|
Proturan
The Protura, or proturans, and sometimes nicknamed coneheads, are very small (0.6-1.5mm long), soil-dwelling animals, so inconspicuous they were not noticed until the 20th century. The Protura constitute an order of hexapods that were previously regarded as insects, and sometimes treated as a class in their own right. Some evidence indicates the Protura are basal to all other hexapods, although not all researchers consider them Hexapoda, rendering the monophyly of Hexapoda unsettled. Uniquely among hexapods, proturans show anamorphic development, whereby body segments are added during moults. There are close to 800 species, described in seven families. Nearly 300 species are contained in a single genus, ''Eosentomon''. Morphology Proturans have no eyes, wings, or antennae, and, lacking pigmentation, are usually white or pale brown. The sensory function of the antennae is fulfilled by the first of three pairs of five-segmented legs, which are held up, pointing forward and have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Entognatha
The Entognatha are a class (biology), class of wingless and Ametabolism, ametabolous arthropods, which, together with the insects, makes up the subphylum Hexapoda. Their Arthropod mouthparts, mouthparts are entognathous, meaning that they are retracted within the head, unlike the insects. Entognatha are apterous, meaning that they lack insect wing, wings. The class contains three Order (biology), orders: Collembola (springtails, 9000 species), Diplura (“two-tail”, 1000 species) and Protura (“first-tail”, 800 species). These three groups were historically united with the now-obsolete order Thysanura to form the class Apterygota, but it has since been recognized that the hexapodous condition of these animals has evolved independently from that of insects, and independently ''within'' each order. The orders may not be closely related, and Entognatha is now considered to be a Polyphyly, polyphyletic group. Morphology These minute arthropods are apterous, unlike some orders o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acerentomon
''Acerentomon'' is a genus of proturans in the family Acerentomidae The Acerentomidae are a family of hexapods in the order Protura. Acerentomids are not tracheated, and instead use cuticular gas exchange. Genera These genera are members of the family Acerentomidae. * '' Acerella'' Berlese, 1909 * ''Acerentomon .... Species * '' Acerentomon aceris'' Rusek, 1965 * '' Acerentomon affine'' Bagnall, 1912 * '' Acerentomon album'' Loksa, 1966 * '' Acerentomon bagnalli'' Womersley, 1927 * '' Acerentomon balcanicum'' Ionesco, 1933 * '' Acerentomon baldense'' Torti, 1986 * '' Acerentomon brevisetosum'' Condé, 1945 * '' Acerentomon carpaticum'' Nosek, 1961 * '' Acerentomon condei'' Nosek & Dallai, 1982 * '' Acerentomon dispar'' Stach, 1954 * '' Acerentomon doderoi'' Silvestri, 1907 * '' Acerentomon dominiaki'' Szeptycki, 1977 * '' Acerentomon fageticola'' Rusek, 1966 * '' Acerentomon franzi'' Nosek, 1965 * '' Acerentomon gallicum'' Ionesco, 1933 * '' Acerentomon giganteum'' Condé, 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Body Segment
Segmentation in biology is the division of some animal and plant body plans into a series of repetitive segments. This article focuses on the segmentation of animal body plans, specifically using the examples of the taxa Arthropoda, Chordata, and Annelida. These three groups form segments by using a "growth zone" to direct and define the segments. While all three have a generally segmented body plan and use a growth zone, they use different mechanisms for generating this patterning. Even within these groups, different organisms have different mechanisms for segmenting the body. Segmentation of the body plan is important for allowing free movement and development of certain body parts. It also allows for regeneration in specific individuals. Definition Segmentation is a difficult process to satisfactorily define. Many taxa (for example the molluscs) have some form of serial repetition in their units but are not conventionally thought of as segmented. Segmented animals are thos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
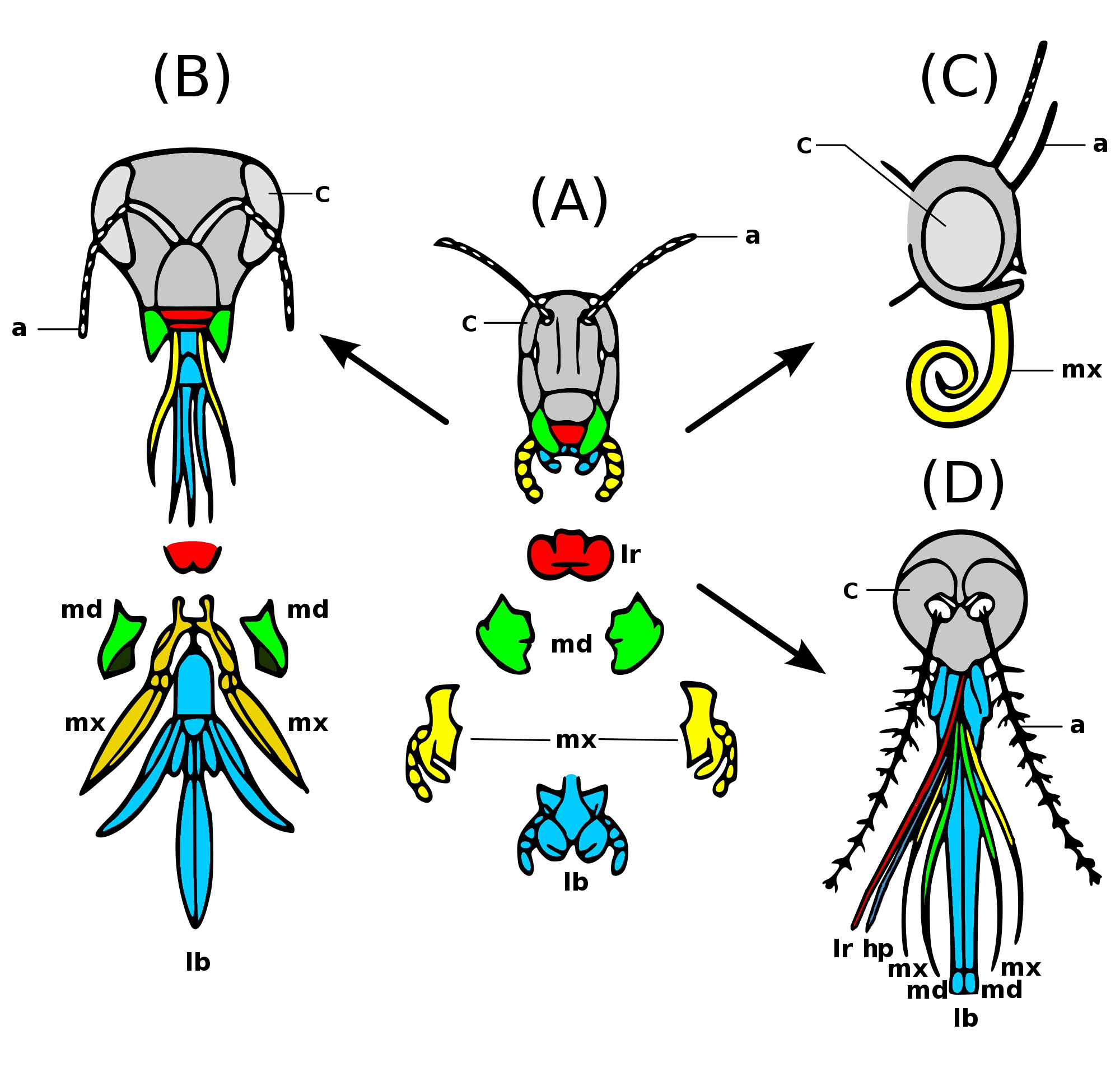
Insect Mouthparts
Insects have mouthparts that may vary greatly across insect species, as they are adapted to particular modes of feeding. The earliest insects had chewing mouthparts. Most specialisation of mouthparts are for piercing and sucking, and this mode of feeding has evolved a number of times idependently. For example, mosquitoes and aphids (which are true bugs) both pierce and suck, however female mosquitoes feed on animal blood whereas aphids feed on plant fluids. Evolution Like most external features of arthropods, the mouthparts of Hexapoda are highly derived. Insect mouthparts show a multitude of different functional mechanisms across the wide diversity of insect species. It is common for significant homology to be conserved, with matching structures forming from matching primordia, and having the same evolutionary origin. However, even if structures are almost physically and functionally identical, they may not be homologous; their analogous functions and appearance might be the pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telson
The telson () is the posterior-most division of the body of an arthropod. Depending on the definition, the telson is either considered to be the final segment of the arthropod body, or an additional division that is not a true segment on account of not arising in the embryo from teloblast areas as other segments. It never carries any appendages, but a forked "tail" called the caudal furca may be present. The shape and composition of the telson differs between arthropod groups. Crustaceans In lobsters, shrimp and other decapods, the telson, along with the uropods, forms the tail fan. This is used as a paddle in the caridoid escape reaction ("lobstering"), whereby an alarmed animal rapidly flexes its tail, causing it to dart backwards. Krill can reach speeds of over 60 cm per second by this means. The trigger time to optical stimulus is, in spite of the low temperatures, only 55 milliseconds. In the Isopoda and Tanaidacea (superorder Peracarida), the last abdominal b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commonwealth Scientific And Industrial Research Organisation
The Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation (CSIRO) is an Australian Government agency responsible for scientific research. CSIRO works with leading organisations around the world. From its headquarters in Canberra, CSIRO maintains more than 50 sites across Australia and in France, Chile and the United States, employing about 5,500 people. Federally funded scientific research began in Australia years ago. The Advisory Council of Science and Industry was established in 1916 but was hampered by insufficient available finance. In 1926 the research effort was reinvigorated by establishment of the Council for Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), which strengthened national science leadership and increased research funding. CSIR grew rapidly and achieved significant early successes. In 1949, further legislated changes included renaming the organisation as CSIRO. Notable developments by CSIRO have included the invention of atomic absorption spectroscopy, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudoculus
In biology, ''pseudoculus'' (plural ''pseudoculi'', ) is the name applied to various eye-like structures which are nevertheless not eyes. Amongst the organisms possessing pseudoculi are Protura, in which their function is not well-known, and Pauropoda Pauropods are small, pale, millipede-like arthropods. Around 830 species in twelve families are found worldwide, living in soil and leaf mold. They look rather like centipedes, or millipedes, and may be a sister group of the latter. However, this ..., whose organs are vibration-sensitive. References Arthropod anatomy {{animal-anatomy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Florida
The University of Florida (Florida or UF) is a public land-grant research university in Gainesville, Florida. It is a senior member of the State University System of Florida, traces its origins to 1853, and has operated continuously on its Gainesville campus since September 1906. After the Florida state legislature's creation of performance standards in 2013, the Florida Board of Governors designated the University of Florida as a "preeminent university". For 2022, '' U.S. News & World Report'' ranked Florida as the fifth (tied) best public university and 28th (tied) best university in the United States. The University of Florida is the only member of the Association of American Universities in Florida and is classified among "R1: Doctoral Universities – Very high research activity". The university is accredited by the Southern Association of Colleges and Schools (SACS). It is the third largest Florida university by student population,Nathan Crabbe, UF is no longer la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthropod Leg
