|
Protoceratops Andrewsi
''Protoceratops'' (; ) is a genus of small protoceratopsid dinosaurs that lived in Asia during the Late Cretaceous, around 75 to 71 million years ago. The genus ''Protoceratops'' includes two species: ''P. andrewsi'' and the larger ''P. hellenikorhinus''. The former was described in 1923 with fossils from the Mongolian Djadokhta Formation, and the latter in 2001 with fossils from the Chinese Bayan Mandahu Formation. ''Protoceratops'' was initially believed to be an ancestor of ankylosaurians and larger ceratopsians, such as ''Triceratops'' and relatives, until the discoveries of other protoceratopsids. Populations of ''P. andrewsi'' may have evolved into ''Bagaceratops'' through anagenesis. ''Protoceratops'' were small ceratopsians, about long and in body mass. While adults were largely quadrupedal, juveniles had the capacity to walk around bipedally if necessary. They were characterized by a proportionally large skull, short and stiff neck, and neck frill. The frill was likel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Cretaceous
The Late Cretaceous (100.5–66 Ma) is the younger of two epochs into which the Cretaceous Period is divided in the geologic time scale. Rock strata from this epoch form the Upper Cretaceous Series. The Cretaceous is named after ''creta'', the Latin word for the white limestone known as chalk. The chalk of northern France and the white cliffs of south-eastern England date from the Cretaceous Period. Climate During the Late Cretaceous, the climate was warmer than present, although throughout the period a cooling trend is evident. The tropics became restricted to equatorial regions and northern latitudes experienced markedly more seasonal climatic conditions. Geography Due to plate tectonics, the Americas were gradually moving westward, causing the Atlantic Ocean to expand. The Western Interior Seaway divided North America into eastern and western halves; Appalachia and Laramidia. India maintained a northward course towards Asia. In the Southern Hemisphere, Australia and Ant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
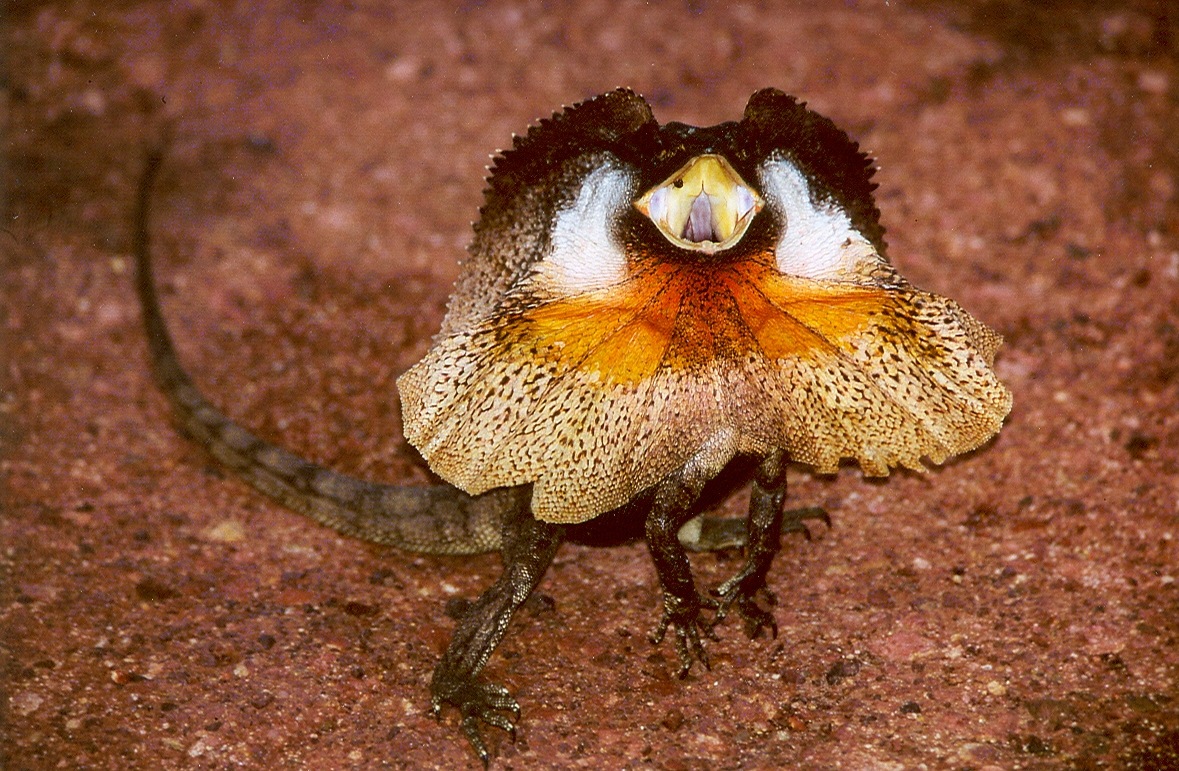
Neck Frill
A neck frill is the relatively extensive margin seen on the back of the heads of reptiles with either a bony support such as those present on the skulls of dinosaurs of the suborder Marginocephalia or a cartilaginous one as in the frill-necked lizard. In technical terms, the bone-supported frill is composed of an enlarged parietal bone flanked by elongated squamosals and sometimes ringed by epoccipitals, bony knobs that gave the margin a jagged appearance. In the early 1900s, the parietal bone was known among paleontologists as the dermosupraoccipital. The feature is now referred to as the parietosquamosal frill. In some genera, such as ''Triceratops'', ''Pentaceratops'', ''Centrosaurus'' and ''Torosaurus'', this extension is very large. Despite the neck frill predominantly being made of hard bone, some neck frills are made of skin, as is the case with the frill-necked lizard of today that resides in Australia. The use of the neck frill in dinosaurs is uncertain; it may have be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metabolic
Metabolism (, from el, μεταβολή ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cellular processes; the conversion of food to building blocks for proteins, lipids, nucleic acids, and some carbohydrates; and the elimination of metabolic wastes. These enzyme-catalyzed reactions allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. The word metabolism can also refer to the sum of all chemical reactions that occur in living organisms, including digestion and the transportation of substances into and between different cells, in which case the above described set of reactions within the cells is called intermediary (or intermediate) metabolism. Metabolic reactions may be categorized as ''catabolic'' – the ''breaking down'' of compounds (for example, of glucose to pyruvate by cel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aquatic Locomotion
Aquatic locomotion or swimming is biologically propelled motion through a liquid medium. The simplest propulsive systems are composed of cilia and flagella. Swimming has evolved a number of times in a range of organisms including arthropods, fish, molluscs, amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals. Evolution of swimming Swimming evolved a number of times in unrelated lineages. Supposed jellyfish fossils occur in the Ediacaran, but the first free-swimming animals appear in the Early to Middle Cambrian. These are mostly related to the arthropods, and include the Anomalocaridids, which swam by means of lateral lobes in a fashion reminiscent of today's cuttlefish. Cephalopods joined the ranks of the nekton in the late Cambrian, and chordates were probably swimming from the Early Cambrian. Many terrestrial animals retain some capacity to swim, however some have returned to the water and developed the capacities for aquatic locomotion. Most apes (including humans), however, lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neural Spine Sail
A neural spine sail is a large, flattish protrusion from the back of an animal formed of a sequence of extended vertebral spinous processes and associated tissues. Such structures are comparatively rare in modern animals, but have been identified in many extinct species of amphibians and amniotes. Paleontologists have proposed a number of ways in which the sail could have functioned in life. Function Varying suggestions have been made for the function of the sail. Thermoregulation The structure may have been used for thermoregulation. The base of the spines have a channel which may have contained a blood vessel supplying abundant blood to the sail. The animal could have used the sail's large surface area to absorb heat from the sun in the morning. As ectotherms they required heat from an external source before their muscles would start to function properly. A predator would thus have an advantage over its slower moving prey. The sail could be used in reverse if the animal wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fossorial
A fossorial () animal is one adapted to digging which lives primarily, but not solely, underground. Some examples are badgers, naked mole-rats, clams, meerkats, and mole salamanders, as well as many beetles, wasps, and bees. Prehistoric evidence The physical adaptation of fossoriality is widely accepted as being widespread among many prehistoric phyla and taxa, such as bacteria and early eukaryotes. Furthermore, fossoriality has evolved independently multiple times, even within a single family. Fossorial animals appeared simultaneously with the colonization of land by arthropods in the late Ordovician period (over 440 million years ago). Other notable early burrowers include ''Eocaecilia'' and possibly ''Dinilysia''. The oldest example of burrowing in synapsids, the lineage which includes modern mammals and their ancestors, is a cynodont, ''Thrinaxodon liorhinus'', found in the Karoo of South Africa, estimated to be 251 million years old. Evidence shows that this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
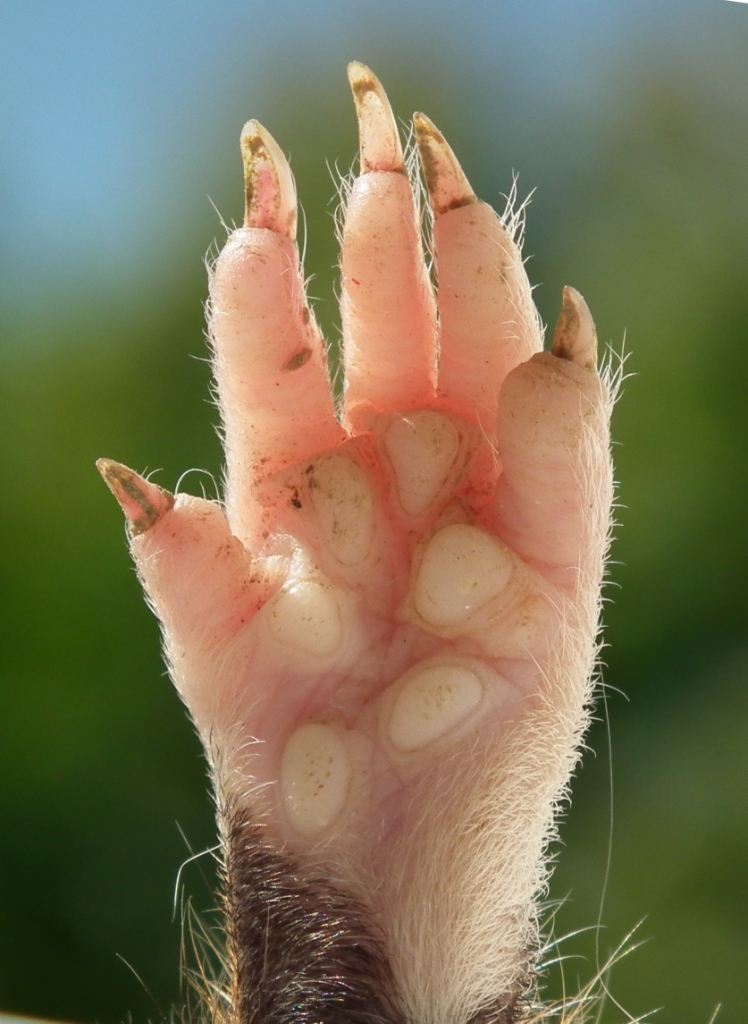
Pes (anatomy)
The pes (Latin for ''foot'') is the zoological term for the distal portion of the hind limb of tetrapod animals. It is the part of the pentadactyl limb that includes the metatarsals and digits (phalanges). During evolution, it has taken many forms and served a variety of functions. It can be represented by the foot of primates, the lower hind limb of hoofed animals, the lower portion of the leg of dinosaurs including birds or the rear paw. It is also represented in the rear 'paddle' of extinct marine reptiles, such as plesiosaurs. The oldest types of tetrapods had seven or eight digits. See also *Manus (anatomy) The manus (Latin for ''hand'', plural manus) is the zoological term for the distal portion of the fore limb of an animal. In tetrapods, it is the part of the pentadactyl limb that includes the metacarpals and digits (phalanges). During evolution ... References Vertebrate anatomy Dinosaur anatomy Lower limb anatomy {{Vertebrate anatomy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
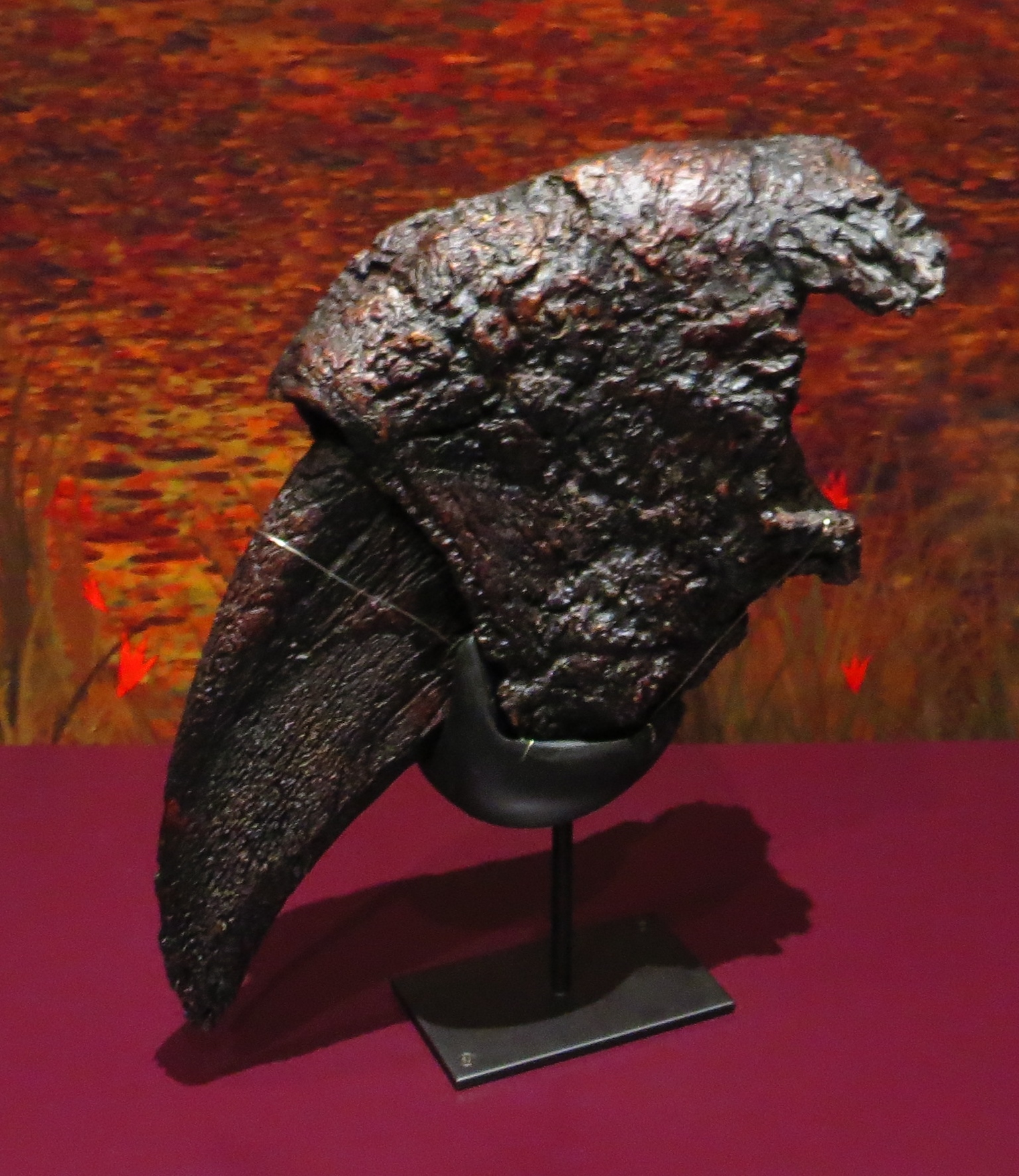
Ungual
An ungual (from Latin ''unguis'', i.e. ''nail'') is a highly modified distal toe bone which ends in a hoof, claw, or nail. Elephants and ungulates have ungual phalanges, as did the sauropods and horned dinosaurs. A claw is a highly modified ungual phalanx. As an adjective, ungual means ''related to nail Nail or Nails may refer to: In biology * Nail (anatomy), toughened protective protein-keratin (known as alpha-keratin, also found in hair) at the end of an animal digit, such as fingernail * Nail (beak), a plate of hard horny tissue at the tip ...'', as in ''periungual'' (around the nail). References External links Mammal anatomy {{animal-anatomy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digit (anatomy)
A digit is one of several most distal parts of a limb, such as fingers or toes, present in many vertebrates. Names Some languages have different names for hand and foot digits (English: respectively "finger" and "toe", German: "Finger" and "Zeh", French: "doigt" and "orteil"). In other languages, e.g. Arabic, Russian, Polish, Spanish, Portuguese, Italian, Czech, Tagalog, Turkish, Bulgarian, and Persian, there are no specific one-word names for fingers and toes; these are called "digit of the hand" or "digit of the foot" instead. In Japanese, yubi (指) can mean either, depending on context. Human digits Humans normally have five digits on each extremity. Each digit is formed by several bones called phalanges, surrounded by soft tissue. Human fingers normally have a nail at the distal phalanx. The phenomenon of polydactyly occurs when extra digits are present; fewer digits than normal are also possible, for instance in ectrodactyly. Whether such a mutation can be surgica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teeth
A tooth ( : teeth) is a hard, calcified structure found in the jaws (or mouths) of many vertebrates and used to break down food. Some animals, particularly carnivores and omnivores, also use teeth to help with capturing or wounding prey, tearing food, for defensive purposes, to intimidate other animals often including their own, or to carry prey or their young. The roots of teeth are covered by gums. Teeth are not made of bone, but rather of multiple tissues of varying density and hardness