|
Prototrichia
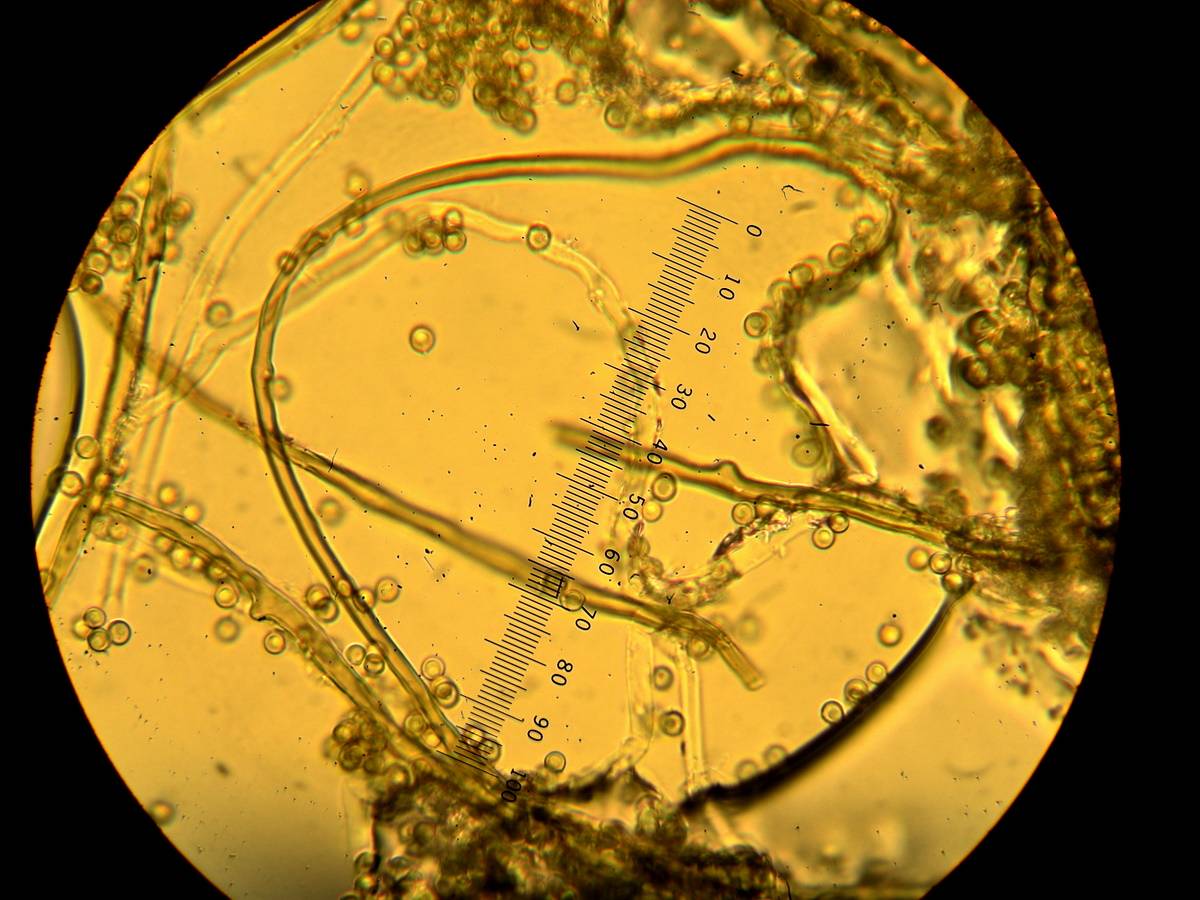
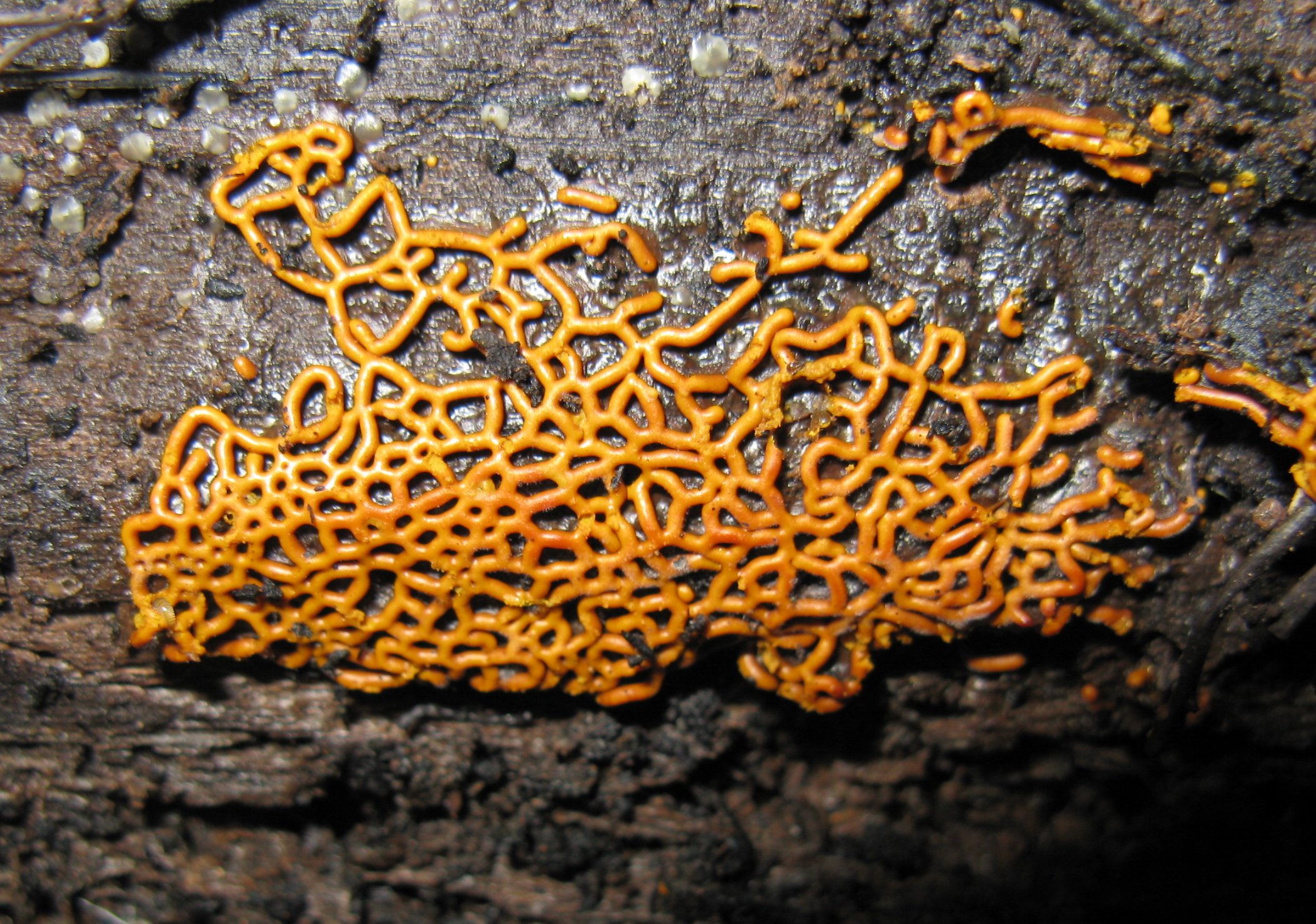
''Prototrichia metallica'' is a slime mould species from the order Trichiida and the only species from the genus ''Prototrichia''. It is mainly distributed on mountains. Characteristics ''Prototrichia metallica'' is a very variable species. The plasmodium is white. The fruit bodies are grouped densely. They are orange brown to dull brown, occasionally pink, short stemmed or are lying on a heavily regenerated edge, rarely plasmodiokarp sporokarps with a diameter from 0.5 to 2.2 mm. The membranous peridium is transparently thin and shinily iridescent-coloured. Its surface is composed of a coarse mesh arrangement of wrinkled lines, along which it later divides into pieces. The capillitium is often irregular, usually due to the presence of several yellow-brown, translucent spirally banded strands, which divide towards the outer end. The branches are often intertwined spirals, which sometimes form a network. Many of the outer ends are fused with the upper part of the peridiu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trichiida
Trichiales (synonymous with Trichiida) is an order of slime moulds in the phylum Amoebozoa. Trichiales is one of five orders in the group Myxomycetes (also called Myxogastria), or the true plasmodial slime molds. It is also currently categorized under the superorder Lucisporidia with its sister group, Liceales. The order was first described by Thomas MacBride in 1922, and has retained the same name and status as a defined order in present phylogeny. In the plasmodium form, members of Trichiales lack a columella but have a well-developed capillitium for spore dispersal. The shape and details of the capillitium are used to define families within the order. Spores are brightly coloured, ranging from clear, white and yellow to pink and red-brown tones. The order currently has 4 families, 14 genera and 174 species. Recent molecular research has shown that while Trichiales probably represents a true taxonomic group, its sister group Liceales is likely paraphyletic, and it has been sugge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trichiidae
Trichiales ( synonymous with Trichiida) is an order of slime moulds in the phylum Amoebozoa. Trichiales is one of five orders in the group Myxomycetes (also called Myxogastria), or the true plasmodial slime molds. It is also currently categorized under the superorder Lucisporidia with its sister group, Liceales. The order was first described by Thomas MacBride in 1922, and has retained the same name and status as a defined order in present phylogeny. In the plasmodium form, members of Trichiales lack a columella but have a well-developed capillitium for spore dispersal. The shape and details of the capillitium are used to define families within the order. Spores are brightly coloured, ranging from clear, white and yellow to pink and red-brown tones. The order currently has 4 families, 14 genera and 174 species. Recent molecular research has shown that while Trichiales probably represents a true taxonomic group, its sister group Liceales is likely paraphyletic, and it has been sug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dianemidae
