|
Ptolemaeus (other)
Ptolemy (c. AD 100 – c. 170) was an Alexandrian mathematician, astronomer, geographer and astrologer. Ptolemy, Ptolemaeus or Tolomeo is a popular name used widely in both the ancient world and modern times that may also refer to: People Ptolemaic dynasty of Egypt Any of 15 Greco-Egyptian pharaohs of the Ptolemaic dynasty (305 BC–30 BC): Also several dynasty members who ruled other territories, but not Egypt: * Ptolemy Apion, King of Cyrene (150–145 BC) * Ptolemy of Mauretania, King of Mauretania (d.40 AD) Early Greek rulers and generals * Ptolemy (King of Thebes) (12th century BC) – mythical ruler of the ancient Greek city of Thebes *Ptolemy of Aloros (ruled 368 to 365 BC) – Regent of Macedon *Ptolemy (somatophylax) (died 334 BC) – Macedonian bodyguard and general of Alexander the Great * Ptolemy (son of Seleucus) (died 333 BC) – Macedonian bodyguard and general of Alexander the Great *Ptolemy (son of Philip) (4th century BC) – Macedonian officer of Alexa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; grc-gre, Πτολεμαῖος, ; la, Claudius Ptolemaeus; AD) was a mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist, who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were of importance to later Byzantine, Islamic, and Western European science. The first is the astronomical treatise now known as the '' Almagest'', although it was originally entitled the ''Mathēmatikē Syntaxis'' or ''Mathematical Treatise'', and later known as ''The Greatest Treatise''. The second is the ''Geography'', which is a thorough discussion on maps and the geographic knowledge of the Greco-Roman world. The third is the astrological treatise in which he attempted to adapt horoscopic astrology to the Aristotelian natural philosophy of his day. This is sometimes known as the ''Apotelesmatika'' (lit. "On the Effects") but more commonly known as the '' Tetrábiblos'', from the Koine Greek meaning "Four Books", or by its Latin equivalent ''Quadrip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ptolemy XIV Philopator
Ptolemy XIV Philopator ( grc-gre, Πτολεμαῖος Φιλοπάτωρ, ; c. 59 – 44 BC) was a Pharaoh of the Ptolemaic Kingdom of Egypt, who reigned from 47 until his death in 44 BC. Biography Following the death of his older brother Ptolemy XIII of Egypt on January 13, 47 BC, and according to his will, he was proclaimed Pharaoh and co-ruler by their older sister and remaining Pharaoh, Cleopatra VII of Egypt. He was about 12 years old when he acceded to the throne. He and his older sister, Cleopatra, were married, but Cleopatra continued to act as lover of Roman dictator Julius Caesar. Ptolemy is considered to have reigned in name only, as a concession to Egyptian tradition, with Cleopatra keeping actual authority. On 15 March 44 BC Caesar was murdered in Rome by a group of conspirators whose most notable members were Brutus and Cassius. Ptolemy soon followed him in death. An inscription mentioning him as alive was dated at 26 July 44 BC. It has been assumed but remain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyrrhus Of Epirus
Pyrrhus (; grc-gre, Πύρρος ; 319/318–272 BC) was a Greek king and statesman of the Hellenistic period.Plutarch. ''Parallel Lives'',Pyrrhus... He was king of the Greek tribe of Molossians, of the royal Aeacid house, and later he became king (Malalas also called him toparch) of Epirus. He was one of the strongest opponents of early Rome, and had been regarded as one of the greatest generals of antiquity. Several of his victorious battles caused him unacceptably heavy losses, from which the term " Pyrrhic victory" was coined. Pyrrhus became king of Epirus in 306 BC at the age of 13, but was dethroned by Cassander four years later. He saw action during the Wars of the Diadochi and regained his throne in 297 BC with the support of Ptolemy I Soter. During what came to be known as the Pyrrhic War, Pyrrhus fought Rome at the behest of Tarentum, scoring costly victories at Heraclea and Asculum. He proceeded to take over Sicily from Carthage but was soon driven out, and lost a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ptolemy (son Of Pyrrhus)