that originate from the embryonic germ layer, the ectoderm. The general structure of teeth is similar across the vertebrates, although there is considerable variation in their form and position. The teeth of mammals have deep roots, and this pattern is also found in some fish, and in crocodilians. In most teleost fish, however, the teeth are attached to the outer surface of the bone, while in lizards they are attached to the inner surface of the jaw by one side. In cartilaginous fish, s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parrot
Parrots, also known as psittacines (), are birds of the roughly 398 species in 92 genera comprising the order Psittaciformes (), found mostly in tropical and subtropical regions. The order is subdivided into three superfamilies: the Psittacoidea ("true" parrots), the Cacatuoidea (cockatoos), and the Strigopoidea (New Zealand parrots). One-third of all parrot species are threatened by extinction, with higher aggregate extinction risk ( IUCN Red List Index) than any other comparable bird group. Parrots have a generally pantropical distribution with several species inhabiting temperate regions in the Southern Hemisphere, as well. The greatest diversity of parrots is in South America and Australasia. Characteristic features of parrots include a strong, curved bill, an upright stance, strong legs, and clawed zygodactyl feet. Many parrots are vividly coloured, and some are multi-coloured. Most parrots exhibit little or no sexual dimorphism in the visual spectrum. They form the most ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sexual Dimorphism
Sexual dimorphism is the condition where the sexes of the same animal and/or plant species exhibit different morphological characteristics, particularly characteristics not directly involved in reproduction. The condition occurs in most animals and some plants. Differences may include secondary sex characteristics, size, weight, colour, markings, or behavioural or cognitive traits. These differences may be subtle or exaggerated and may be subjected to sexual selection and natural selection. The opposite of dimorphism is ''monomorphism'', which is when both biological sexes are phenotypically indistinguishable from each other. Overview Ornamentation and coloration Common and easily identified types of dimorphism consist of ornamentation and coloration, though not always apparent. A difference in coloration of sexes within a given species is called sexual dichromatism, which is commonly seen in many species of birds and reptiles. Sexual selection leads to the exaggerated dim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |