|
Prussian Guelders
Prussian Guelders or Prussian G(u)elderland ( nl, Pruisisch Gelre; german: Preußisch Geldern) was the part of the Duchy of Guelders ruled by the Kingdom of Prussia from 1713. Its capital was Geldern. The Upper Quarter of the Duchy of Guelders was part of the Spanish-ruled Southern Netherlands by the end of the 17th century. In the 1713 Treaty of Utrecht during the War of the Spanish Succession, the Upper Quarter was partitioned between the Dutch Republic, Austria, and Prussia. Besides Geldern, other towns in the Prussian duchy were Horst, Venray, and Viersen, the latter of which was an exclave surrounded by the Duchy of Jülich. Prussian Guelders was part of the Lower Rhenish-Westphalian Circle within the Holy Roman Empire. Prussian Guelders was occupied by Revolutionary France in 1794 and later annexed into the First French Empire as part of the Roer Department. After the Napoleonic Wars, the western regions became part of the Kingdom of the Netherlands, while the eastern reg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duchy Of Guelders
The Duchy of Guelders ( nl, Gelre, french: Gueldre, german: Geldern) is a historical duchy, previously county, of the Holy Roman Empire, located in the Low Countries. Geography The duchy was named after the town of Geldern (''Gelder'') in present-day Germany. Though the present province of Gelderland (English also ''Guelders'') in the Netherlands occupies most of the area, the former duchy also comprised parts of the present Dutch province of Limburg as well as those territories in the present-day German state of North Rhine-Westphalia that were acquired by Prussia in 1713. Four parts of the duchy had their own centres, as they were separated by rivers: * the quarter of Roermond, also called Upper Quarter or Upper Guelders – upstream on both sides of the Maas, comprising the town of Geldern as well as Erkelenz, Goch, Nieuwstadt, Venlo and Straelen; spatially separated from the Lower Quarters (Gelderland): * the quarter of the county Zutphen, also called the Achterhoek – ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lower Rhenish-Westphalian Circle
Lower may refer to: *Lower (surname) *Lower Township, New Jersey *Lower Receiver (firearms) *Lower Wick Lower Wick is a small hamlet located in the county of Gloucestershire, England. It is situated about five miles south west of Dursley, eighteen miles southwest of Gloucester and fifteen miles northeast of Bristol. Lower Wick is within the civil ... Gloucestershire, England See also * Nizhny {{Disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1794 Disestablishments
Events January–March * January 1 – The Stibo Group is founded by Niels Lund as a printing company in Aarhus (Denmark). * January 13 – The U.S. Congress enacts a law providing for, effective May 1, 1795, a United States flag of 15 stars and 15 stripes, in recognition of the recent admission of Vermont and Kentucky as the 14th and 15th states. A subsequent act restores the number of stripes to 13, but provides for additional stars upon the admission of each additional state. * January 21 – King George III of Great Britain delivers the speech opening Parliament and recommends a continuation of Britain's war with France. * February 4 – French Revolution: The National Convention of the French First Republic abolishes slavery. * February 8 – Wreck of the Ten Sail on Grand Cayman. * February 11 – The first session of the United States Senate is open to the public. * March 4 – The Eleventh Amendment to the United States Constit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1713 Establishments In Prussia
Events January–March * January 17 – Tuscarora War: Colonel James Moore leads the Carolina militia out of Albemarle County, North Carolina, in a second offensive against the Tuscarora. Heavy snows force the troops to take refuge in Fort Reading, on the Pamlico River. * February 1 – Skirmish at Bender, Moldova: Charles XII of Sweden is defeated by the Ottoman Empire. * February 4 – Tuscarora War: The Carolina militia under Colonel James Moore leaves Fort Reading, to continue the campaign against the Tuscarora. * February 25 – Frederick William I of Prussia begins his reign. * March 1 – Tuscarora War: Colonel James Moore's Carolina militia lays siege to the Tuscaroran stronghold of Fort Neoheroka, located a few miles up Contentnea Creek from Fort Hancock. * March 20 – Tuscarora War: Colonel James Moore's Carolina militia launches a major offensive against Fort Neoheroka. * March 23 – Tuscarora War: Fort Neoheroka falls to the C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germanization
Germanisation, or Germanization, is the spread of the German language, people and culture. It was a central idea of German conservative thought in the 19th and the 20th centuries, when conservatism and ethnic nationalism went hand in hand. In linguistics, Germanisation of non-German languages also occurs when they adopt many German words. Under the policies of states such as the Teutonic Order, Austria, the German Empire and Nazi Germany, non-Germans were often prohibited from using their native language, and had their traditions and culture suppressed in the goal of gradually eliminating foreign cultures, a form of ethnic cleansing. In addition, colonists and settlers were used to upset the population balance. During the Nazi era, Germanisation turned into a policy of genocide against some non-German ethnic groups. Forms Historically there are different forms and degrees of the expansion of the German language and of elements of German culture. There are examples of complete a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Netherlands
) , anthem = ( en, "William of Nassau") , image_map = , map_caption = , subdivision_type = Sovereign state , subdivision_name = Kingdom of the Netherlands , established_title = Before independence , established_date = Spanish Netherlands , established_title2 = Act of Abjuration , established_date2 = 26 July 1581 , established_title3 = Peace of Münster , established_date3 = 30 January 1648 , established_title4 = Kingdom established , established_date4 = 16 March 1815 , established_title5 = Liberation Day (Netherlands), Liberation Day , established_date5 = 5 May 1945 , established_title6 = Charter for the Kingdom of the Netherlands, Kingdom Charter , established_date6 = 15 December 1954 , established_title7 = Dissolution of the Netherlands Antilles, Caribbean reorganisation , established_date7 = 10 October 2010 , official_languages = Dutch language, Dutch , languages_type = Regional languages , languages_sub = yes , languages = , languages2_type = Reco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Province Of Jülich-Cleves-Berg
The Province of Jülich-Cleves-Berg (german: Provinz Jülich-Kleve-Berg) was a province of Prussia from 1815 to 1822. Jülich-Cleves-Berg was established in 1815 from part restored and part newly annexed lands by the Kingdom of Prussia from France's Grand Duchy of Berg. Jülich-Cleves-Berg was dissolved in 1822 when it was merged with the Grand Duchy of the Lower Rhine to form Rhine Province. Cologne was the provincial capital. History After the Napoleonic Wars, the Congress of Vienna restored the Duchy of Cleves to the Kingdom of Prussia, which combined them with the other Rhenish lands restored from France (Prussian Guelders and the Principality of Moers) with the Rhenish lands gained at Vienna — the old Duchy of Jülich and County of Berg along with parts of the Electorate of Cologne and the Free and Hanseatic City of Cologne and some other smaller territories. On 30 April 1815, Prussian authorities reorganised the states of the kingdom into 10 provinces with the ' ( en, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Kingdom Of The Netherlands
The United Kingdom of the Netherlands ( nl, Verenigd Koninkrijk der Nederlanden; french: Royaume uni des Pays-Bas) is the unofficial name given to the Kingdom of the Netherlands as it existed between 1815 and 1839. The United Netherlands was created in the aftermath of the Napoleonic Wars through the fusion of territories that had belonged to the former Dutch Republic, Austrian Netherlands, and Prince-Bishopric of Liège in order to form a buffer state between the major European powers. The polity was a constitutional monarchy, ruled by William I of the House of Orange-Nassau. The polity collapsed in 1830 with the outbreak of the Belgian Revolution. With the ''de facto'' secession of Belgium, the Netherlands was left as a rump state and refused to recognise Belgian independence until 1839 when the Treaty of London was signed, fixing the border between the two states and guaranteeing Belgian independence and neutrality as the Kingdom of Belgium. Background Before the French ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Napoleonic Wars
The Napoleonic Wars (1803–1815) were a series of major global conflicts pitting the French Empire and its allies, led by Napoleon I, against a fluctuating array of European states formed into various coalitions. It produced a period of French domination over most of continental Europe. The wars stemmed from the unresolved disputes associated with the French Revolution and the French Revolutionary Wars consisting of the War of the First Coalition (1792–1797) and the War of the Second Coalition (1798–1802). The Napoleonic Wars are often described as five conflicts, each termed after the coalition that fought Napoleon: the Third Coalition (1803–1806), the Fourth (1806–1807), the Fifth (1809), the Sixth (1813–1814), and the Seventh (1815) plus the Peninsular War (1807–1814) and the French invasion of Russia (1812). Napoleon, upon ascending to First Consul of France in 1799, had inherited a republic in chaos; he subsequently created a state with stable financ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
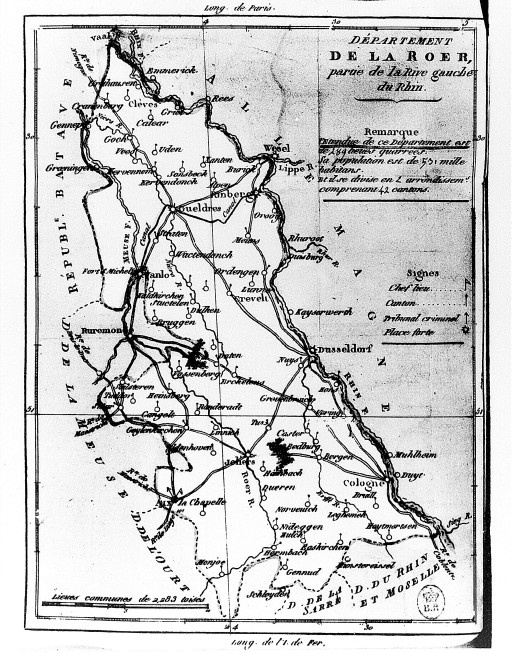
Roer (department)
Roer was a department of the French First Republic and later First French Empire in present-day Germany and the Netherlands. It was named after the river Roer (Rur), which flows through the department. It was formed in 1797, when the left bank of the Rhine was occupied by the French. The department was formed from the duchies of Jülich and Cleves, the part of the Archbishopric of Cologne left of the Rhine, the Free City of Aachen, the Prussian part of the duchy of Guelders and some smaller territories. In 1805 the city of Wesel was added to the department. The capital was Aix-la-Chapelle (''Aachen''). The department was subdivided in the following arrondissements and cantons (situation in 1812):Almanach Impérial an bissextil MDCCCXII p. 458-9, accessed in [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First French Empire
The First French Empire, officially the French Republic, then the French Empire (; Latin: ) after 1809, also known as Napoleonic France, was the empire ruled by Napoleon Bonaparte, who established French hegemony over much of continental Europe at the beginning of the 19th century. It lasted from 18 May 1804 to 11 April 1814 and again briefly from 20 March 1815 to 7 July 1815. Although France had already established a colonial empire overseas since the early 17th century, the French state had remained a kingdom under the Bourbons and a republic after the French Revolution. Historians refer to Napoleon's regime as the ''First Empire'' to distinguish it from the restorationist ''Second Empire'' (1852–1870) ruled by his nephew Napoleon III. The First French Empire is considered by some to be a " Republican empire." On 18 May 1804, Napoleon was granted the title Emperor of the French (', ) by the French and was crowned on 2 December 1804, signifying the end of the French ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Revolutionary France
The French Revolution ( ) was a period of radical political and societal change in France that began with the Estates General of 1789 and ended with the formation of the French Consulate in November 1799. Many of its ideas are considered fundamental principles of liberal democracy, while phrases like ''liberté, égalité, fraternité'' reappeared in other revolts, such as the 1917 Russian Revolution, and inspired campaigns for the abolition of slavery and universal suffrage. The values and institutions it created dominate French politics to this day. Its causes are generally agreed to be a combination of social, political and economic factors, which the ''Ancien Régime'' proved unable to manage. In May 1789, widespread social distress led to the convocation of the Estates General, which was converted into a National Assembly in June. Continuing unrest culminated in the Storming of the Bastille on 14 July, which led to a series of radical measures by the Assembly, inc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)