|
Proto-Indo-European Nominals
Proto-Indo-European nominals include nouns, adjectives, and pronouns. Their grammatical forms and meanings have been reconstructed by modern linguists, based on similarities found across all Indo-European languages. This article discusses nouns and adjectives; Proto-Indo-European pronouns are treated elsewhere. The Proto-Indo-European language (PIE) had eight or nine cases, three numbers (singular, dual and plural) and probably originally two genders (animate and neuter), with the animate later splitting into the masculine and the feminine. Nominals fell into multiple different declensions. Most of them had word stems ending in a consonant (called athematic stems) and exhibited a complex pattern of accent shifts and/or vowel changes (ablaut) among the different cases. Two declensions ended in a vowel (The asterisk (*) indicates that the form is not directly attested but has been reconstructed on the basis of other linguistic material.) and are called ''thematic''; they were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Noun
A noun () is a word that generally functions as the name of a specific object or set of objects, such as living creatures, places, actions, qualities, states of existence, or ideas.Example nouns for: * Living creatures (including people, alive, dead or imaginary): ''mushrooms, dogs, Afro-Caribbeans, rosebushes, Nelson Mandela, bacteria, Klingons'', etc. * Physical objects: ''hammers, pencils, Earth, guitars, atoms, stones, boots, shadows'', etc. * Places: ''closets, temples, rivers, Antarctica, houses, Grand Canyon, utopia'', etc. * Actions: ''swimming, exercises, diffusions, explosions, flight, electrification, embezzlement'', etc. * Qualities: ''colors, lengths, deafness, weights, roundness, symmetry, warp speed,'' etc. * Mental or physical states of existence: ''jealousy, sleep, heat, joy, stomachache, confusion, mind meld,'' etc. Lexical categories (parts of speech) are defined in terms of the ways in which their members combine with other kinds of expressions. The syn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
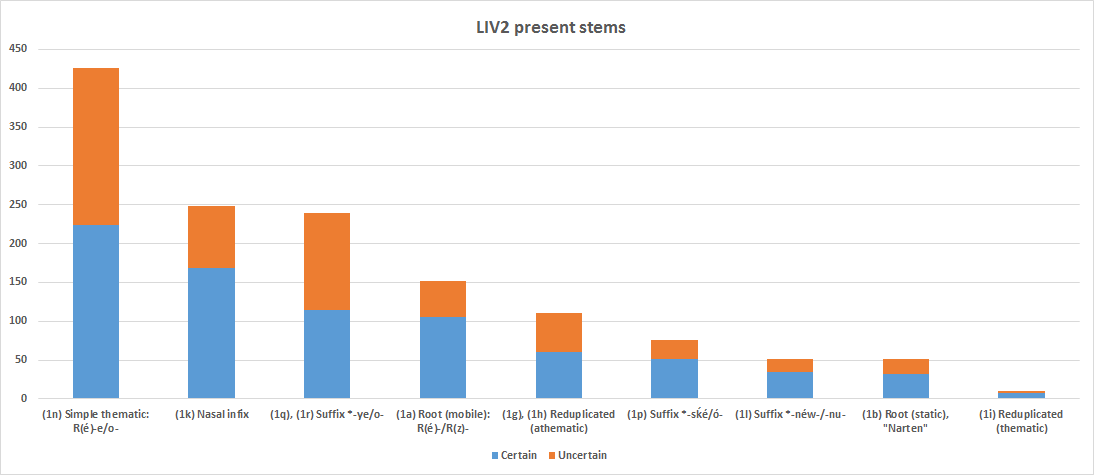
PIE Verb
Proto-Indo-European verbs reflect a complex system of morphology, more complicated than the substantive, with verbs categorized according to their aspect, using multiple grammatical moods and voices, and being conjugated according to person, number and tense. In addition to finite forms thus formed, non-finite forms such as participles are also extensively used.Beekes, 18.1.1. The verbal system is clearly represented in Ancient Greek and Vedic Sanskrit, which closely correspond, in nearly all aspects of their verbal systems, and are two of the most well-understood of the early daughter languages of Proto-Indo-European. Basics Verb conjugation in Proto-Indo-European involves the interplay of six dimensions (number, person, voice, mood, aspect and tense) with the following variables identified under the ''Cowgill-Rix'' system, which is one of the methodologies proposed and applies only to certain subfamilies: Further, participles can be considered part of the verbal syst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Null Morpheme
In morphology, a null morpheme or zero morpheme is a morpheme that has no phonetic form. In simpler terms, a null morpheme is an "invisible" affix. It is a concept useful for analysis, by contrasting null morphemes with alternatives that do have some phonetic realization. The null morpheme is represented as either the figure zero (''0'') or the empty set symbol ∅. In most languages, it is the affixes that are realized as null morphemes, indicating that the derived form does not differ from the stem. For example, plural form ''sheep'' can be analyzed as combination of ''sheep'' with added null affix for the plural. The process of adding a null affix is called ''null affixation'', ''null derivation'' or ''zero derivation''. The concept was first used by the 4th century BCE Sanskrit grammarian from ancient India, Pāṇini, in his Sanskrit grammar. In English Inflection The existence of a null morpheme in a word can also be theorized by contrast with other forms of the same wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germanic Strong Verb
In the Germanic languages, a strong verb is a verb that marks its past tense by means of changes to the stem vowel (ablaut). The majority of the remaining verbs form the past tense by means of a dental suffix (e.g. ''-ed'' in English), and are known as '' weak verbs''. In modern English, strong verbs include ''sing'' (present ''I sing'', past ''I sang'', past participle ''I have sung'') and ''drive'' (present ''I drive'', past ''I drove'', past participle ''I have driven''), as opposed to weak verbs such as ''open'' (present ''I open'', past ''I opened'', past participle ''I have opened''). Not all verbs with a change in the stem vowel are strong verbs, however; they may also be irregular weak verbs such as ''bring, brought, brought'' or ''keep, kept, kept''. The key distinction is that most strong verbs have their origin in the earliest sound system of Proto-Indo-European, whereas weak verbs use a dental ending (in English usually ''-ed'' or ''-t'') that developed later with the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germanic Languages
The Germanic languages are a branch of the Indo-European language family spoken natively by a population of about 515 million people mainly in Europe, North America, Oceania and Southern Africa. The most widely spoken Germanic language, English, is also the world's most widely spoken language with an estimated 2 billion speakers. All Germanic languages are derived from Proto-Germanic, spoken in Iron Age Scandinavia. The West Germanic languages include the three most widely spoken Germanic languages: English with around 360–400 million native speakers; German language, German, with over 100 million native speakers; and Dutch language, Dutch, with 24 million native speakers. Other West Germanic languages include Afrikaans, an offshoot of Dutch, with over 7.1 million native speakers; Low German, considered a separate collection of Standard language, unstandardized dialects, with roughly 4.35–7.15 million native speakers and probably 6.7–10 million people who can understand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic period (), and the Classical period (). Ancient Greek was the language of Homer and of fifth-century Athenian historians, playwrights, and philosophers. It has contributed many words to English vocabulary and has been a standard subject of study in educational institutions of the Western world since the Renaissance. This article primarily contains information about the Epic and Classical periods of the language. From the Hellenistic period (), Ancient Greek was followed by Koine Greek, which is regarded as a separate historical stage, although its earliest form closely resembles Attic Greek and its latest form approaches Medieval Greek. There were several regional dialects of Ancient Greek, of which Attic Greek developed into Koine. Dia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; attributively , ; nominally , , ) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in South Asia after its predecessor languages had diffused there from the northwest in the late Bronze Age. Sanskrit is the sacred language of Hinduism, the language of classical Hindu philosophy, and of historical texts of Buddhism and Jainism. It was a link language in ancient and medieval South Asia, and upon transmission of Hindu and Buddhist culture to Southeast Asia, East Asia and Central Asia in the early medieval era, it became a language of religion and high culture, and of the political elites in some of these regions. As a result, Sanskrit had a lasting impact on the languages of South Asia, Southeast Asia and East Asia, especially in their formal and learned vocabularies. Sanskrit generally connotes several Old Indo-Aryan language varieties. The most archaic of these is the Vedic Sanskrit found in the Rig Veda, a colle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vowels
A vowel is a syllabic speech sound pronounced without any stricture in the vocal tract. Vowels are one of the two principal classes of speech sounds, the other being the consonant. Vowels vary in quality, in loudness and also in quantity (length). They are usually voiced and are closely involved in prosodic variation such as tone, intonation and stress. The word ''vowel'' comes from the Latin word , meaning "vocal" (i.e. relating to the voice). In English, the word ''vowel'' is commonly used to refer both to vowel sounds and to the written symbols that represent them (a, e, i, o, u, and sometimes y). Definition There are two complementary definitions of vowel, one phonetic and the other phonological. *In the phonetic definition, a vowel is a sound, such as the English "ah" or "oh" , produced with an open vocal tract; it is median (the air escapes along the middle of the tongue), oral (at least some of the airflow must escape through the mouth), frictionless an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allophone
In phonology, an allophone (; from the Greek , , 'other' and , , 'voice, sound') is a set of multiple possible spoken soundsor ''phones''or signs used to pronounce a single phoneme in a particular language. For example, in English, (as in ''stop'' ) and the aspirated form (as in ''top'' ) are allophones for the phoneme , while these two are considered to be different phonemes in some languages such as Thai. On the other hand, in Spanish, (as in ''dolor'' ) and (as in ''nada'' ) are allophones for the phoneme , while these two are considered to be different phonemes in English. The specific allophone selected in a given situation is often predictable from the phonetic context, with such allophones being called positional variants, but some allophones occur in free variation. Replacing a sound by another allophone of the same phoneme usually does not change the meaning of a word, but the result may sound non-native or even unintelligible. Native speakers of a given languag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genitive
In grammar, the genitive case (abbreviated ) is the grammatical case that marks a word, usually a noun, as modifying another word, also usually a noun—thus indicating an attributive relationship of one noun to the other noun. A genitive can also serve purposes indicating other relationships. For example, some verbs may feature arguments in the genitive case; and the genitive case may also have adverbial uses (see adverbial genitive). Genitive construction includes the genitive case, but is a broader category. Placing a modifying noun in the genitive case is one way of indicating that it is related to a head noun, in a genitive construction. However, there are other ways to indicate a genitive construction. For example, many Afroasiatic languages place the head noun (rather than the modifying noun) in the construct state. Possessive grammatical constructions, including the possessive case, may be regarded as a subset of genitive construction. For example, the genitive construc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nominative
In grammar, the nominative case (abbreviated ), subjective case, straight case or upright case is one of the grammatical cases of a noun or other part of speech, which generally marks the subject of a verb or (in Latin and formal variants of English) the predicate noun or predicate adjective, as opposed to its object or other verb arguments. Generally, the noun "that is doing something" is in the nominative, and the nominative is often the form listed in dictionaries. Etymology The English word ''nominative'' comes from Latin ''cāsus nominātīvus'' "case for naming", which was translated from Ancient Greek ὀνομαστικὴ πτῶσις, ''onomastikḗ ptôsis'' "inflection for naming", from ''onomázō'' "call by name", from ''ónoma'' "name". Dionysius Thrax in his The Art of Grammar refers to it as ''orthḗ'' or ''eutheîa'' "straight", in contrast to the oblique or "bent" cases. Characteristics The reference form (more technically, the ''least marked'') of ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Athematic Accent/ablaut Classes
In Indo-European studies, a thematic vowel or theme vowel is the vowel or from ablaut placed before the ending of a Proto-Indo-European (PIE) word. Nouns, adjectives, and verbs in the Indo-European languages with this vowel are thematic, and those without it are athematic. Used more generally, a thematic vowel is any vowel found at the end of the stem of a word. Outside Indo-European, the term "thematic vowel" is also used in the grammar of Kartvelian languages (see Georgian verb paradigm for more information on thematic vowels). Proto-Indo-European PIE verbs and nominals (nouns and adjectives) consist of three parts: :\underbrace_ The thematic vowel, if present, occurs at the end of the suffix (which may include other vowels or consonants) and before the ending: * 'heat' > Ancient Greek (''thérmos'') * '(he) bears' > Sanskrit ''bhárati'', Gothic Athematic forms, by contrast, have a suffix ending in a consonant, or no suffix at all (or arguably a null suffix): * 'fath ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |