|
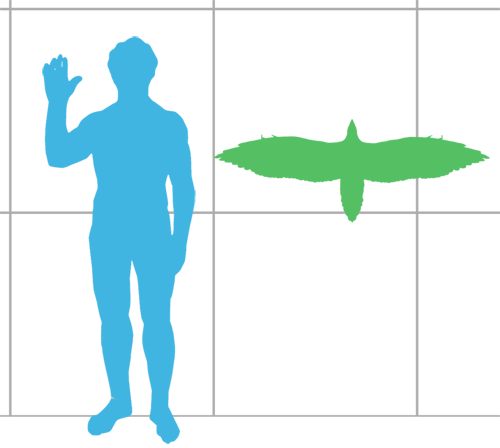
Protobird
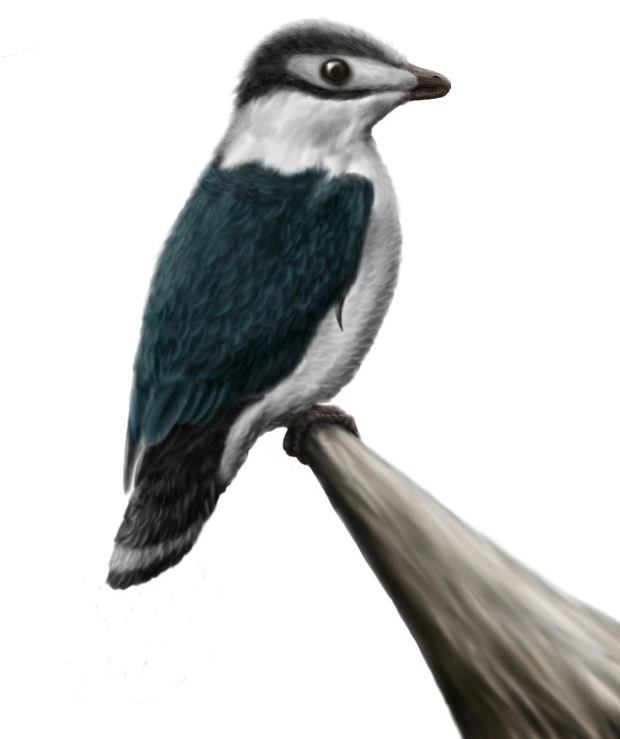
"Protobird" is an informal term that has been used by some paleontologists when discussing animals that, while technically classified as non-avian dinosaurs, possess many features normally associated with birds. All protobirds are extinct. Zhou and Farlow (2001), for example, used the term "protobird" for primitive members of the clade Avialae. In this sense, protobirds would include animals like ''Confuciusornis'', ''Sapeornis'', and the Enantiornithes. These animals were small, flying, feathered, and closely related to birds. The authors restricted the term "bird" to refer only to Aves, which they used to mean only modern ("crown group") birds.Zhou, Z. and Farlow, J.O. (2001). "Flight Capability and habits of Confuciusornis." Pp. 237-245 in ''New Perspectives on the Origin and Early Evolution of Birds''. Peabody Museum of Natural History, Yale University, New Haven, USA. Gregory S. Paul used the term "protobird" in a wider sense in 1988, to refer to the extremely bird-like non-a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleontologist
Paleontology (), also spelled palaeontology or palæontology, is the scientific study of life that existed prior to, and sometimes including, the start of the Holocene epoch (roughly 11,700 years before present). It includes the study of fossils to classify organisms and study their interactions with each other and their environments (their paleoecology). Paleontological observations have been documented as far back as the 5th century BC. The science became established in the 18th century as a result of Georges Cuvier's work on comparative anatomy, and developed rapidly in the 19th century. The term itself originates from Greek (, "old, ancient"), (, ( gen. ), "being, creature"), and (, "speech, thought, study"). Paleontology lies on the border between biology and geology, but differs from archaeology in that it excludes the study of anatomically modern humans. It now uses techniques drawn from a wide range of sciences, including biochemistry, mathematics, and engineering. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dinosaur
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of reptiles of the clade Dinosauria. They first appeared during the Triassic period, between 243 and 233.23 million years ago (mya), although the exact origin and timing of the evolution of dinosaurs is the subject of active research. They became the dominant terrestrial vertebrates after the Triassic–Jurassic extinction event 201.3 mya; their dominance continued throughout the Jurassic and Cretaceous periods. The fossil record shows that birds are feathered dinosaurs, having evolved from earlier theropods during the Late Jurassic epoch, and are the only dinosaur lineage known to have survived the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event approximately 66 mya. Dinosaurs can therefore be divided into avian dinosaurs—birds—and the extinct non-avian dinosaurs, which are all dinosaurs other than birds. Dinosaurs are varied from taxonomic, morphological and ecological standpoints. Birds, at over 10,700 living species, are among ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bird
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the laying of hard-shelled eggs, a high metabolic rate, a four-chambered heart, and a strong yet lightweight skeleton. Birds live worldwide and range in size from the bee hummingbird to the ostrich. There are about ten thousand living species, more than half of which are passerine, or "perching" birds. Birds have whose development varies according to species; the only known groups without wings are the extinct moa and elephant birds. Wings, which are modified forelimbs, gave birds the ability to fly, although further evolution has led to the loss of flight in some birds, including ratites, penguins, and diverse endemic island species. The digestive and respiratory systems of birds are also uniquely adapted for flight. Some bird species of aquatic environments, particularly seabirds and some waterbirds, have further evolved for swimming. B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extinct
Extinction is the termination of a kind of organism or of a group of kinds (taxon), usually a species. The moment of extinction is generally considered to be the death of the last individual of the species, although the capacity to breed and recover may have been lost before this point. Because a species' potential range may be very large, determining this moment is difficult, and is usually done retrospectively. This difficulty leads to phenomena such as Lazarus taxa, where a species presumed extinct abruptly "reappears" (typically in the fossil record) after a period of apparent absence. More than 99% of all species that ever lived on Earth, amounting to over five billion species, are estimated to have died out. It is estimated that there are currently around 8.7 million species of eukaryote globally, and possibly many times more if microorganisms, like bacteria, are included. Notable extinct animal species include non-avian dinosaurs, saber-toothed cats, dodos, m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avialae
Avialae ("bird wings") is a clade containing the only living dinosaurs, the birds. It is usually defined as all theropod dinosaurs more closely related to birds (Aves) than to deinonychosaurs, though alternative definitions are occasionally used (see below). ''Archaeopteryx lithographica'', from the late Jurassic Period Solnhofen Formation of Germany, is possibly the earliest known avialan which may have had the capability of powered flight, though it might have been a deinonychosaur instead. Several older (but non flight-capable) avialans are known from the late Jurassic Tiaojishan Formation of China, dated to about 160 million years ago. Definition Most researchers define Avialae as branch-based clade, though definitions vary. Many authors have used a definition similar to "all theropods closer to birds than to ''Deinonychus''."Weishampel, David B.; Dodson, Peter; Osmólska, Halszka (eds.) (2004). ''The Dinosauria'', Second Edition. University of California Press., 861 pp. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Confuciusornis
''Confuciusornis'' is a genus of basal crow-sized avialan from the Early Cretaceous Period of the Yixian and Jiufotang Formations of China, dating from 125 to 120 million years ago. Like modern birds, ''Confuciusornis'' had a toothless beak, but closer and later relatives of modern birds such as ''Hesperornis'' and ''Ichthyornis'' were toothed, indicating that the loss of teeth occurred convergently in ''Confuciusornis'' and living birds. It is the oldest known bird to have a beak. It was named after the Chinese moral philosopher Confucius (551–479 BC). ''Confuciusornis'' is one of the most abundant vertebrates found in the Yixian Formation, and several hundred complete specimens have been found. History of discovery In November 1993, the Chinese paleontologists Hou Lianhai and Hu Yoaming of the Institute of Vertebrate Paleontology and Paleoanthropology (IVPP) at Beijing, visited fossil collector Zhang He at his home in Jinzhou, where he showed them a fossil bird specimen t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sapeornis
''Sapeornis'' is a monotypic genus of avialan which lived during the early Cretaceous period ( late Barremian to early Aptian, roughly 125-120 mya). ''Sapeornis'' contains only one species, ''Sapeornis chaoyangensis''. Description ''Sapeornis'' was large for an early avialan, about long in life, excluding the tail feathers. The hand of ''Sapeornis'' was far more derived than that of ''Archaeopteryx''. It had three fingers, the outer ones with two and the middle one with three phalanges, and a well-fused carpometacarpus. Its arms were about half again as long as the legs, suggesting a large wing area. On the other hand, its shoulder girdle was apparently ill-adapted to flapping flight and its furcula was unusual, with a hypocleidum similar to more advanced avialans but a general anatomy even more basal than in ''Archaeopteryx''. The humerus was large and bore holes, apparently to save weight, as in the Confuciusornithidae. The skull has a handful of teeth in the upper jawtip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enantiornithes
The Enantiornithes, also known as enantiornithines or enantiornitheans in literature, are a group of extinct avialans ("birds" in the broad sense), the most abundant and diverse group known from the Mesozoic era. Almost all retained teeth and clawed fingers on each wing, but otherwise looked much like modern birds externally. Over eighty species of Enantiornithes have been named, but some names represent only single bones, so it is likely that not all are valid. The Enantiornithes became extinct at the Cretaceous–Paleogene boundary, along with Hesperornithes and all other non-avian dinosaurs. Discovery and naming The first Enantiornithes to be discovered were incorrectly referred to modern bird groups. For example, the first known species of Enantiornithes, ''Gobipteryx minuta'', was originally considered a paleognath related to ostriches and tinamou. The Enantiornithes were first recognized as a distinct lineage, or "subclass" of birds, by Cyril A. Walker in 1981. Walker mad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aves
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the laying of hard-shelled eggs, a high metabolic rate, a four-chambered heart, and a strong yet lightweight skeleton. Birds live worldwide and range in size from the bee hummingbird to the ostrich. There are about ten thousand living species, more than half of which are passerine, or "perching" birds. Birds have whose development varies according to species; the only known groups without wings are the extinct moa and elephant birds. Wings, which are modified forelimbs, gave birds the ability to fly, although further evolution has led to the loss of flight in some birds, including ratites, penguins, and diverse endemic island species. The digestive and respiratory systems of birds are also uniquely adapted for flight. Some bird species of aquatic environments, particularly seabirds and some waterbirds, have further evolved for swimming. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gregory S
Gregory may refer to: People and fictional characters * Gregory (given name), including a list of people and fictional characters with the given name * Gregory (surname), a surname Places Australia *Gregory, Queensland, a town in the Shire of Burke **Electoral district of Gregory, Queensland, Australia *Gregory, Western Australia. United States *Gregory, South Dakota *Gregory, Tennessee *Gregory, Texas Outer space *Gregory (lunar crater) *Gregory (crater on Venus) Other uses * "Gregory" (''The Americans''), the third episode of the first season of the television series ''The Americans'' See also * Greg (other) * Greggory * Gregoire (other) * Gregor (other) * Gregores (other) * Gregorian (other) * Gregory County (other) * Gregory Highway, Queensland * Gregory National Park, Northern Territory * Gregory River in the Shire of Burke, Queensland * Justice Gregory (other) Justice Gregory may refer to: * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maniraptora
Maniraptora is a clade of coelurosaurian dinosaurs which includes the birds and the non-avian dinosaurs that were more closely related to them than to ''Ornithomimus velox''. It contains the major subgroups Avialae, Deinonychosauria, Oviraptorosauria and Therizinosauria. '' Ornitholestes'' and the Alvarezsauroidea are also often included. Together with the next closest sister group, the Ornithomimosauria, Maniraptora comprises the more inclusive clade Maniraptoriformes. Maniraptorans first appear in the fossil record during the Jurassic Period (see '' Eshanosaurus''), and survive today as living birds. Description Maniraptorans are characterized by long arms and three-fingered hands (though reduced or fused in some lineages), as well as a "half-moon shaped" (semi-lunate) bone in the wrist (carpus). In 2004, Tom Holtz and Halszka Osmólska pointed out six other maniraptoran characters relating to specific details of the skeleton. Unlike most other saurischian dinosaurs, which h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oviraptorosauria
Oviraptorosaurs ("egg thief lizards") are a group of feathered maniraptoran dinosaurs from the Cretaceous Period of what are now Asia and North America. They are distinct for their characteristically short, beaked, parrot-like skulls, with or without bony crests atop the head. They ranged in size from ''Caudipteryx'', which was the size of a turkey, to the 8-meter-long, 1.4-ton ''Gigantoraptor''. The group (along with all maniraptoran dinosaurs) is close to the ancestry of birds. Some researchers such as Maryanska ''et al'' (2002) and Osmólska ''et al.'' (2004) have proposed that they may represent primitive flightless birds.Osmólska, Halszka, Currie, Philip J., Brasbold, Rinchen (2004) "The Dinosauria" Weishampel, Dodson, Osmólska. "Chapter 8 Oviraptorosauria" University of California Press. The most complete oviraptorosaur specimens have been found in Asia. The North American oviraptorosaur record is sparse.Varricchio, D. J. 2001. Late Cretaceous oviraptorosaur (Theropoda) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)