Trichiales (synonymous with Trichiida) is an order of slime moulds in the phylum Amoebozoa. Trichiales is one of five orders in the group Myxomycetes (also called Myxogastria), or the true plasmodial slime molds. It is also currently categorized under the superorder Lucisporidia with its sister group, Liceales. The order was first described by Thomas MacBride in 1922, and has retained the same name and status as a defined order in present phylogeny. In the plasmodium form, members of Trichiales lack a columella but have a well-developed capillitium for spore dispersal. The shape and details of the capillitium are used to define families within the order. Spores are brightly coloured, ranging from clear, white and yellow to pink and red-brown tones. The order currently has 4 families, 14 genera and 174 species. Recent molecular research has shown that while Trichiales probably represents a true taxonomic group, its sister group Liceales is likely paraphyletic, and it has been sugge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amoebozoa
Amoebozoa is a major taxonomic group containing about 2,400 described species of amoeboid protists, often possessing blunt, fingerlike, lobose pseudopods and tubular mitochondrial cristae. In traditional and currently no longer supported classification schemes, Amoebozoa is ranked as a phylum within either the kingdom Protista or the kingdom Protozoa. In the classification favored by the International Society of Protistologists, it is retained as an unranked " supergroup" within Eukaryota. Molecular genetic analysis supports Amoebozoa as a monophyletic clade. Modern studies of eukaryotic phylogenetic trees identify it as the sister group to Opisthokonta, another major clade which contains both fungi and animals as well as several other clades comprising some 300 species of unicellular eukaryotes. Amoebozoa and Opisthokonta are sometimes grouped together in a high-level taxon, variously named Unikonta, Amorphea or Opimoda. Amoebozoa includes many of the best-known amoeboid orga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peridium
The peridium is the protective layer that encloses a mass of spores in fungi. This outer covering is a distinctive feature of gasteroid fungi. Description Depending on the species, the peridium may vary from being paper-thin to thick and rubbery or even hard. Typically, peridia consist of one to three layers. If there is only a single layer, it is called a peridium. If two layers are present, the outer layer is called the exoperidium and the inner layer the endoperidium. If three layers are present, they are the exoperidium, the mesoperidium and the endoperidium. In the simplest subterranean forms, the peridium remains closed until the spores are mature, and even then shows no special arrangement for dehiscence or opening, but has to decay before the spores are liberated. Puffballs For most fungi, the peridium is ornamented with scales or spines. In species that become raised above ground during their development, generally known as the "puffballs", the peridium is usually di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Meylan
Charles Meylan (23 June 1868, Le Brassus – 3 June 1941, Sainte-Croix) was a Swiss botanist. From 1888 to 1926 he was a schoolteacher in the community of La Chaux, located near Sainte-Croix (Canton of Vaud). In 1922 he obtained an honorary doctorate from the University of Lausanne.Geschichte der Bryologie in der Schweiz Moosflora der Schweiz (includes bibliography) He made contributions in the fields of and ( mosses and |
Józef Rostafiński
Józef Tomasz Rostafiński (14 August 1850 – 5 May 1928) was a Polish botanist. Life He was born in Warsaw, and studied in (1866–1869), Jena, Halle, and Strasbourg, where he achieved his PhD before being appointed lecturer at the university of Kraków. Retrieved : 2011-11-06 One of his books, the ''Przewodnik do oznaczania roślin w Polsce dziko rosnących'' (''Guide to Wild Plants in Poland''), had 21 editions between 1886 and 1979. In one of his notable works, Józef Rostafiński did extensive research about the Polesie region in eastern Poland, and claimed it lacked certain type of trees due to the soil and ground. Streets bearing his name can be found in the Polish cities of Kraków, Warsaw, and |
Miles Joseph Berkeley
Miles Joseph Berkeley (1 April 1803 – 30 July 1889) was an English cryptogamist and clergyman, and one of the founders of the science of plant pathology. Life Berkeley was born at Biggin Hall, Benefield, Northamptonshire, and educated at Rugby School and Christ's College, Cambridge. Taking holy orders, he became incumbent of Apethorpe in 1837, and vicar of Sibbertoft, near Market Harborough, in 1868. He acquired an enthusiastic love of cryptogamic botany (lichens) in his early years, and soon was recognized as the leading British authority on fungi and plant pathology. Christ's College made him an honorary fellow in 1883. He was well known as a systematist in mycology with some 6000 species of fungi being credited to him, but his ''Introduction to Cryptogamic Botany'', published in 1857, and his papers on Vegetable Pathology in the ''Gardener's Chronicle'' in 1854 and onwards, show that he had a broad grasp of the whole domain of physiology and morphology as understood in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tasmania
) , nickname = , image_map = Tasmania in Australia.svg , map_caption = Location of Tasmania in AustraliaCoordinates: , subdivision_type = Country , subdivision_name = Australia , established_title = Before federation , established_date = Colony of Tasmania , established_title2 = Federation , established_date2 = 1 January 1901 , named_for = Abel Tasman , demonym = , capital = Hobart , largest_city = capital , coordinates = , admin_center = 29 local government areas , admin_center_type = Administration , leader_title1 = Monarch , leader_name1 = Charles III , leader_title2 = Governor , leader_name2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spore