Ptolemy (295–272 BC) was the oldest son of king Pyrrhus of Epirus and his first wife Antigone, who probably died in childbirth.. He was named in honour of his mother's stepfather, king Ptolemy I Soter of Egypt, who was a benefactor to Pyrrhus in his youth. When Pyrrhus returned from Italy in 274 BC Ptolemy captured the island of Corcyra for his father in an audacious attack with only 60 men. He also distinguished himself in a naval battle, and during the following invasion of Macedonia he dislodged king Antigonus II Gonatas from Thessalonike. In 272 BC Ptolemy accompanied his father on a military campaign in the Peloponnese, where he commanded his personal guard. During the retreat from Sparta he was attacked by a Lacedaemonian force under Eualcus and slain by the Cretan Oroissus of Aptera.Plutarch, ''Pyrrhus'' 30 His father avenged his death killing Eualcus, but fell a few days later in the streets of Argos. Ptolemy had an older sister called Olympias and two younger hal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ptolemy (general)
Ptolemaeus ( grc, Πτολεμαῖος, Ptolemaios) or Ptolemy (died 309 BC) was a nephew and general of Antigonus I Monophthalmus, one of the Successors of Alexander the Great. His father was also called Ptolemy and was a brother of Antigonus. Ptolemy, the nephew, was Antigonus's right-hand-man until his son Demetrius took on a more prominent role. He is first mentioned as being present with his uncle at the siege of Nora in 319 BC, when he was given up to Eumenes as a hostage for the safety of the latter during a conference with Antigonus. A few years later we find him entrusted by his uncle with commands of importance. In 315 BC, when Antigonus moved against the coalition of Diadochi formed against him, he placed Ptolemy at the head of an army which marched against the generals of Cassander in Asia Minor. The young general successfully carried out his mission, relieving Amisus, which was besieged by Asclepiodorus, and recovered the whole satrapy of Cappadocia; after which he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander The Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, wikt:Ἀλέξανδρος, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia (ancient kingdom), Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip II of Macedon, Philip II to the throne in 336 BC at the age of 20, and spent most of his ruling years conducting a lengthy military campaign throughout Western Asia and ancient Egypt, Egypt. By the age of thirty, he had created one of the List of largest empires, largest empires in history, stretching from Greece to northwestern Historical India, India. He was undefeated in battle and is widely considered to be one of history's greatest and most successful military commanders. Until the age of 16, Alexander was tutored by Aristotle. In 335 BC, shortly after his assumption of kingship over Macedon, he Alexander's Balkan campaign, campaigned in the Balkans and reasserted control ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ptolemy (son Of Philip)
Ptolemy, son of Philip ( el, Πτολεμαῖος ὁ Φιλίππου) was an officer who commanded the leading squadron of Macedonian cavalry (that of Socrates) at the Battle of the Granicus. Both Gronovius and Droysen, suppose that he is the same man that Alexander left with a force of 3,000 infantry and 200 cavalry to defend the province of Caria, and who subsequently, together with Asander the governor of Lydia, defeated the Persian general Orontobates, 332 BC.Arrian ''Anabasis Alexandri ''The Anabasis of Alexander'' ( grc-gre, Ἀλεξάνδρου Ἀνάβασις, ''Alexándrou Anábasis''; la, Anabasis Alexandri) was composed by Arrian of Nicomedia in the second century AD, most probably during the reign of Hadrian. The ...'' I.14, I.23, II.5 Notes References *Who's Who in the Age of Alexander the Great by Waldemar Heckel {{DEFAULTSORT:Ptolemy (Son Of Philip) Generals of Alexander the Great ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ptolemy (son Of Seleucus)
Ptolemy ( el, ); died 333 BC) son of Seleucus from Orestis or Tymphaia,''Who's Who in the Age of Alexander the Great'Page 234 By Waldemar Heckel was one of the select officers called Somatophylaces, or guards of the king's person; he combined with that distinguished post the command of one of the divisions of the phalanx. Ptolemy was from an upper noble family. He was lately married when he accompanied Alexander on his expedition to Asia, 334 BC, on which account he was selected by the king to command the body of Macedonians, who were allowed to return home for the winter at the end of the first campaign. In the following spring he rejoined Alexander at Gordium, with the troops under his command, accompanied by fresh reinforcements. At the Battle of Issus (333 BC) his division of the phalanx was one of those opposed to the Greek mercenaries under Darius III, and upon which the real brunt of the action consequently devolved; and he himself fell in the conflict, after displaying the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ptolemy (somatophylax)
Ptolemy ( grc, Πτολεμαῖος) was one of the selected officers of Alexander the Great, called somatophylaces. He was killed at the siege of Halicarnassus, 334 BC, commanding two ''taxeis'' of Hypaspists, those of Adaeus and Timander. References *Arrian Arrian of Nicomedia (; Greek: ''Arrianos''; la, Lucius Flavius Arrianus; ) was a Greek historian, public servant, military commander and philosopher of the Roman period. ''The Anabasis of Alexander'' by Arrian is considered the best ..., Anab. i. 22 *Who's Who in the Age of Alexander the Great by Waldemar Heckel 334 BC deaths Somatophylakes Ancient Macedonian generals Ancient Greeks killed in battle 4th-century BC Macedonians Year of birth unknown {{AncientGreece-bio-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ptolemy Of Aloros
Ptolemy of Aloros ( grc-gre, Πτολεμαῖος), was sent by King Amyntas III of Macedon as an envoy to Athens c. 375–373 BC. After Amyntas' death, he began a liaison with his widow, Eurydice. In 368 BC, he assassinated her son, Alexander II, in order to gain control of the throne. His actions were not well-regarded by the leading families of Macedon, who called in the Theban general, Pelopidas, to re-establish peace. As part of the peace settlement, Philip, Alexander II's younger brother, was taken as a hostage back to Thebes. As Alexander II's younger brother, Perdiccas III, was under-age when Alexander II was killed, Ptolemy of Aloros ruled as regent. Ptolemy ruled as a regent for Perdiccas III until Perdiccas killed him in 365 BC. It is suggested that Ptolemy was descended from Amyntas II's brother, Menelaus, son of Alexander I Alexander I may refer to: * Alexander I of Macedon, king of Macedon 495–454 BC * Alexander I of Epirus (370–331 BC), king of Epirus * Po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ptolemy (King Of Thebes)
In Greek mythology, Ptolemy or Ptolomeus (;Ancient Greek: Πτολεμαῖος) was an ancestral ruler of Thebes, in ancient Greece living in the 12th century BCE. His father was Damasichthon; his son, Xanthus. Since the Homeric root to Ptolemy includes no " T", the name is reconstructed as Polemy.The change from ''polemos'' to ''ptolemos'' is an example of a type of linguistic compounding called terpsimbrotos. The ''pt-'' in ''ptolemos'' (vs. earlier ''polemos'') "war" is thought to arise from a re-analysis of the compound word ''*phere-t-polemos'', metathesised to ''phere-ptolemos''. George Dunkel, "Two old problems in Greek: πτόλεμος and τερψίμβροτος", ''Glotta'' 70:3/4:197-225 (1992) . Notes References * Pausanias Pausanias ( el, Παυσανίας) may refer to: *Pausanias of Athens, lover of the poet Agathon and a character in Plato's ''Symposium'' *Pausanias the Regent, Spartan general and regent of the 5th century BC * Pausanias of Sicily ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
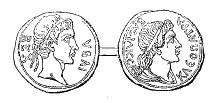
Ptolemy Of Mauretania
Ptolemy of Mauretania ( grc-gre, Πτολεμαῖος, ''Ptolemaîos''; la, Gaius Iulius Ptolemaeus; 13 9BC–AD40) was the last Roman client king and ruler of Mauretania for Rome. He was the son of Juba II, the king of Numidia and a member of the Berber Massyles tribe, as well as a descendant of the Ptolemaic dynasty via his mother Cleopatra Selene II. Early life Ptolemy was the son of King Juba II and Queen Cleopatra Selene II of Mauretania. His birth date is not certainly known but must have occurred before his mother's death, which has been estimated to have taken place in 5BC. He had a sister (possibly younger) who is evidenced by an Athenian inscription, but her name has not been preserved. She may have been called Drusilla. His father Juba II was the son of King Juba I of Numidia, who was descended from the Berbers of North Africa and was an ally to the Roman Triumvir Pompey. His mother Cleopatra Selene II was the daughter of the Ptolemaic Greek Queen Cleopat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |