|
Pseudolikelihood
In statistical theory, a pseudolikelihood is an approximation to the joint probability distribution of a collection of random variables. The practical use of this is that it can provide an approximation to the likelihood function of a set of observed data which may either provide a computationally simpler problem for estimation, or may provide a way of obtaining explicit estimates of model parameters. The pseudolikelihood approach was introduced by Julian Besag in the context of analysing data having spatial dependence. Definition Given a set of random variables X = X_1, X_2, \ldots, X_n the pseudolikelihood of X = x = (x_1,x_2, \ldots, x_n) is :L(\theta) := \prod_i \mathrm_\theta(X_i = x_i\mid X_j = x_j \text j \neq i)=\prod_i \mathrm _\theta (X_i = x_i \mid X_=x_) in discrete case and :L(\theta) := \prod_i p_\theta(x_i \mid x_j \text j \neq i)=\prod_i p _\theta (x_i \mid x_)=\prod _i p_\theta (x_i \mid x_1,\ldots, \hat x_i, \ldots, x_n) in continuous one. Here X is a vector ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Likelihood Function
The likelihood function (often simply called the likelihood) represents the probability of random variable realizations conditional on particular values of the statistical parameters. Thus, when evaluated on a given sample, the likelihood function indicates which parameter values are more ''likely'' than others, in the sense that they would have made the observed data more probable. Consequently, the likelihood is often written as \mathcal(\theta\mid X) instead of P(X \mid \theta), to emphasize that it is to be understood as a function of the parameters \theta instead of the random variable X. In maximum likelihood estimation, the arg max of the likelihood function serves as a point estimate for \theta, while local curvature (approximated by the likelihood's Hessian matrix) indicates the estimate's precision. Meanwhile in Bayesian statistics, parameter estimates are derived from the converse of the likelihood, the so-called posterior probability, which is calculated via Bayes' r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statistical Theory
The theory of statistics provides a basis for the whole range of techniques, in both study design and data analysis, that are used within applications of statistics. The theory covers approaches to statistical-decision problems and to statistical inference, and the actions and deductions that satisfy the basic principles stated for these different approaches. Within a given approach, statistical theory gives ways of comparing statistical procedures; it can find a best possible procedure within a given context for given statistical problems, or can provide guidance on the choice between alternative procedures. Apart from philosophical considerations about how to make statistical inferences and decisions, much of statistical theory consists of mathematical statistics, and is closely linked to probability theory, to utility theory, and to optimization. Scope Statistical theory provides an underlying rationale and provides a consistent basis for the choice of methodology used in ap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Approximation
An approximation is anything that is intentionally similar but not exactly equality (mathematics), equal to something else. Etymology and usage The word ''approximation'' is derived from Latin ''approximatus'', from ''proximus'' meaning ''very near'' and the prefix ''ad-'' (''ad-'' before ''p'' becomes ap- by assimilation (phonology), assimilation) meaning ''to''. Words like ''approximate'', ''approximately'' and ''approximation'' are used especially in technical or scientific contexts. In everyday English, words such as ''roughly'' or ''around'' are used with a similar meaning. It is often found abbreviated as ''approx.'' The term can be applied to various properties (e.g., value, quantity, image, description) that are nearly, but not exactly correct; similar, but not exactly the same (e.g., the approximate time was 10 o'clock). Although approximation is most often applied to numbers, it is also frequently applied to such things as Function (mathematics), mathematical functio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joint Probability Distribution
Given two random variables that are defined on the same probability space, the joint probability distribution is the corresponding probability distribution on all possible pairs of outputs. The joint distribution can just as well be considered for any given number of random variables. The joint distribution encodes the marginal distributions, i.e. the distributions of each of the individual random variables. It also encodes the conditional probability distributions, which deal with how the outputs of one random variable are distributed when given information on the outputs of the other random variable(s). In the formal mathematical setup of measure theory, the joint distribution is given by the pushforward measure, by the map obtained by pairing together the given random variables, of the sample space's probability measure. In the case of real-valued random variables, the joint distribution, as a particular multivariate distribution, may be expressed by a multivariate cumulativ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Random Variable
A random variable (also called random quantity, aleatory variable, or stochastic variable) is a mathematical formalization of a quantity or object which depends on random events. It is a mapping or a function from possible outcomes (e.g., the possible upper sides of a flipped coin such as heads H and tails T) in a sample space (e.g., the set \) to a measurable space, often the real numbers (e.g., \ in which 1 corresponding to H and -1 corresponding to T). Informally, randomness typically represents some fundamental element of chance, such as in the roll of a dice; it may also represent uncertainty, such as measurement error. However, the interpretation of probability is philosophically complicated, and even in specific cases is not always straightforward. The purely mathematical analysis of random variables is independent of such interpretational difficulties, and can be based upon a rigorous axiomatic setup. In the formal mathematical language of measure theory, a random var ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Estimation Theory
Estimation theory is a branch of statistics that deals with estimating the values of parameters based on measured empirical data that has a random component. The parameters describe an underlying physical setting in such a way that their value affects the distribution of the measured data. An ''estimator'' attempts to approximate the unknown parameters using the measurements. In estimation theory, two approaches are generally considered: * The probabilistic approach (described in this article) assumes that the measured data is random with probability distribution dependent on the parameters of interest * The set-membership approach assumes that the measured data vector belongs to a set which depends on the parameter vector. Examples For example, it is desired to estimate the proportion of a population of voters who will vote for a particular candidate. That proportion is the parameter sought; the estimate is based on a small random sample of voters. Alternatively, it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Julian Besag
Julian Ernst Besag FRS (26 March 1945 – 6 August 2010) was a British statistician known chiefly for his work in spatial statistics (including its applications to epidemiology, image analysis and agricultural science), and Bayesian inference (including Markov chain Monte Carlo algorithms). Early life and education Besag was born in Loughborough and was educated at Loughborough Grammar School. He began studying engineering at the University of Cambridge but moved to the University of Birmingham to study statistics, obtaining his BSc in 1968. Career He then spent a year as a research assistant to Maurice Bartlett at the University of Oxford before obtaining a lectureship at the University of Liverpool. Inspired by John Tukey, he visited Princeton for a year. He moved to the University of Durham in 1975, where he became a professor in 1986. He was a visiting professor at the University of Washington in Seattle during 1989–90 and, after a year at Newcastle University ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spatial Dependence
Spatial analysis or spatial statistics includes any of the formal techniques which studies entities using their topological, geometric, or geographic properties. Spatial analysis includes a variety of techniques, many still in their early development, using different analytic approaches and applied in fields as diverse as astronomy, with its studies of the placement of galaxies in the cosmos, to chip fabrication engineering, with its use of "place and route" algorithms to build complex wiring structures. In a more restricted sense, spatial analysis is the technique applied to structures at the human scale, most notably in the analysis of geographic data or transcriptomics data. Complex issues arise in spatial analysis, many of which are neither clearly defined nor completely resolved, but form the basis for current research. The most fundamental of these is the problem of defining the spatial location of the entities being studied. Classification of the techniques of spatial a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Markov Random Field
In the domain of physics and probability, a Markov random field (MRF), Markov network or undirected graphical model is a set of random variables having a Markov property described by an undirected graph. In other words, a random field is said to be a Markov random field if it satisfies Markov properties. The concept originates from the Sherrington–Kirkpatrick model. A Markov network or MRF is similar to a Bayesian network in its representation of dependencies; the differences being that Bayesian networks are directed and acyclic, whereas Markov networks are undirected and may be cyclic. Thus, a Markov network can represent certain dependencies that a Bayesian network cannot (such as cyclic dependencies ); on the other hand, it can't represent certain dependencies that a Bayesian network can (such as induced dependencies ). The underlying graph of a Markov random field may be finite or infinite. When the joint probability density of the random variables is strictly positive, it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bayesian Network
A Bayesian network (also known as a Bayes network, Bayes net, belief network, or decision network) is a probabilistic graphical model that represents a set of variables and their conditional dependencies via a directed acyclic graph (DAG). Bayesian networks are ideal for taking an event that occurred and predicting the likelihood that any one of several possible known causes was the contributing factor. For example, a Bayesian network could represent the probabilistic relationships between diseases and symptoms. Given symptoms, the network can be used to compute the probabilities of the presence of various diseases. Efficient algorithms can perform inference and learning in Bayesian networks. Bayesian networks that model sequences of variables (''e.g.'' speech signals or protein sequences) are called dynamic Bayesian networks. Generalizations of Bayesian networks that can represent and solve decision problems under uncertainty are called influence diagrams. Graphical mode ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maximum Likelihood
In statistics, maximum likelihood estimation (MLE) is a method of estimation theory, estimating the Statistical parameter, parameters of an assumed probability distribution, given some observed data. This is achieved by Mathematical optimization, maximizing a likelihood function so that, under the assumed statistical model, the Realization (probability), observed data is most probable. The point estimate, point in the parameter space that maximizes the likelihood function is called the maximum likelihood estimate. The logic of maximum likelihood is both intuitive and flexible, and as such the method has become a dominant means of statistical inference. If the likelihood function is Differentiable function, differentiable, the derivative test for finding maxima can be applied. In some cases, the first-order conditions of the likelihood function can be solved analytically; for instance, the ordinary least squares estimator for a linear regression model maximizes the likelihood when ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
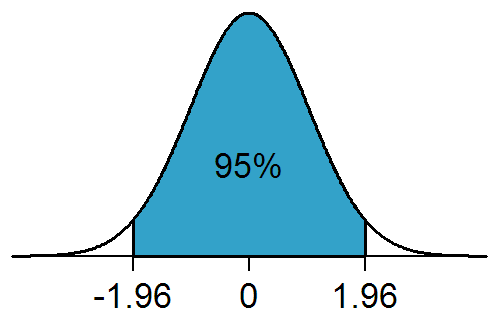
Statistical Significance
In statistical hypothesis testing, a result has statistical significance when it is very unlikely to have occurred given the null hypothesis (simply by chance alone). More precisely, a study's defined significance level, denoted by \alpha, is the probability of the study rejecting the null hypothesis, given that the null hypothesis is true; and the ''p''-value of a result, ''p'', is the probability of obtaining a result at least as extreme, given that the null hypothesis is true. The result is statistically significant, by the standards of the study, when p \le \alpha. The significance level for a study is chosen before data collection, and is typically set to 5% or much lower—depending on the field of study. In any experiment or observation that involves drawing a sample from a population, there is always the possibility that an observed effect would have occurred due to sampling error alone. But if the ''p''-value of an observed effect is less than (or equal to) the significanc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |