|
Protocetus
''Protocetus atavus'' ("first whale") is an extinct species of primitive cetacean from Egypt. It lived during the middle Eocene period 45 million years ago. The first discovered protocetid, ''Protocetus atavus'' was described by based on a cranium and a number of associated vertebrae and ribs found in middle Lutetian Tethyan marine limestone from Gebel Mokattam near Cairo, Egypt. Description ''Protocetus'' are believed to have had a streamlined, whale-like body around long, but was probably primitive in some respects.Palmer D (ed.) (1999). ''The Marshall Illustrated Encyclopedia of Dinosaurs and Prehistoric Animals''. London: Marshall Editions. p. 230. . Many protocetids (like ''Maiacetus'', ''Rodhocetus'') possessed well developed innominates and hind limbs, often attached to the backbone with a sacrum. ''Protocetus'' are known to have had at least one sacral vertebrate,Gingerich P.D. (2010). "Cetacea". In Werdelin L & Sanders W.J. (eds.). ''Cenozoic mammals of africa''. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protocetidae
Protocetidae, the protocetids, form a diverse and heterogeneous group of extinct cetaceans known from Asia, Europe, Africa, South America, and North America. Description There were many genera, and some of these are very well known (e.g., '' Rodhocetus''). Known protocetids had large fore- and hindlimbs that could support the body on land, and it is likely that they lived amphibiously: in the sea and on land. It is unclear at present whether protocetids had flukes (the horizontal tail fin of modern cetaceans). However, what is clear is that they are adapted even further to an aquatic life-style. In '' Rodhocetus'', for example, the sacrum – a bone that in land-mammals is a fusion of five vertebrae that connects the pelvis with the rest of the vertebral column – was divided into loose vertebrae. However, the pelvis retain a sacroiliac joint. Furthermore, the nasal openings are now halfway up the snout; a first step towards the telescoped condition in modern whale ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
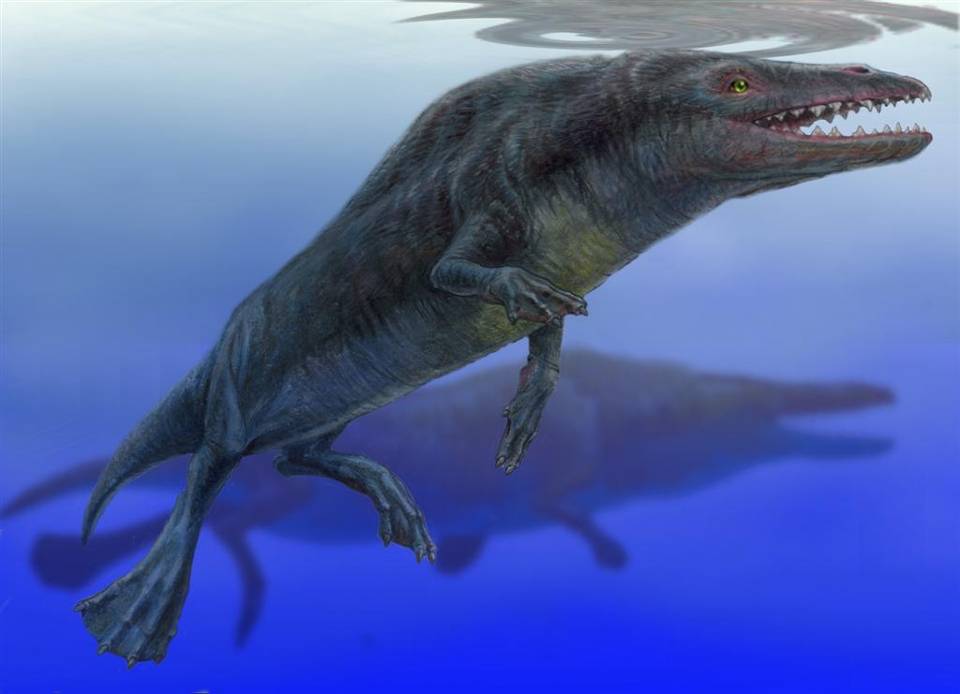
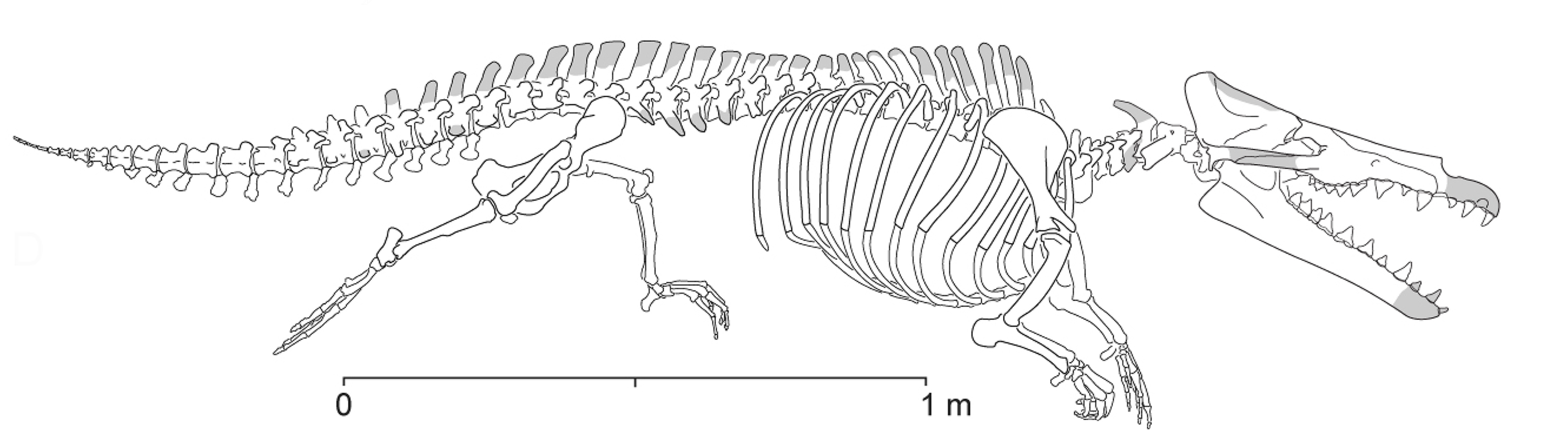
Rodhocetus
''Rodhocetus'' (from ''Rodho'', the geological anticline at the type locality, and ''cetus'', Latin for whale) is an extinct genus of protocetid early whale known from the Lutetian of Pakistan. The best-known protocetid, ''Rodhocetus'' is known from two partial skeletons that taken together give a complete image of an Eocene whale that had short limbs with long hands and feet that were probably webbed and a sacrum that was immobile with four partially fused sacral vertebrae. It is one of several extinct whale genera that possess land mammal characteristics, thus demonstrating the evolutionary transition from land to sea. Description left, Size of ''Rodhocetus'' relative to a human. ''Rodhocetus'' was a small whale measuring long. Throughout the 1990s, a close relationship between cetaceans and mesonychids, an extinct group of cursorial, wolf-like ungulates, was generally accepted based on morphological analyses. In the late 1990s, however, cladistic analyses based on mole ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evolution Of Cetaceans
The evolution of cetaceans is thought to have begun in the Indian subcontinent from even-toed ungulates 50 million years ago (mya) and to have proceeded over a period of at least 15 million years. Cetaceans are fully aquatic marine mammals belonging to the order Artiodactyla and branched off from other artiodactyls around 50 mya. Cetaceans are thought to have evolved during the Eocene (56-34 mya), the second epoch of the present-extending Cenozoic Era. Molecular and morphological analyses suggest Cetacea share a relatively recent closest common ancestor with hippopotami and that they are sister groups. Being mammals, they surface to breathe air; they have 5 finger bones (even-toed) in their fins; they nurse their young; and, despite their fully aquatic life style, they retain many skeletal features from their terrestrial ancestors.Thewissen, J. G. M., L. N. Cooper, J. C. George, and S. Bajpai. 2009. From land to water: the origin of whales, dolphins, and porpoises. Evol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eocene
The Eocene ( ) Epoch is a geological epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (mya). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period in the modern Cenozoic Era. The name ''Eocene'' comes from the Ancient Greek (''ēṓs'', " dawn") and (''kainós'', "new") and refers to the "dawn" of modern ('new') fauna that appeared during the epoch. The Eocene spans the time from the end of the Paleocene Epoch to the beginning of the Oligocene Epoch. The start of the Eocene is marked by a brief period in which the concentration of the carbon isotope 13C in the atmosphere was exceptionally low in comparison with the more common isotope 12C. The end is set at a major extinction event called the ''Grande Coupure'' (the "Great Break" in continuity) or the Eocene–Oligocene extinction event, which may be related to the impact of one or more large bolides in Siberia and in what is now Chesapeake Bay. As with other geologic periods, the strata that define the start and e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pakicetus
''Pakicetus'' is an extinct genus of amphibious cetacean of the family Pakicetidae, which was endemic to Pakistan during the Eocene, about 50 million years ago. It was a wolf-like animal, about to long, and lived in and around water where it ate fish and small animals. The vast majority of paleontologists regard it as the most basal whale, representing a transitional stage between land mammals and whales. It belongs to the even-toed ungulates with the closest living non-cetacean relative being the hippopotamus. Description Based on the sizes of specimens, and to a lesser extent on composite skeletons, species of ''Pakicetus'' are thought to have been to in length. ''Pakicetus'' looked very different from modern cetaceans, and its body shape more resembled those of land-dwelling hoofed mammals. Unlike all later cetaceans, it had four fully functional long legs. ''Pakicetus'' had a long snout; a typical complement of teeth that included incisors, canines, premolars, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fossil Taxa Described In 1904
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved in amber, hair, petrified wood and DNA remnants. The totality of fossils is known as the ''fossil record''. Paleontology is the study of fossils: their age, method of formation, and evolutionary significance. Specimens are usually considered to be fossils if they are over 10,000 years old. The oldest fossils are around 3.48 billion years old to 4.1 billion years old. Early edition, published online before print. The observation in the 19th century that certain fossils were associated with certain rock strata led to the recognition of a geological timescale and the relative ages of different fossils. The development of radiometric dating techniques in the early 20th century allowed scientists to quantitatively measure the ab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prehistoric Cetacean Genera
Prehistory, also known as pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the use of the first stone tools by hominins 3.3 million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The use of symbols, marks, and images appears very early among humans, but the earliest known writing systems appeared 5000 years ago. It took thousands of years for writing systems to be widely adopted, with writing spreading to almost all cultures by the 19th century. The end of prehistory therefore came at very different times in different places, and the term is less often used in discussing societies where prehistory ended relatively recently. In the early Bronze Age, Sumer in Mesopotamia, the Indus Valley Civilisation, and ancient Egypt were the first civilizations to develop their own scripts and to keep historical records, with their neighbors following. Most other civilizations reached the end of prehistory during the following Iron Ag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olfaction
The sense of smell, or olfaction, is the special sense through which smells (or odors) are perceived. The sense of smell has many functions, including detecting desirable foods, hazards, and pheromones, and plays a role in taste. In humans, it occurs when an odor binds to a receptor within the nasal cavity, transmitting a signal through the olfactory system. Glomeruli aggregate signals from these receptors and transmit them to the olfactory bulb, where the sensory input will start to interact with parts of the brain responsible for smell identification, memory, and emotion. There are many different causes for alteration, lack, or disturbance to a normal sense of smell, and can include damage to the nose or smell receptors, or central problems affecting the brain. Some causes include upper respiratory infections, traumatic brain injury, and neurodegenerative disease. History of study Early scientific study of the sense of smell includes the extensive doctoral dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animal Echolocation
Echolocation, also called bio sonar, is a biological sonar used by several animal species. Echolocating animals emit calls out to the environment and listen to the echoes of those calls that return from various objects near them. They use these echoes to locate and identify the objects. Echolocation is used for navigation, foraging, and hunting in various environments. Echolocating animals include some mammals (most notably Laurasiatheria) and a few birds, especially some bat species and odontocetes (toothed whales and dolphins), but also in simpler forms in other groups such as shrews, and two cave-dwelling bird groups, the so-called cave swiftlets in the genus '' Aerodramus'' (formerly ''Collocalia'') and the unrelated oilbird ''Steatornis caripensis''. Early research The term ''echolocation'' was coined in 1938 by the American zoologist Donald Griffin, who, with Robert Galambos, first demonstrated the phenomenon in bats. As Griffin described in his book, the 18t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teeth
A tooth ( : teeth) is a hard, calcified structure found in the jaws (or mouths) of many vertebrates and used to break down food. Some animals, particularly carnivores and omnivores, also use teeth to help with capturing or wounding prey, tearing food, for defensive purposes, to intimidate other animals often including their own, or to carry prey or their young. The roots of teeth are covered by gums. Teeth are not made of bone, but rather of multiple tissues of varying density and hardness that originate from the embryonic germ layer, the ectoderm. The general structure of teeth is similar across the vertebrates, although there is considerable variation in their form and position. The teeth of mammals have deep roots, and this pattern is also found in some fish, and in crocodilians. In most teleost fish, however, the teeth are attached to the outer surface of the bone, while in lizards they are attached to the inner surface of the jaw by one side. In cartilaginous fish, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
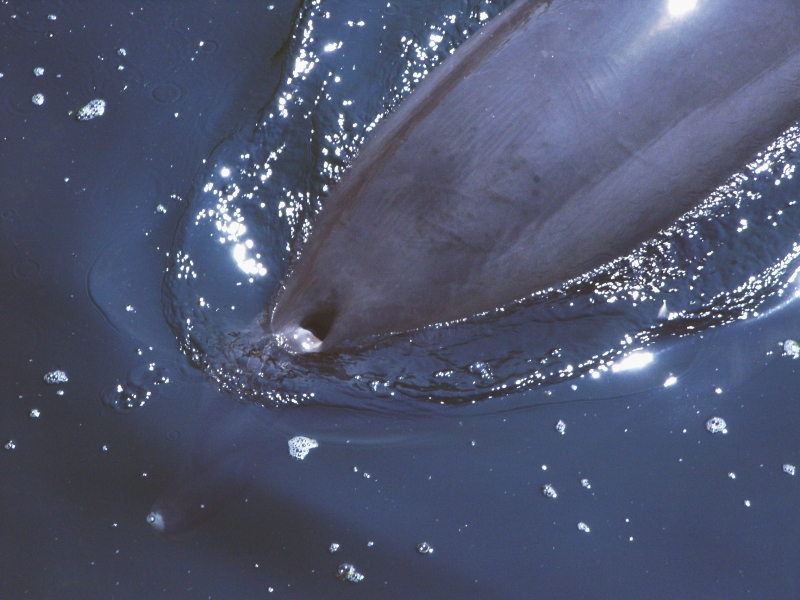
Blowhole (anatomy)
In cetology, the study of whales and other cetaceans, a blowhole is the hole (or spiracle) at the top of the head through which the animal breathes air. In baleen whales, these are in pairs. It is homologous with the nostril of other mammals, and evolved via gradual movement of the nostrils to the top of the head. The posterior placement of blowholes on cetacean heads is believed to minimize the energy used when breathing at the water's surface. As whales reach the water surface to breathe, they forcefully expel air through the blowhole. The exhalation is released into the comparably lower-pressure, colder atmosphere, and any water vapor condenses. This spray, known as the ''blow'', is often visible from far away as a white splash, which can also be caused by water resting on top of the blowhole. Purpose and mechanism Air sacs just below the blowhole allow whales to produce sounds for communication and, for toothed whales, echolocation. These air sacs are filled with air, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |