|
Pseudo-nitzschia
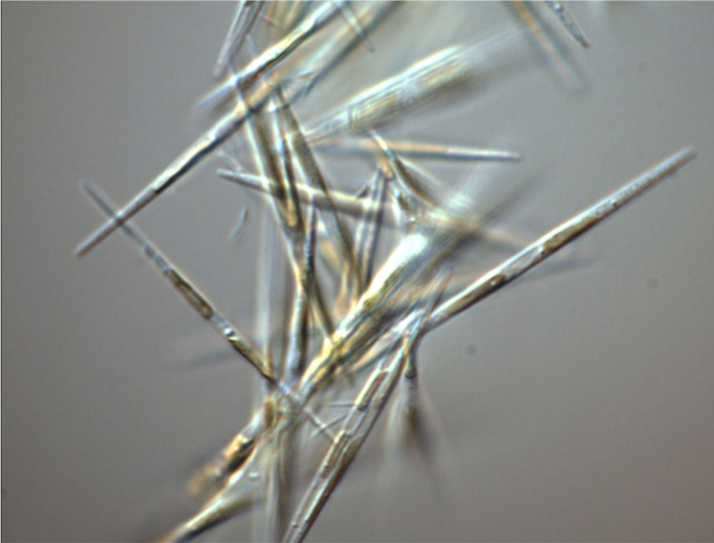
''Pseudo-nitzschia'' is a marine planktonic diatom genus that accounts for 4.4% of pennate diatoms found worldwide. Some species are capable of producing the neurotoxin domoic acid (DA), which is responsible for the neurological disorder in humans known as amnesic shellfish poisoning (ASP). Currently, 58 species are known, 28 of which have been shown to produced DA. It was originally hypothesized that only dinoflagellates could produce harmful algal toxins, but a deadly bloom of ''Pseudo-nitzschia'' occurred in 1987 in the bays of Prince Edward Island, Canada, and led to an outbreak of ASP. Over 100 people were affected by this outbreak after consuming contaminated mussels; three people died. Since this event, no additional deaths have been attributed to ASP, though the prevalence of toxic diatoms and DA has increased worldwide. This anomaly is likely due to increased awareness of harmful algal blooms (HABs) and their implications for human and ecosystem health. Blooms have since ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudo-nitzschia Batesiana
''Pseudo-nitzschia'' is a marine planktonic diatom genus that accounts for 4.4% of pennate diatoms found worldwide. Some species are capable of producing the neurotoxin domoic acid (DA), which is responsible for the neurological disorder in humans known as amnesic shellfish poisoning (ASP). Currently, 58 species are known, 28 of which have been shown to produced DA. It was originally hypothesized that only dinoflagellates could produce harmful algal toxins, but a deadly bloom of ''Pseudo-nitzschia'' occurred in 1987 in the bays of Prince Edward Island, Canada, and led to an outbreak of ASP. Over 100 people were affected by this outbreak after consuming contaminated mussels; three people died. Since this event, no additional deaths have been attributed to ASP, though the prevalence of toxic diatoms and DA has increased worldwide. This anomaly is likely due to increased awareness of harmful algal blooms (HABs) and their implications for human and ecosystem health. Blooms have since ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudo-nitzschia Antarctica
''Pseudo-nitzschia'' is a marine planktonic diatom genus that accounts for 4.4% of pennate diatoms found worldwide. Some species are capable of producing the neurotoxin domoic acid (DA), which is responsible for the neurological disorder in humans known as amnesic shellfish poisoning (ASP). Currently, 58 species are known, 28 of which have been shown to produced DA. It was originally hypothesized that only dinoflagellates could produce harmful algal toxins, but a deadly bloom of ''Pseudo-nitzschia'' occurred in 1987 in the bays of Prince Edward Island, Canada, and led to an outbreak of ASP. Over 100 people were affected by this outbreak after consuming contaminated mussels; three people died. Since this event, no additional deaths have been attributed to ASP, though the prevalence of toxic diatoms and DA has increased worldwide. This anomaly is likely due to increased awareness of harmful algal blooms (HABs) and their implications for human and ecosystem health. Blooms have sinc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudo-nitzschia
''Pseudo-nitzschia'' is a marine planktonic diatom genus that accounts for 4.4% of pennate diatoms found worldwide. Some species are capable of producing the neurotoxin domoic acid (DA), which is responsible for the neurological disorder in humans known as amnesic shellfish poisoning (ASP). Currently, 58 species are known, 28 of which have been shown to produced DA. It was originally hypothesized that only dinoflagellates could produce harmful algal toxins, but a deadly bloom of ''Pseudo-nitzschia'' occurred in 1987 in the bays of Prince Edward Island, Canada, and led to an outbreak of ASP. Over 100 people were affected by this outbreak after consuming contaminated mussels; three people died. Since this event, no additional deaths have been attributed to ASP, though the prevalence of toxic diatoms and DA has increased worldwide. This anomaly is likely due to increased awareness of harmful algal blooms (HABs) and their implications for human and ecosystem health. Blooms have since ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudo-nitzschia Abrensis
''Pseudo-nitzschia'' is a marine planktonic diatom genus that accounts for 4.4% of pennate diatoms found worldwide. Some species are capable of producing the neurotoxin domoic acid (DA), which is responsible for the neurological disorder in humans known as amnesic shellfish poisoning (ASP). Currently, 58 species are known, 28 of which have been shown to produced DA. It was originally hypothesized that only dinoflagellates could produce harmful algal toxins, but a deadly bloom of ''Pseudo-nitzschia'' occurred in 1987 in the bays of Prince Edward Island, Canada, and led to an outbreak of ASP. Over 100 people were affected by this outbreak after consuming contaminated mussels; three people died. Since this event, no additional deaths have been attributed to ASP, though the prevalence of toxic diatoms and DA has increased worldwide. This anomaly is likely due to increased awareness of harmful algal blooms (HABs) and their implications for human and ecosystem health. Blooms have sinc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudo-nitzschia Allochrona
''Pseudo-nitzschia'' is a marine planktonic diatom genus that accounts for 4.4% of pennate diatoms found worldwide. Some species are capable of producing the neurotoxin domoic acid (DA), which is responsible for the neurological disorder in humans known as amnesic shellfish poisoning (ASP). Currently, 58 species are known, 28 of which have been shown to produced DA. It was originally hypothesized that only dinoflagellates could produce harmful algal toxins, but a deadly bloom of ''Pseudo-nitzschia'' occurred in 1987 in the bays of Prince Edward Island, Canada, and led to an outbreak of ASP. Over 100 people were affected by this outbreak after consuming contaminated mussels; three people died. Since this event, no additional deaths have been attributed to ASP, though the prevalence of toxic diatoms and DA has increased worldwide. This anomaly is likely due to increased awareness of harmful algal blooms (HABs) and their implications for human and ecosystem health. Blooms have sinc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudo-nitzschia Americana
''Pseudo-nitzschia'' is a marine planktonic diatom genus that accounts for 4.4% of pennate diatoms found worldwide. Some species are capable of producing the neurotoxin domoic acid (DA), which is responsible for the neurological disorder in humans known as amnesic shellfish poisoning (ASP). Currently, 58 species are known, 28 of which have been shown to produced DA. It was originally hypothesized that only dinoflagellates could produce harmful algal toxins, but a deadly bloom of ''Pseudo-nitzschia'' occurred in 1987 in the bays of Prince Edward Island, Canada, and led to an outbreak of ASP. Over 100 people were affected by this outbreak after consuming contaminated mussels; three people died. Since this event, no additional deaths have been attributed to ASP, though the prevalence of toxic diatoms and DA has increased worldwide. This anomaly is likely due to increased awareness of harmful algal blooms (HABs) and their implications for human and ecosystem health. Blooms have sinc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudo-nitzschia Arctica
''Pseudo-nitzschia'' is a marine planktonic diatom genus that accounts for 4.4% of pennate diatoms found worldwide. Some species are capable of producing the neurotoxin domoic acid (DA), which is responsible for the neurological disorder in humans known as amnesic shellfish poisoning (ASP). Currently, 58 species are known, 28 of which have been shown to produced DA. It was originally hypothesized that only dinoflagellates could produce harmful algal toxins, but a deadly bloom of ''Pseudo-nitzschia'' occurred in 1987 in the bays of Prince Edward Island, Canada, and led to an outbreak of ASP. Over 100 people were affected by this outbreak after consuming contaminated mussels; three people died. Since this event, no additional deaths have been attributed to ASP, though the prevalence of toxic diatoms and DA has increased worldwide. This anomaly is likely due to increased awareness of harmful algal blooms (HABs) and their implications for human and ecosystem health. Blooms have sinc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudo-nitzschia Arenysensis
''Pseudo-nitzschia'' is a marine planktonic diatom genus that accounts for 4.4% of pennate diatoms found worldwide. Some species are capable of producing the neurotoxin domoic acid (DA), which is responsible for the neurological disorder in humans known as amnesic shellfish poisoning (ASP). Currently, 58 species are known, 28 of which have been shown to produced DA. It was originally hypothesized that only dinoflagellates could produce harmful algal toxins, but a deadly bloom of ''Pseudo-nitzschia'' occurred in 1987 in the bays of Prince Edward Island, Canada, and led to an outbreak of ASP. Over 100 people were affected by this outbreak after consuming contaminated mussels; three people died. Since this event, no additional deaths have been attributed to ASP, though the prevalence of toxic diatoms and DA has increased worldwide. This anomaly is likely due to increased awareness of harmful algal blooms (HABs) and their implications for human and ecosystem health. Blooms have sinc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudo-nitzschia Granii
''Pseudo-nitzschia'' is a marine planktonic diatom genus that accounts for 4.4% of pennate diatoms found worldwide. Some species are capable of producing the neurotoxin domoic acid (DA), which is responsible for the neurological disorder in humans known as amnesic shellfish poisoning (ASP). Currently, 58 species are known, 28 of which have been shown to produced DA. It was originally hypothesized that only dinoflagellates could produce harmful algal toxins, but a deadly bloom of ''Pseudo-nitzschia'' occurred in 1987 in the bays of Prince Edward Island, Canada, and led to an outbreak of ASP. Over 100 people were affected by this outbreak after consuming contaminated mussels; three people died. Since this event, no additional deaths have been attributed to ASP, though the prevalence of toxic diatoms and DA has increased worldwide. This anomaly is likely due to increased awareness of harmful algal blooms (HABs) and their implications for human and ecosystem health. Blooms have since ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudo-nitzschia Australis
''Pseudo-nitzschia australis'' is a pennate diatom found in temperate and sub-tropic marine waters, such as off the coast of California and Argentina. This diatom is a Harmful Micro Algae that produces toxic effects on a variety of organisms through its production of domoic acid, a neurotoxin. Toxic effects have been observed in a variety of predatory organisms such as pelicans, sea lions, and humans. If exposed to a high enough dose, these predators will die as a result, and there is no known antidote. The potential indirect mortality associated with ''P. australis'' is of great concern to humans as toxic algae blooms, including blooms of ''P. australis,'' continue to increase in frequency and severity over recent years. Blooms of ''P. australis'' are believed to result from high concentrations of nitrates and phosphates in stream and river runoff, as well as coastal upwelling, which are also sources of other harmful algae blooms. Morphology ''Pseudo-nitzschia australis'' are a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amnesic Shellfish Poisoning
Amnesic shellfish poisoning (ASP) is an illness caused by consumption of shellfish that contain the marine biotoxin called domoic acid. In mammals, including humans, domoic acid acts as a neurotoxin, causing permanent short-term memory loss, brain damage, and death in severe cases. This toxin is produced naturally by marine diatoms belonging to the genus ''Pseudo-nitzschia'' and the species '' Nitzschia navis-varingica''. When accumulated in high concentrations by shellfish during filter feeding, domoic acid can then be passed on to birds, marine mammals, and humans by consumption of the contaminated shellfish. Although human illness due to domoic acid has only been associated with shellfish, the toxin can bioaccumulate in many marine organisms that consume phytoplankton, such as anchovies and sardines. Intoxication by domoic acid in nonhuman organisms is frequently referred to as domoic acid poisoning. Symptoms and treatment In the brain, domoic acid especially damages the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
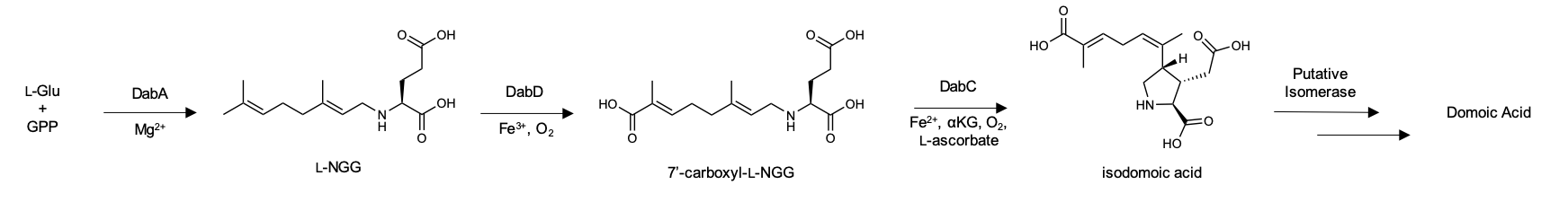
Domoic Acid
Domoic acid (DA) is a kainic acid-type neurotoxin that causes amnesic shellfish poisoning (ASP). It is produced by algae and accumulates in shellfish, sardines, and anchovies. When sea lions, otters, cetaceans, humans, and other predators eat contaminated animals, poisoning may result. Exposure to this compound affects the brain, causing seizures, and possibly death. History There has been little use of domoic acid throughout history except for in Japan, where it has been used as an anthelmintic for centuries. Domoic acid was first isolated in 1959 from a species of red algae, '' Chondria armata'', in Japan, which is commonly referred to as ''dōmoi'' (ドウモイ) in the Tokunoshima dialect, or ''hanayanagi''. Poisonings in history have been rare, or undocumented; however, it is thought that the increase in human activities is resulting in an increasing frequency of harmful algal blooms along coastlines in recent years. In 2015, the North American Pacific coast was heavily impac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |