|
Pseudogymnoascus
''Pseudogymnoascus'' is a genus of fungi in the family Pseudeurotiaceae. History It was circumscribed by A. Raillo in 1929 for two species, ''P. roseus'' and ''P. vinaceus''. No type specimens were retained by Raillo. In 1972, Samson designated a neotype for ''P. roseus'', recognized three species (''P. roseus'' Raillo, ''P. bhattii'' Samson and ''P. caucasicus'' Cejp & Milko) and synonymized ''P. vinaceus'' with ''P. roseus''. In 1982, Müller described a fourth species, ''P. alpinus''. In 2006, Rice and Currah described two additional species, ''P. appendiculatus'' and ''P. verrucosus''. In 2013, ''Geomyces destructans'' the casual agent of bat white nose syndrome was transferred to this genus and is now referred to as ''P. destructans''. Since 2006, intensive cave sampling has identified numerous ''Pseudogymnoascus'' isolates that have yet to be described. Species Characteristics ''Pseudogymnoascus alpinus'' Müller ascospores are described as navicular-fusiform in shap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudogymnoascus Roseus
''Pseudogymnoascus'' is a genus of fungi in the family Pseudeurotiaceae. History It was circumscribed by A. Raillo in 1929 for two species, ''P. roseus'' and ''P. vinaceus''. No type specimens were retained by Raillo. In 1972, Samson designated a neotype for ''P. roseus'', recognized three species (''P. roseus'' Raillo, ''P. bhattii'' Samson and ''P. caucasicus'' Cejp & Milko) and synonymized ''P. vinaceus'' with ''P. roseus''. In 1982, Müller described a fourth species, ''P. alpinus''. In 2006, Rice and Currah described two additional species, ''P. appendiculatus'' and ''P. verrucosus''. In 2013, ''Geomyces destructans'' the casual agent of bat white nose syndrome was transferred to this genus and is now referred to as ''P. destructans''. Since 2006, intensive cave sampling has identified numerous ''Pseudogymnoascus'' isolates that have yet to be described. Species Characteristics ''Pseudogymnoascus alpinus'' Müller ascospores are described as navicular-fusiform in shap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudogymnoascus Caucasicus
''Pseudogymnoascus'' is a genus of fungi in the family Pseudeurotiaceae. History It was circumscribed by A. Raillo in 1929 for two species, ''P. roseus'' and ''P. vinaceus''. No type specimens were retained by Raillo. In 1972, Samson designated a neotype for ''P. roseus'', recognized three species (''P. roseus'' Raillo, ''P. bhattii'' Samson and ''P. caucasicus'' Cejp & Milko) and synonymized ''P. vinaceus'' with ''P. roseus''. In 1982, Müller described a fourth species, ''P. alpinus''. In 2006, Rice and Currah described two additional species, ''P. appendiculatus'' and ''P. verrucosus''. In 2013, ''Geomyces destructans'' the casual agent of bat white nose syndrome was transferred to this genus and is now referred to as ''P. destructans''. Since 2006, intensive cave sampling has identified numerous ''Pseudogymnoascus'' isolates that have yet to be described. Species Characteristics ''Pseudogymnoascus alpinus'' Müller ascospores are described as navicular-fusiform in shap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudogymnoascus Verrucocus
''Pseudogymnoascus'' is a genus of fungi in the family Pseudeurotiaceae. History It was circumscribed by A. Raillo in 1929 for two species, ''P. roseus'' and ''P. vinaceus''. No type specimens were retained by Raillo. In 1972, Samson designated a neotype for ''P. roseus'', recognized three species (''P. roseus'' Raillo, ''P. bhattii'' Samson and ''P. caucasicus'' Cejp & Milko) and synonymized ''P. vinaceus'' with ''P. roseus''. In 1982, Müller described a fourth species, ''P. alpinus''. In 2006, Rice and Currah described two additional species, ''P. appendiculatus'' and ''P. verrucosus''. In 2013, ''Geomyces destructans'' the casual agent of bat white nose syndrome was transferred to this genus and is now referred to as ''P. destructans''. Since 2006, intensive cave sampling has identified numerous ''Pseudogymnoascus'' isolates that have yet to be described. Species Characteristics ''Pseudogymnoascus alpinus'' Müller ascospores are described as navicular-fusiform in shap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudogymnoascus Alpinus
''Pseudogymnoascus'' is a genus of fungi in the family Pseudeurotiaceae. History It was circumscribed by A. Raillo in 1929 for two species, ''P. roseus'' and ''P. vinaceus''. No type specimens were retained by Raillo. In 1972, Samson designated a neotype for ''P. roseus'', recognized three species (''P. roseus'' Raillo, ''P. bhattii'' Samson and ''P. caucasicus'' Cejp & Milko) and synonymized ''P. vinaceus'' with ''P. roseus''. In 1982, Müller described a fourth species, ''P. alpinus''. In 2006, Rice and Currah described two additional species, ''P. appendiculatus'' and ''P. verrucosus''. In 2013, ''Geomyces destructans'' the casual agent of bat white nose syndrome was transferred to this genus and is now referred to as ''P. destructans''. Since 2006, intensive cave sampling has identified numerous ''Pseudogymnoascus'' isolates that have yet to be described. Species Characteristics ''Pseudogymnoascus alpinus'' Müller ascospores are described as navicular-fusiform in shap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudogymnoascus Appendiculatus
''Pseudogymnoascus'' is a genus of fungi in the family Pseudeurotiaceae. History It was circumscribed by A. Raillo in 1929 for two species, ''P. roseus'' and ''P. vinaceus''. No type specimens were retained by Raillo. In 1972, Samson designated a neotype for ''P. roseus'', recognized three species (''P. roseus'' Raillo, ''P. bhattii'' Samson and ''P. caucasicus'' Cejp & Milko) and synonymized ''P. vinaceus'' with ''P. roseus''. In 1982, Müller described a fourth species, ''P. alpinus''. In 2006, Rice and Currah described two additional species, ''P. appendiculatus'' and ''P. verrucosus''. In 2013, ''Geomyces destructans'' the casual agent of bat white nose syndrome was transferred to this genus and is now referred to as ''P. destructans''. Since 2006, intensive cave sampling has identified numerous ''Pseudogymnoascus'' isolates that have yet to be described. Species Characteristics ''Pseudogymnoascus alpinus'' Müller ascospores are described as navicular-fusiform in shap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudogymnoascus Bhattii
''Pseudogymnoascus'' is a genus of fungi in the family Pseudeurotiaceae. History It was circumscribed by A. Raillo in 1929 for two species, ''P. roseus'' and ''P. vinaceus''. No type specimens were retained by Raillo. In 1972, Samson designated a neotype for ''P. roseus'', recognized three species (''P. roseus'' Raillo, ''P. bhattii'' Samson and ''P. caucasicus'' Cejp & Milko) and synonymized ''P. vinaceus'' with ''P. roseus''. In 1982, Müller described a fourth species, ''P. alpinus''. In 2006, Rice and Currah described two additional species, ''P. appendiculatus'' and ''P. verrucosus''. In 2013, ''Geomyces destructans'' the casual agent of bat white nose syndrome was transferred to this genus and is now referred to as ''P. destructans''. Since 2006, intensive cave sampling has identified numerous ''Pseudogymnoascus'' isolates that have yet to be described. Species Characteristics ''Pseudogymnoascus alpinus'' Müller ascospores are described as navicular-fusiform in shap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geomyces Destructans
''Pseudogymnoascus destructans'' (formerly known as ''Geomyces destructans'') is a psychrophilic (cold-loving) fungus that causes white-nose syndrome (WNS), a fatal disease that has devastated bat populations in parts of the United States and Canada. Unlike species of ''Geomyces'', ''P. destructans'' forms asymmetrically curved conidia. ''Pseudogymnoascus destructans'' grows very slowly on artificial media and cannot grow at temperatures above 20 °C. It can grow around 4 °C to 20 °C, which encompasses the temperatures found in winter bat hibernacula. Phylogenic evaluation has revealed this organism should be reclassified under the family ''Pseudeurotiaceae'', changing its name to ''Pseudogymnoascus destructans''. History In 2008, Blehert ''et al.'' described the fungus associated with white-nose syndrome as a member of the genus ''Geomyces''. In 2009, Gargas ''et al.'' were the first to describe the fungus as a unique species; the specific name they chose, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudogymnoascus Destructans
''Pseudogymnoascus destructans'' (formerly known as ''Geomyces destructans'') is a psychrophilic (cold-loving) fungus that causes white-nose syndrome (WNS), a fatal disease that has devastated bat populations in parts of the United States and Canada. Unlike species of ''Geomyces'', ''P. destructans'' forms asymmetrically curved conidia. ''Pseudogymnoascus destructans'' grows very slowly on artificial media and cannot grow at temperatures above 20 °C. It can grow around 4 °C to 20 °C, which encompasses the temperatures found in winter bat hibernacula. Phylogenic evaluation has revealed this organism should be reclassified under the family ''Pseudeurotiaceae'', changing its name to ''Pseudogymnoascus destructans''. History In 2008, Blehert ''et al.'' described the fungus associated with white-nose syndrome as a member of the genus ''Geomyces''. In 2009, Gargas ''et al.'' were the first to describe the fungus as a unique species; the specific name they chose, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
White Nose Syndrome
White-nose syndrome (WNS) is a fungal disease in North American bats which has resulted in the dramatic decrease of the bat population in the United States and Canada, reportedly killing millions as of 2018. The condition is named for a distinctive fungal growth around the muzzles and on the wings of hibernating bats. It was first identified from a February 2006 photo taken in a cave located in Schoharie County, New York. The syndrome has rapidly spread since then. In early 2018, it was identified in 33 U.S. states and seven Canadian provinces; plus the fungus, albeit sans syndrome, had been found in three additional states. Most cases are in the eastern half of both countries, but in March 2016, it was confirmed in a little brown bat in Washington state. In 2019, evidence of the fungus was detected in California for the first time, although no affected bats were found. The disease is caused by the fungus ''Pseudogymnoascus destructans'', which colonizes the bat's skin. No obviou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudeurotiaceae
The ''Pseudeurotiaceae'' are a family of fungi in the division Ascomycota. This family can not yet be taxonomically classified in any of the ascomycetous classes and orders with any degree of certainty (incertae sedis). General characteristics The general characteristics for members within this family include hyaline or brown ascospores, within a thin-walled ascus inside a cleistothecial ascomata An ascocarp, or ascoma (), is the fruiting body ( sporocarp) of an ascomycete phylum fungus. It consists of very tightly interwoven hyphae and millions of embedded asci, each of which typically contains four to eight ascospores. Ascocarps are mos .... See also * List of Ascomycota families ''incertae sedis'' References Ascomycota enigmatic taxa Fungus families {{ascomycota-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
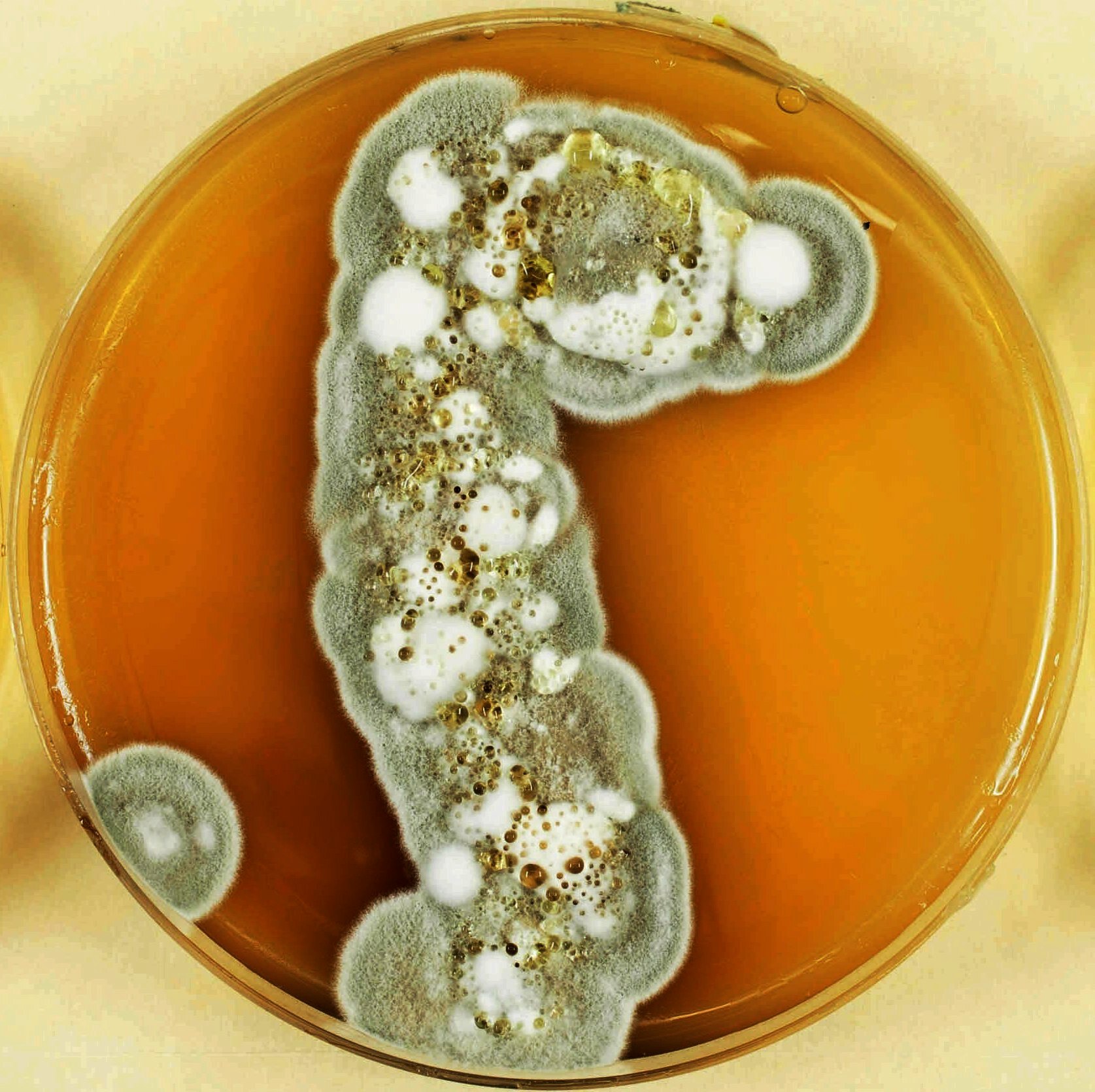
Geomyces Destructans In Culture
''Geomyces'' is a genus of filamentous fungi in the family Myxotrichaceae. Members of the genus are widespread in distribution, especially in northern temperate regions. Known to be psychrotolerant and associated with Arctic permafrost soils,''National Geographic'': they are equally prevalent in the air of domestic dwellings, and children's sandpits. Species of ''Geomyces'' have previously been placed in the genus ''Chrysosporium''. Description This genus is characterized by short but distinct branched conidiophores that have chains of spores formed directly from the cells of the branches. Sometimes only the tips of the branches become spores. The spores (conidia) are 1-celled, and either white or yellow. The teleomorph of species in this genus, if they exist, are in ''Pseudogymnoascus'' or '' Gymnostellatospora''. ''Geomyces'' species are known to form ericoid mycorrhizae with the roots of alpine Ericales and other perennial hosts, helping these plants adapt to low-nutrient env ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sphagnum
''Sphagnum'' is a genus of approximately 380 accepted species of mosses, commonly known as sphagnum moss, peat moss, also bog moss and quacker moss (although that term is also sometimes used for peat). Accumulations of ''Sphagnum'' can store water, since both living and dead plants can hold large quantities of water inside their cells; plants may hold 16 to 26 times as much water as their dry weight, depending on the species.Bold, H. C. 1967. Morphology of Plants. second ed. Harper and Row, New York. p. 225-229. The empty cells help retain water in drier conditions. As sphagnum moss grows, it can slowly spread into drier conditions, forming larger mires, both raised bogs and blanket bogs. Thus, sphagnum can influence the composition of such habitats, with some describing sphagnum as 'habitat manipulators'. These peat accumulations then provide habitat for a wide array of peatland plants, including sedges and Calcifuges, ericaceous shrubs, as well as orchids and carnivorous plant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |