|
Psorosperm
Psorosperm (from the Greek ŽłŽēŽü╬▒ itch and ŽāŽĆ╬ĄŽü╬╝╬▒ seed) is a former name of a number of parasitic protozoa that produce cystlike or sporelike structures in the tissue of hosts. The term is now essentially obsolete. * Some that affect vertebrate hosts are now called coccidia. * Others, such as the cause of p├®brine in silkworms, are now recognized as microsporidians, and some are myxosporidians. * The genus ''Psorospermium'' (which includes the species '' Psorospermium haeckeli'') itself is a parasite of crayfishes, and belongs to an enigmatic group of unicellular organisms that some biologists think may be related to the common ancestors of animals and fungi. J. M├╝ller introduced the term in German (as ''Psorospermien'') in 1841. Psorosperm was at one point believed to be the cause of Darier's disease.F. J. Darier. De la psorospermose folliculaire v├®g├®tante. ├ētude anatomo-pathologique d'une affection cutan├®e non d├®crite ou comprise dans le groupe des acn├®s sebac├ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microsporidia
Microsporidia are a group of spore-forming unicellular parasites. These spores contain an extrusion apparatus that has a coiled polar tube ending in an anchoring disc at the apical part of the spore. They were once considered protozoans or protists, but are now known to be fungi, or a sister group to fungi. These fungal microbes are obligate eukaryotic parasites that use a unique mechanism to infect host cells. They have recently been discovered in a 2017 Cornell study to infect Coleoptera on a large scale. So far, about 1500 of the probably more than one million species are named. Microsporidia are restricted to animal hosts, and all major groups of animals host microsporidia. Most infect insects, but they are also responsible for common diseases of crustaceans and fish. The named species of microsporidia usually infect one host species or a group of closely related taxa. Approximately 10 percent of the species are parasites of vertebrates ŌĆöseveral species, most of which are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parasitic
Parasitism is a close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives on or inside another organism, the host, causing it some harm, and is adapted structurally to this way of life. The entomologist E. O. Wilson has characterised parasites as "predators that eat prey in units of less than one". Parasites include single-celled protozoans such as the agents of malaria, sleeping sickness, and amoebic dysentery; animals such as hookworms, lice, mosquitoes, and vampire bats; fungi such as honey fungus and the agents of ringworm; and plants such as mistletoe, dodder, and the broomrapes. There are six major parasitic strategies of exploitation of animal hosts, namely parasitic castration, directly transmitted parasitism (by contact), trophicallytransmitted parasitism (by being eaten), vector-transmitted parasitism, parasitoidism, and micropredation. One major axis of classification concerns invasiveness: an endoparasite lives inside the host's body; an e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protozoa
Protozoa (singular: protozoan or protozoon; alternative plural: protozoans) are a group of single-celled eukaryotes, either free-living or parasitic, that feed on organic matter such as other microorganisms or organic tissues and debris. Historically, protozoans were regarded as "one-celled animals", because they often possess animal-like behaviours, such as motility and predation, and lack a cell wall, as found in plants and many algae. When first introduced by Georg Goldfuss (originally spelled Goldfu├¤) in 1818, the taxon Protozoa was erected as a class within the Animalia, with the word 'protozoa' meaning "first animals". In later classification schemes it was elevated to a variety of higher ranks, including phylum, subkingdom and kingdom, and sometimes included within Protoctista or Protista. The approach of classifying Protozoa within the context of Animalia was widespread in the 19th and early 20th century, but not universal. By the 1970s, it became usual to require th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coccidia
Coccidia (Coccidiasina) are a subclass of microscopic, spore-forming, single-celled obligate intracellular parasites belonging to the apicomplexan class Conoidasida. As obligate intracellular parasites, they must live and reproduce within an animal cell. Coccidian parasites infect the intestinal tracts of animals, and are the largest group of apicomplexan protozoa. Infection with these parasites is known as coccidiosis. Coccidia can infect all mammals, some birds, some fish, some reptiles, and some amphibians. Most species of coccidia are species-specific in their host. An exception is ''Toxoplasma gondii'', which can infect all mammals, although it can only undergo sexual reproduction in cats. Depending on the species of coccidia, infection can cause fever, vomiting, diarrhea, muscle pain, and nervous system effects and changes to behavior, and may lead to death. Healthy adults may recover without medicationŌĆöbut those who are immunocompromised or young almost certainly requi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
P├®brine
P├®brine, or "pepper disease," is a disease of silkworms, which is caused by protozoan microsporidian parasites, mainly ''Nosema bombycis'' and, to a lesser extent, ''Vairimorpha'', '' Pleistophora'' and '' Thelohania'' species. The parasites infect eggs and are therefore transmitted to the next generation. The silkworm larvae infected by p├®brine are usually covered in brown dots and are unable to spin silkworm thread. Antoine B├®champ was the first one to recognize the cause of this disease when a plague of the disease spread across France. ''Nosema bombycis'' is a microsporidium that kills all of the silkworms hatched from infected eggs and comes from the food that silkworms eat. If silkworms acquire this microsporidium in their larval stage, there are no visible signs; however, mother moths will pass the microsporidium onto the eggs, and all of the worms hatching from the infected eggs will die in their larval stage. Therefore, it is extremely important to rule out all eggs fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myxosporidia
Myxosporea is a class of microscopic parasites, belonging to the Myxozoa clade within Cnidaria. They have a complex life cycle which comprises vegetative forms in two hosts, an aquatic invertebrate (generally an annelid but sometimes a bryozoan) and an ectothermic vertebrate, usually a fish. Each host releases a different type of spore. The two forms of spore are so different that until relatively recently they were treated as belonging to different classes within the Myxozoa. Taxonomic status The taxonomy of both actinosporeans and myxosporeans was originally based on spore morphology. In 1994 the phylum Myxozoa was redefined to solve the taxonomic and nomenclatural problems arising from the two-host life cycle of myxozoans. The distinction between the two previously recognised classes Actinosporea and Myxosporea disappeared and the class ''Actinosporea'' was suppressed, becoming a synonym of the class ''Myxosporea'' (B├╝tschli, 1881). The generic names of actinosporeans were r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
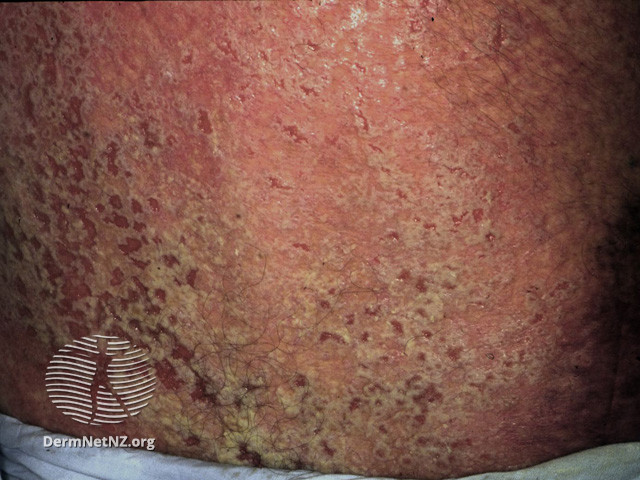
Darier's Disease
Darier's disease (DAR) is an inherited skin disorder that presents with multiple greasy, crusting, thick brown bumps that merge into patches. It is an autosomal dominant disorder discovered by French dermatologist Ferdinand-Jean Darier. Darier's is characterized by dark crusty patches on the skin that are mildly greasy and that emit a strong odor. These patches, also known as keratotic papules, keratosis follicularis, or dyskeratosis follicularis, most often appear on the scalp, forehead, upper arms, chest, back, knees, elbows, and behind the ear. Mild forms of the disease are the most common, consisting solely of skin rashes that flare up under certain conditions such as high humidity, high stress, or tight-fitting clothes. Short stature, when combined with poorly-formed fingernails that contain vertical striations, is diagnostic even for mild forms of DAR. Symptoms will usually appear in late childhood or early adulthood┬Ābetween the ages of 15 to 30 years and will vary over th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ICD-9
The International Classification of Diseases (ICD) is a globally used diagnostic tool for epidemiology, health management and clinical purposes. The ICD is maintained by the World Health Organization (WHO), which is the directing and coordinating authority for health within the United Nations System. The ICD is originally designed as a health care classification system, providing a system of diagnostic codes for classifying diseases, including nuanced classifications of a wide variety of signs, symptoms, abnormal findings, complaints, social circumstances, and external causes of injury or disease. This system is designed to map health conditions to corresponding generic categories together with specific variations, assigning for these a designated code, up to six characters long. Thus, major categories are designed to include a set of similar diseases. The ICD is published by the WHO and used worldwide for morbidity and mortality statistics, reimbursement systems, and automated de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |