|
Prussian Lithuanian
The Prussian Lithuanians, or Lietuvininkai (singular: ''Lietuvininkas'', plural: ''Lietuvininkai''), are Lithuanians, originally Lithuanian language speakers, who formerly inhabited a territory in northeastern East Prussia called Prussian Lithuania, or Lithuania Minor ( lt, Prūsų Lietuva, Mažoji Lietuva, german: Preußisch-Litauen, Kleinlitauen), instead of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and, later, the Republic of Lithuania (Lithuania Major, or Lithuania proper). Prussian Lithuanians contributed greatly to the development of written Lithuanian, which for a long time was considerably more widespread and in more literary use in Lithuania Minor than in Lithuania proper. Unlike most Lithuanians, who remained Roman Catholic after the Protestant Reformation, most Lietuvininkai became Lutheran-Protestants (Evangelical-Lutheran). There were 121,345 speakers of Lithuanian in the Prussian census of 1890. Almost all Prussian Lithuanians were executed or expelled after World War II, when ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Language
German ( ) is a West Germanic languages, West Germanic language mainly spoken in Central Europe. It is the most widely spoken and Official language, official or co-official language in Germany, Austria, Switzerland, Liechtenstein, and the Italy, Italian province of South Tyrol. It is also a co-official language of Luxembourg and German-speaking Community of Belgium, Belgium, as well as a national language in Namibia. Outside Germany, it is also spoken by German communities in France (Bas-Rhin), Czech Republic (North Bohemia), Poland (Upper Silesia), Slovakia (Bratislava Region), and Hungary (Sopron). German is most similar to other languages within the West Germanic language branch, including Afrikaans, Dutch language, Dutch, English language, English, the Frisian languages, Low German, Luxembourgish, Scots language, Scots, and Yiddish. It also contains close similarities in vocabulary to some languages in the North Germanic languages, North Germanic group, such as Danish lan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lutherans
Lutheranism is one of the largest branches of Protestantism, identifying primarily with the theology of Martin Luther, the 16th-century German monk and reformer whose efforts to reform the theology and practice of the Catholic Church launched the Protestant Reformation. The reaction of the government and church authorities to the international spread of his writings, beginning with the ''Ninety-five Theses'', divided Western Christianity. During the Reformation, Lutheranism became the state religion of numerous states of northern Europe, especially in northern Germany, Scandinavia and the then-Livonian Order. Lutheran clergy became civil servants and the Lutheran churches became part of the state. The split between the Lutherans and the Roman Catholics was made public and clear with the 1521 Edict of Worms: the edicts of the Diet condemned Luther and officially banned citizens of the Holy Roman Empire from defending or propagating his ideas, subjecting advocates of Lutheranism ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fighting occurring throughout Europe, the Middle East, Africa, the Pacific, and parts of Asia. An estimated 9 million soldiers were killed in combat, plus another 23 million wounded, while 5 million civilians died as a result of military action, hunger, and disease. Millions more died in genocides within the Ottoman Empire and in the 1918 influenza pandemic, which was exacerbated by the movement of combatants during the war. Prior to 1914, the European great powers were divided between the Triple Entente (comprising France, Russia, and Britain) and the Triple Alliance (containing Germany, Austria-Hungary, and Italy). Tensions in the Balkans came to a head on 28 June 1914, following the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dovas Zaunius
Dovas Zaunius (19 June 1892 – 22 February 1940) was a Lithuanian lawyer, politician and diplomat who served as Ambassador to Switzerland from 1925 until 1927 and Lithuanian Foreign Minister from 1929 to 1934. Biography Zaunius was born in East Prussia as the youngest son of Dovas Zaunius (senior) who was a political and public figure in Lithuania Minor. In 1911, he graduated from the Tilsit Gymnasium from there he went on to study law at the University of Munich. In 1917, Zaunius defended his doctoral thesis in criminal and civil law at the University of Königsberg. During his studies Zaunius joined the Lithuanian Conservative Election Societies headed by his father Dovas Zaunius. During World War I, he served in the German Army and after the German capitulation he was invited to work at the Lithuanian Ministry of Foreign Affairs as a qualified lawyer. From 1919 to 1920, he served as acting director of the Policy Department. In 1920, he was appointed Lithuanian affairs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ieva Simonaitytė
Ieva Simonaitytė or Ewa Simoneit (23 January 1897 – 27 August 1978) was a Lithuanian writer. She represented the culture of Lithuania Minor and Klaipėda Region, territories of German East Prussia with historically large, but dwindling, Lithuanian populations. She received critical acclaim for her novel ''Aukštujų Šimonių likimas'' (''The Fate of Šimoniai from Aukštujai'', 1935). Biography Simonaitytė was born in a small village of Vanagai (then Wannaggen in German East Prussia) in Klaipėda district. At the age of five, she became ill with tuberculosis, that affected her bones, and she had to walk with canes since then. Hailing from a poor peasant family and growing up without a father, she had to work since young age as a gooseherd or babysitter. Learning to read and write from her mother, Simonaitytė was largely self-taught. From 1912 to 1914 Simonaitytė received treatment for tuberculosis in Angerburg. She returned in better health and, influenced by World War ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samogitia
Samogitia or Žemaitija ( Samogitian: ''Žemaitėjė''; see below for alternative and historical names) is one of the five cultural regions of Lithuania and formerly one of the two core administrative divisions of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania alongside Lithuania proper. Žemaitija is located in northwestern Lithuania. Its largest city is Šiauliai. Žemaitija has a long and distinct cultural history, reflected in the existence of the Samogitian language. Etymology and alternative names Ruthenian sources mentioned the region as жемотьская земля, ''Žemot'skaja zemlja''; this gave rise to its Polish form, , and probably to the Middle High German . In Latin texts, the name is usually written as etc. The area has long been known to its residents and to other Lithuanians exclusively as Žemaitija (the name Samogitia is no longer in use within Lithuania and has not been used for at least two centuries); Žemaitija means "lowlands" in Lithuanian. The region is also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exonym
An endonym (from Greek: , 'inner' + , 'name'; also known as autonym) is a common, ''native'' name for a geographical place, group of people, individual person, language or dialect, meaning that it is used inside that particular place, group, or linguistic community in question; it is their self-designated name for themselves, their homeland, or their language. An exonym (from Greek: , 'outer' + , 'name'; also known as xenonym) is an established, ''non-native'' name for a geographical place, group of people, individual person, language or dialect, meaning that it is used only outside that particular place, group, or linguistic community. Exonyms exist not only for historico-geographical reasons but also in consideration of difficulties when pronouncing foreign words. For instance, is the endonym for the country that is also known by the exonym ''Germany'' in English, in Spanish and in French. Naming and etymology The terms ''autonym'', ''endonym'', ''exonym'' and ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synonym
A synonym is a word, morpheme, or phrase that means exactly or nearly the same as another word, morpheme, or phrase in a given language. For example, in the English language, the words ''begin'', ''start'', ''commence'', and ''initiate'' are all synonyms of one another: they are ''synonymous''. The standard test for synonymy is substitution: one form can be replaced by another in a sentence without changing its meaning. Words are considered synonymous in only one particular sense: for example, ''long'' and ''extended'' in the context ''long time'' or ''extended time'' are synonymous, but ''long'' cannot be used in the phrase ''extended family''. Synonyms with exactly the same meaning share a seme or denotational sememe, whereas those with inexactly similar meanings share a broader denotational or connotational sememe and thus overlap within a semantic field. The former are sometimes called cognitive synonyms and the latter, near-synonyms, plesionyms or poecilonyms. Lexicograph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethnonyms
An ethnonym () is a name applied to a given ethnic group. Ethnonyms can be divided into two categories: exonyms (whose name of the ethnic group has been created by another group of people) and autonyms, or endonyms (whose name is created and used by the ethnic group itself). As an example, the largest ethnic group in Germany is Germans. The ethnonym ''Germans'' is a Latin-derived exonym used in the English language. Conversely, the Germans call themselves the , an endonym. The German people are identified by a variety of exonyms across Europe, such as ( French), (Italian), (Swedish) and (Polish). As a sub-field of anthroponymy, the study of ethnonyms is called ethnonymy or ethnonymics. Ethnonyms should not be confused with demonyms, distinctive terms that designate all people related to a specific territory, regardless of any ethnic, religious, linguistic or some other distinctions that may exist within the population of that territory. Variations Numerous ethnonyms can a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simon Grunau
Simon Grunau (c. 1470 – c. 1530) was the author of ''Preussische Chronik'',Full title: ''Cronika und beschreibung allerlüstlichenn, nützlichsten und waaren historien des namkundigenn landes zu Prewssen'' or ''Chronicle and description of the most amusing, useful and true known history of the Prussian land'' the first comprehensive history of Prussia. The only personal information available is what he wrote himself in his work: that he was a Dominican priest from Tolkemit (Tolkmicko) near Frauenburg (Frombork) just north of Elbing (Elbląg) in the Monastic State of the Teutonic Order. He preached in Danzig (Gdańsk) and claimed to have met Pope Leo X and Polish King Sigismund I the Old. The chronicle was written in the German language sometime between 1517 and 1529. Its 24 chapters deal with Prussian landscape, agriculture, inhabitants, their customs, and history from earliest times to up to 1525 when the Protestant Duchy of Prussia was created. It also contains a short (about a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
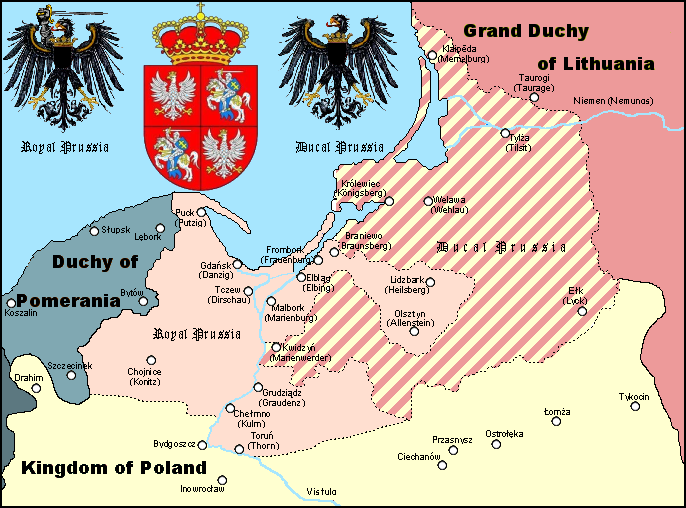
Klaipėda Region
The Klaipėda Region ( lt, Klaipėdos kraštas) or Memel Territory (german: Memelland or ''Memelgebiet'') was defined by the 1919 Treaty of Versailles in 1920 and refers to the northernmost part of the German province of East Prussia, when as Memelland it was put under the administration of the Entente's Council of Ambassadors. The Memel Territory, together with other areas severed from Germany (the Saar and Danzig) was to remain under the control of the League of Nations until a future day when the people of these regions would be allowed to vote on whether the land would return to Germany or not. Today, the former Memel Territory is controlled by Lithuania as part of Klaipėda and Tauragė counties. Historical overview In 1226 Duke Konrad I of Masovia requested assistance against the Prussians and other Baltic tribes, including the Skalvians who lived along the Neman (Memel) River. In March 1226, Holy Roman Emperor Frederick II issued the Golden Bull of Rimini, which p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kaliningrad Oblast
Kaliningrad Oblast (russian: Калинингра́дская о́бласть, translit=Kaliningradskaya oblast') is the westernmost federal subject of Russia. It is a semi-exclave situated on the Baltic Sea. The largest city and administrative centre of the province (oblast) is the city of Kaliningrad, formerly known as Königsberg. The port city of Baltiysk is Russia's only port on the Baltic Sea that remains ice-free in winter. Kaliningrad Oblast had a population of roughly 1 million in the Russian Census of 2010. The oblast is bordered by Poland to the south, Lithuania to the north and east and the Baltic Sea to the north-west. The territory was formerly the northern part of the Prussian province of East Prussia; the remaining southern part of the province is today part of the Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship in Poland. With the defeat of Nazi Germany in World War II, the territory was annexed to the Russian SFSR by the Soviet Union. Following the post-war migrat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)