|
Protragocerus
''Protragocerus'' is an extinct genus of antelope from the late Serravallian age (geology), Age (around 13 to 11 million years ago) of the Miocene epoch (geology), Epoch. Fossils of the genus have been found in France, India, and Saudi Arabia. It is classified under the tribe (biology), tribe Boselaphini, subfamily Bovinae of the family (biology), family Bovidae. The genus was first established by the French paleontologist Charles Depéret in 1887. One former species, ''Protragocerus labidotus'' of Kenya, has been reclassified in its own genus, ''Kipsigicerus''. See also *''Eotragus'' *''Tetracerus'' *''Boselaphus'' References Miocene even-toed ungulates Bovines Prehistoric bovids Fossil taxa described in 1987 Prehistoric even-toed ungulate genera Miocene mammals of Europe Miocene mammals of Asia {{paleo-eventoedungulate-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kipsigicerus
''Kipsigicerus'' is an extinct genus of East African antelope from the Middle Miocene. Its closest living relative is the Four-horned Antelope, four-horned-antelope. It was discovered in Fort Ternan, Kenya and was originally described as a species of ''Protragocerus''. The horn cores were distinct, being highly compressed with eaxh horn growing forward to one another. Because of the unique horn morphology, the genus ''Kipsigicerus'' was erected for this species. Sources * Classification of Mammals by Malcolm C. McKenna and Susan K. Bell References Prehistoric bovids Miocene even-toed ungulates Prehistoric even-toed ungulate genera Miocene mammals of Africa {{paleo-eventoedungulate-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
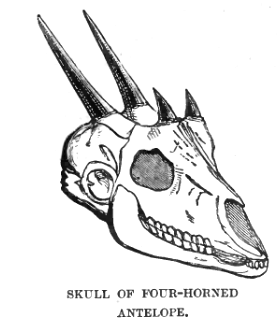
Tetracerus
The four-horned antelope (''Tetracerus quadricornis''), or ''chousingha'', is a small antelope found in India and Nepal. Its four horns distinguish it from most other bovids, which have two horns (with a few exceptions, such as the Jacob sheep). The sole member of the genus ''Tetracerus'', the species was first described by French zoologist Henri Marie Ducrotay de Blainville in 1816. Three subspecies are recognised. The four-horned antelope stands nearly at the shoulder and weighs nearly . Slender with thin legs and a short tail, the four-horned antelope has a yellowish brown to reddish coat. One pair of horns is located between the ears, and the other on the forehead. The posterior horns are always longer than the anterior horns, which might be mere fur-covered studs. While the posterior horns measure , the anterior ones are long. The four-horned antelope is diurnal (active mainly during the day). Though solitary by nature, four-horned antelopes may form loose groups of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Depéret
Charles Jean Julien Depéret (25 June 1854 – 18 May 1929) was a French geologist and paleontologist. He was a member of the French Academy of Sciences, the Société géologique de FranceObituary at ''Annales des Mines'' and dean of the Science faculty of .Obituary at ''Les Études rhodaniennes'', Year 1929, Vol. 5, Issue 5-2, pp. 342-343 [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boselaphini
Boselaphini is a tribe of bovines. It contains only two extant genera, each with a single extant species. Description The Boselaphini or four-horned antelope tribe are the last survivors of a form very similar to that of the ancestors of the broader subfamily. The oldest fossil members of the tribe, such as ''Eotragus'', date to the Miocene about 18 to 20 million years ago. Such fossils possessed horns very similar to those of males belonging to the two living species, although in some cases, they were also present in females. Both extant species have relatively primitive anatomical and behavioural characteristics and the females have no horns. They are native to the rapidly diminishing forests of India, and tend to avoid open plains. The nilgai has been introduced into southern Texas where a population of a little under 15,000 animals provides some long-term insurance for its survival. Genera Extant species Phylogeny The following are the genera classified under the tribe. G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Miocene
The Late Miocene (also known as Upper Miocene) is a sub-epoch of the Miocene epoch (geology), Epoch made up of two faunal stage, stages. The Tortonian and Messinian stages comprise the Late Miocene sub-epoch, which lasted from 11.63 Ma (million years ago) to 5.333 Ma. The evolution of life The gibbons (family Hylobatidae) and orangutans (genus ''Pongo'') are the first groups to split from the line leading to the hominins, including humans, then gorillas (genus ''Gorilla''), and finally, chimpanzees and bonobos (genus ''Pan (genus), Pan''). The splitting date between hominin and chimpanzee lineages is placed by some between 4 to 8 million years ago, that is, during the Late Miocene. References External links GeoWhen Database - Late Miocene Miocene, .03 Miocene geochronology, 03 Messinian, * Tortonian, * {{geochronology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prehistoric Even-toed Ungulate Genera
Prehistory, also known as pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the use of the first stone tools by hominins 3.3 million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The use of symbols, marks, and images appears very early among humans, but the earliest known writing systems appeared 5000 years ago. It took thousands of years for writing systems to be widely adopted, with writing spreading to almost all cultures by the 19th century. The end of prehistory therefore came at very different times in different places, and the term is less often used in discussing societies where prehistory ended relatively recently. In the early Bronze Age, Sumer in Mesopotamia, the Indus Valley Civilisation, and ancient Egypt were the first civilizations to develop their own scripts and to keep historical records, with their neighbors following. Most other civilizations reached the end of prehistory during the following Iron Age. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fossil Taxa Described In 1987