In biology, a spore is a unit of sexual or asexual reproduction that may be adapted for dispersal and for survival, often for extended periods of time, in unfavourable conditions. Spores form part of the life cycles of many plants, algae, fungi and protozoa. Bacterial spores are not part of a sexual cycle, but are resistant structures used for survival under unfavourable conditions. Myxozoan spores release amoeboid infectious germs ("amoebulae") into their hosts for parasitic infection, but also reproduce within the hosts through the pairing of two nuclei within the plasmodium, which develops from the amoebula. In plants, spores are usually haploid and unicellular and are produced by meiosis in the sporangium of a diploid sporophyte. Under favourable conditions the spore can develop into a new organism using mitotic division, producing a multicellular gametophyte, which eventually goes on to produce gametes. Two gametes fuse to form a zygote which develops into a new s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capillitium
Capillitium (pl. capillitia) is a mass of sterile fibers within a fruit body interspersed among spores. It is found in Mycetozoa (slime molds) and gasteroid fungi of the fungal subdivision Agaricomycotina The subdivision Agaricomycotina, also known as the hymenomycetes, is one of three taxa of the fungal division Basidiomycota (fungi bearing spores on basidia). The Agaricomycotina contain some 20,000 species, and about 98% of these are in the cla .... In the fungi, the form of the capillitia, including shape, size, branching patterns, presence or absence of slits or pores, thickness of the walls, and color, are features that can be used to identify certain species or genera. References {{Reflist, refs= {{cite book , title=Poisonous Mushrooms of the northern United States and Canada , vauthors=Ammirati J, Traquair JA, Horgen PA , year=1985 , publisher=Fitzhenry & Whiteside in cooperation with Agriculture Canada , location=Markham, Ontario , isbn=978-0889029774 , page=30, 376 , ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plasmodiokarp
A plasmodiocarp is a special form of fruit bodies of slime moulds. It is produced if the plasmodium concentrates during the fructification and pull back into the venetion of the plasmodium, from which the fruit body is created. The fruit body traces the process of the venetion, whereby the structure of its subsurface becomes plainly strand-shaped, branched, net or ring-shaped. The production of plasmodiocarps can be generic, or can be also caused by the deranged development of sporocarps or aethalia. Slime moulds with plasmodiocarps including '' Physarum aeneum'', '' Physarum bivalve'', ''Physarum lateritium'', ''Diderma effusum'', '' Physarella oblonga'', '' Willkommlangea reticulata'' or ''Hemitrichia serpula ''Hemitrichia'' is a genus of slime molds, of the family Trichiidae, found within the order Trichiida. It was first described by Josef Rostafinksi in 1873 and remains a well-defined genus of the slime molds. ''Hemitrichia'' species exhibit either ...''.Steven L Stephen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)



