the purchase from the reg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Accountability
Accountability, in terms of ethics and governance, is equated with answerability, blameworthiness, liability, and the expectation of account-giving. As in an aspect of governance, it has been central to discussions related to problems in the public sector, nonprofit and private (corporate) and individual contexts. In leadership roles, accountability is the acknowledgment and assumption of responsibility for actions, products, decisions, and policies including the administration, governance, and implementation within the scope of the role or employment position and encompassing the obligation to report, explain and be answerable for resulting consequences. In governance, accountability has expanded beyond the basic definition of "being called to account for one's actions". It is frequently described as an account giving relationship between individuals, e.g. "A is accountable to B when A is obliged to inform B about A's (past or future) actions and decisions, to justify them, and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malpractice
In the law of torts, malpractice, also known as professional negligence, is an "instance of negligence or incompetence on the part of a professional".Malpractice definition, Professionals who may become the subject of malpractice actions include: * medical professionals: a medical malpractice claim may be brought against a doctor or other healthcare provider who fails to exercise the degree of care and skill that a similarly situated professional of the same medical specialty would provide under the circumstances. * lawyers: a legal malpractice claim may be brought against a lawyer who fails to render services with the level of skill, care and diligence that a reasonable lawyer would apply under similar circumstances. * financial professionals: professionals such as accountants, financial planners and stockbrokers, may be subject to claims for professional negligence based upon their failure to meet professional standards when providing services to their clients. * architec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wayback Machine
The Wayback Machine is a digital archive of the World Wide Web founded by the Internet Archive, a nonprofit based in San Francisco, California. Created in 1996 and launched to the public in 2001, it allows the user to go "back in time" and see how websites looked in the past. Its founders, Brewster Kahle and Bruce Gilliat, developed the Wayback Machine to provide "universal access to all knowledge" by preserving archived copies of defunct web pages. Launched on May 10, 1996, the Wayback Machine had more than 38.2 million records at the end of 2009. , the Wayback Machine had saved more than 760 billion web pages. More than 350 million web pages are added daily. History The Wayback Machine began archiving cached web pages in 1996. One of the earliest known pages was saved on May 10, 1996, at 2:08p.m. Internet Archive founders Brewster Kahle and Bruce Gilliat launched the Wayback Machine in San Francisco, California, in October 2001, primarily to address the problem of web co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ration
Rationing is the controlled distribution of scarce resources, goods, services, or an artificial restriction of demand. Rationing controls the size of the ration, which is one's allowed portion of the resources being distributed on a particular day or at a particular time. There are many forms of rationing, although rationing by price is most prevalent. Rationing is often done to keep price below the market clearing, market-clearing price determined by the process of supply and demand in an free market, unfettered market. Thus, rationing can be complementary to incomes policies, price controls. An example of rationing in the face of rising prices took place in the various countries where there was rationing of gasoline during the 1973 energy crisis. A reason for setting the price lower than would clear the market may be that there is a shortage, which would drive the market price very high. High prices, especially in the case of necessities, are undesirable with regard to those ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ministry Of Consumer Affairs, Food And Public Distribution (India)
The Ministry of Consumer Affairs, Food and Public Distribution is a government ministry of India. The ministry is headed by a Cabinet rank minister. Departments The ministry is divided into two departments, the Department of Food and Public Distribution and the Department of Consumer Affairs. Department of Food and Public Distribution The objectives of the department are to ensure: *remunerative rates for the farmers. *supply of food grains at reasonable prices through the public distribution system. Public Distribution System The Indian Public Distribution System (PDS) is a national food security system that distributes subsidised food to India's poor. Major commodities include wheat, rice, sugar and kerosene. Surpluses of food from increased crop yields (as a result of the Green Revolution and good monsoon seasons) are managed by the Food Corporation of India, established by the Food Corporation Act 1964. The system implements national policy for farm price support ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Green Revolution
The Green Revolution, also known as the Third Agricultural Revolution, was a period of technology transfer initiatives that saw greatly increased crop yields and agricultural production. These changes in agriculture began in developed countries after World War II and spread globally till the late 1980s. In the late 1960s, farmers began incorporating new technologies such as high-yielding varieties of cereals, particularly dwarf wheat and rice, and the widespread use of chemical fertilizers, pesticides, and controlled irrigation. Agriculture also saw the adoption of newer methods of cultivation, including mechanization. These changes were often implemented as a package of practices meant to replace traditional agricultural technology. Both the Ford Foundation and the Rockefeller Foundation were heavily involved in its initial development in Mexico. One key leader was agricultural scientist Norman Borlaug, the "Father of the Green Revolution", who received the Nobel Peace Prize ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.png)