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved in amber, hair, petrified wood and DNA remnants. The totality of fossils is known as the ''fossil record''. Paleontology is the study of fossils: their age, method of formation, and evolutionary significance. Specimens are usually considered to be fossils if they are over 10,000 years old. The oldest fossils are around 3.48 billion years old to 4.1 billion years old. Early edition, published online before print. The observation in the 19th century that certain fossils were associated with certain rock strata led to the recognition of a geological timescale and the relative ages of different fossils. The development of radiometric dating techniques in the early 20th century allowed scientists to quantitatively measure the abso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prehistoric Bovids
Prehistory, also known as pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the use of the first stone tools by hominins 3.3 million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The use of symbols, marks, and images appears very early among humans, but the earliest known writing systems appeared 5000 years ago. It took thousands of years for writing systems to be widely adopted, with writing spreading to almost all cultures by the 19th century. The end of prehistory therefore came at very different times in different places, and the term is less often used in discussing societies where prehistory ended relatively recently. In the early Bronze Age, Sumer in Mesopotamia, the Indus Valley Civilisation, and ancient Egypt were the first civilizations to develop their own scripts and to keep historical records, with their neighbors following. Most other civilizations reached the end of prehistory during the following Iron Age. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bovines
Bovines ( subfamily Bovinae) comprise a diverse group of 10 genera of medium to large-sized ungulates, including cattle, bison, African buffalo, water buffalos, and the four-horned and spiral-horned antelopes. The evolutionary relationship between the members of the group is still debated, and their classification into loose tribes rather than formal subgroups reflects this uncertainty. General characteristics include cloven hooves and usually at least one of the sexes of a species having true horns. The largest extant bovine is the gaur. In many countries, bovid milk and meat is used as food by humans. Cattle are kept as livestock almost everywhere except in parts of India and Nepal, where they are considered sacred by most Hindus. Bovids are used as draft animals and as riding animals. Small breeds of domestic bovid, such as the Miniature Zebu, are kept as pets. Bovid leather is durable and flexible and is used to produce a wide range of goods including clothing and bags. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miocene Even-toed Ungulates
The Miocene ( ) is the first geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and means "less recent" because it has 18% fewer modern marine invertebrates than the Pliocene has. The Miocene is preceded by the Oligocene and is followed by the Pliocene. As Earth went from the Oligocene through the Miocene and into the Pliocene, the climate slowly cooled towards a series of ice ages. The Miocene boundaries are not marked by a single distinct global event but consist rather of regionally defined boundaries between the warmer Oligocene and the cooler Pliocene Epoch. During the Early Miocene, the Arabian Peninsula collided with Eurasia, severing the connection between the Mediterranean and Indian Ocean, and allowing a faunal interchange to occur between Eurasia and Africa, including the dispersal of proboscideans into Eurasia. During the late ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boselaphus
''Boselaphus'' is a genus of bovid. The nilgai is the sole living representative, although one other species is known from the fossil record. The nilgai along with the four-horned antelope are the only living members of the tribe Boselaphini Boselaphini is a tribe of bovines. It contains only two extant genera, each with a single extant species. Description The Boselaphini or four-horned antelope tribe are the last survivors of a form very similar to that of the ancestors of the bro .... References {{Taxonbar, from=Q10740872 Mammal genera Mammal genera with one living species Taxa named by Henri Marie Ducrotay de Blainville Bovines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eotragus
''Eotragus'' is an extinct genus of early bovid. Species belonging to the genus inhabited Europe, Africa, and Asia during the Miocene some 20-18 million years ago. It is related to the modern nilgai and four-horned antelope. It was small and probably lived in woodland A woodland () is, in the broad sense, land covered with trees, or in a narrow sense, synonymous with wood (or in the U.S., the ''plurale tantum'' woods), a low-density forest forming open habitats with plenty of sunlight and limited shade (se ... environments. External linksBovidae: Bovinae: Boselaphini Prehistoric bovids Miocene even-toed un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_male.jpg)