The arthropod leg is a form of jointed appendage of arthropods, usually used for walking. Many of the terms used for arthropod leg segments (called podomeres) are of Latin origin, and may be confused with terms for bones: ''coxa'' (meaning hip, plural ''coxae''), ''trochanter'', ''femur'' (plural ''femora''), ''tibia'' (plural ''tibiae''), ''tarsus'' (plural ''tarsi''), ''ischium'' (plural ''ischia''), ''metatarsus'', ''carpus'', ''dactylus'' (meaning finger), ''patella'' (plural ''patellae''). Homologies of leg segments between groups are difficult to prove and are the source of much argument. Some authors posit up to eleven segments per leg for the most recent common ancestor of extant arthropods but modern arthropods have eight or fewer. It has been argued that the ancestral leg need not have been so complex, and that other events, such as successive loss of function of a ''Hox''-gene, could result in parallel gains of leg segments. In arthropods, each of the leg segments ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pigment
A pigment is a colored material that is completely or nearly insoluble in water. In contrast, dyes are typically soluble, at least at some stage in their use. Generally dyes are often organic compounds whereas pigments are often inorganic compounds. Pigments of prehistoric and historic value include ochre, charcoal, and lapis lazuli. Economic impact In 2006, around 7.4 million tons of inorganic, organic, and special pigments were marketed worldwide. Estimated at around US$14.86 billion in 2018 and will rise at over 4.9% CAGR from 2019 to 2026. The global demand for pigments was roughly US$20.5 billion in 2009. According to an April 2018 report by ''Bloomberg Businessweek'', the estimated value of the pigment industry globally is $30 billion. The value of titanium dioxide – used to enhance the white brightness of many products – was placed at $13.2 billion per year, while the color Ferrari red is valued at $300 million each year. Physical principles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eosentomon
''Eosentomon'' is a genus of proturans in the family Eosentomidae The Eosentomidae are a family of hexapods in the order Protura The Protura, or proturans, and sometimes nicknamed coneheads, are very small (0.6-1.5mm long), soil-dwelling animals, so inconspicuous they were not noticed until the 20th century. .... Species * '' Eosentomon actitum'' Zhang, 1983 * '' Eosentomon adakense'' Bernard, 1985 * '' Eosentomon adami'' Condé, 1961 * '' Eosentomon affine'' Tuxen, 1967 * '' Eosentomon afrorostratum'' Tuxen, 1977 * '' Eosentomon agaeophthalmum'' Yin & Zhang, 1982 * '' Eosentomon ailaoense'' Imadaté, Yin & Xie, 1995 * '' Eosentomon alaskaense'' Nosek, 1977 * '' Eosentomon alcirae'' Najt & Vidal Sarmiento, 1972 * '' Eosentomon angolae'' Tuxen, 1977 * '' Eosentomon ankarafantsikaense'' Nosek, 1978 * '' Eosentomon antrimense'' Bernard, 1975 * '' Eosentomon aquilinum'' Nosek, 1980 * '' Eosentomon armatum'' Stach, 1926 * '' Eosentomon asahi'' Imadaté, 1961 * '' Eosentomon asak ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family (taxonomy), family. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus. :E.g. ''Panthera leo'' (lion) and ''Panthera onca'' (jaguar) are two species within the genus ''Panthera''. ''Panthera'' is a genus within the family Felidae. The composition of a genus is determined by taxonomy (biology), taxonomists. The standards for genus classification are not strictly codified, so different authorities often produce different classifications for genera. There are some general practices used, however, including the idea that a newly defined genus should fulfill these three criteria to be descriptively useful: # monophyly – all descendants ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_(10353381334).jpg)


_p174_GAINESVILLE%2C_EAST_FLORIDA_SEMINARY.jpg)


