|
Protective Put
A protective option or married option is a financial transaction in which the holder of securities buys a type of financial options contract known as a "call" or a " put" against stock that they own or are shorting. The buyer of a protective option pays compensation, or "premium", for this transaction, which can limit losses on their stock position. One protective option is purchased for every hundred shares the buyer wishes to cover. A protective option constructed with a put to cover shares of stock that an investor owns is called a protective put or married put, while one constructed with a call to cover shorted stock is a protective call or married call. In equilibrium, a protective put will have the same net payoff as merely buying a call option, and a protective call will have the same net payoff as merely buying a put option. A protective option could be used instead of a stop-loss order to limit losses on a stock position, especially in a fast-moving market. Although buye ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Long Call Option
Long may refer to: Measurement * Long, characteristic of something of great time, duration * Long, characteristic of something of great length * Longitude (abbreviation: long.), a geographic coordinate * Longa (music), note value in early music mensural notation Places Asia * Long District, Laos * Long District, Phrae, Thailand * Longjiang (other) or River Long (lit. "dragon river"), one of several rivers in China * Yangtze River or Changjiang (lit. "Long River"), China Elsewhere * Long, Somme, France People * Long (Chinese surname) * Long (Western surname) Fictional characters * Long (Bloody Roar), Long (''Bloody Roar''), in the video game series * Long, Aeon of Permanence in Honkai: Star Rail Sports * Long, a Fielding (cricket)#Modifiers, fielding term in cricket * Long, in tennis and similar games, beyond the service line during a serve and beyond the baseline during play Other uses * , a U.S. Navy ship name * Long (finance), a position in finance, especially sto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Long Put Option
Long may refer to: Measurement * Long, characteristic of something of great duration * Long, characteristic of something of great length * Longitude (abbreviation: long.), a geographic coordinate * Longa (music), note value in early music mensural notation Places Asia * Long District, Laos * Long District, Phrae, Thailand * Longjiang (other) or River Long (lit. "dragon river"), one of several rivers in China * Yangtze River or Changjiang (lit. "Long River"), China Elsewhere * Long, Somme, France People * Long (Chinese surname) * Long (Western surname) Fictional characters * Long (''Bloody Roar''), in the video game series * Long, Aeon of Permanence in Honkai: Star Rail Sports * Long, a fielding term in cricket * Long, in tennis and similar games, beyond the service line during a serve and beyond the baseline during play Other uses * , a U.S. Navy ship name * Long (finance), a position in finance, especially stock markets * Lòng, name for a laneway in Sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Security (finance)
A security is a tradable financial asset. The term commonly refers to any form of financial instrument, but its legal definition varies by jurisdiction. In some countries and languages people commonly use the term "security" to refer to any form of financial instrument, even though the underlying legal and regulatory regime may not have such a broad definition. In some jurisdictions the term specifically excludes financial instruments other than equity and fixed income instruments. In some jurisdictions it includes some instruments that are close to equities and fixed income, e.g., equity warrants. Securities may be represented by a certificate or, more typically, they may be "non-certificated", that is in electronic ( dematerialized) or " book entry only" form. Certificates may be ''bearer'', meaning they entitle the holder to rights under the security merely by holding the security, or ''registered'', meaning they entitle the holder to rights only if they appear on a securi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Option (finance)
In finance, an option is a contract which conveys to its owner, the ''holder'', the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell a specific quantity of an underlying asset or instrument at a specified strike price on or before a specified date, depending on the style of the option. Options are typically acquired by purchase, as a form of compensation, or as part of a complex financial transaction. Thus, they are also a form of asset (or contingent liability) and have a valuation that may depend on a complex relationship between underlying asset price, time until expiration, market volatility, the risk-free rate of interest, and the strike price of the option. Options may be traded between private parties in '' over-the-counter'' (OTC) transactions, or they may be exchange-traded in live, public markets in the form of standardized contracts. Definition and application An option is a contract that allows the holder the right to buy or sell an underlying asset or financia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Call Option
In finance, a call option, often simply labeled a "call", is a contract between the buyer and the seller of the call Option (finance), option to exchange a Security (finance), security at a set price. The buyer of the call option has the right, but not the obligation, to buy an agreed quantity of a particular commodity or financial instrument (the underlying) from the seller of the option at or before a certain time (the Expiration (options), expiration date) for a certain price (the strike price). This effectively gives the buyer a Long (finance), ''long'' position in the given asset. The seller (or "writer") is obliged to sell the commodity or financial instrument to the buyer if the buyer so decides. This effectively gives the seller a Short (finance), ''short'' position in the given asset. The buyer pays a fee (called a Insurance, premium) for this right. The term "call" comes from the fact that the owner has the right to "call the stock away" from the seller. Price of opt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Put Option
In finance, a put or put option is a derivative instrument in financial markets that gives the holder (i.e. the purchaser of the put option) the right to sell an asset (the ''underlying''), at a specified price (the ''strike''), by (or on) a specified date (the '' expiry'' or ''maturity'') to the ''writer'' (i.e. seller) of the put. The purchase of a put option is interpreted as a negative sentiment about the future value of the underlying stock. page 15 , 4.2.3 Positive and negative sentiment The term "put" comes from the fact that the owner has the right to "put up for sale" the stock or index. Puts may also be combined with other derivatives as part of more complex investment strategies, and in particular, may be useful for hedging. Holding a European put option is equivalent to holding the corresponding call option and selling an appropriate forward contract. This equivalence is called " put-call parity". Put options are most commonly used in the stock market to prot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Short (finance)
In finance, being short in an asset means investing in such a way that the investor will profit if the market value of the asset falls. This is the opposite of the more common Long (finance), long Position (finance), position, where the investor will profit if the market value of the asset rises. An investor that sells an asset short is, as to that asset, a short seller. There are a number of ways of achieving a short position. The most basic is physical selling short or short-selling, by which the short seller Securities lending, borrows an asset (often a security (finance), security such as a share (finance), share of stock or a bond (finance), bond) and sells it. The short seller must later buy the same amount of the asset to return it to the lender. If the market price of the asset has fallen in the meantime, the short seller will have made a profit equal to the difference in price. Conversely, if the price has risen then the short seller will bear a loss. The short seller ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Order (exchange)
An order is an instruction to buy or sell on a trading venue such as a stock market, bond market, commodity market, financial derivative market or cryptocurrency exchange. These instructions can be simple or complicated, and can be sent to either a broker or directly to a trading venue via direct market access. There are some standard instructions for such orders. Market order A market order is a buy or sell order to be executed immediately at the ''current'' ''market'' prices. As long as there are willing sellers and buyers, market orders are filled. Market orders are used when certainty of execution is a priority over the price of execution. A market order is the simplest of the order types. This order type does not allow any control over the price received. The order is filled at the best price available at the relevant time. In fast-moving markets, the price paid or received may be quite different from the last price quoted before the order was entered. A market order may b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strike Price
In finance, the strike price (or exercise price) of an option is a fixed price at which the owner of the option can buy (in the case of a call), or sell (in the case of a put), the underlying security or commodity. The strike price may be set by reference to the spot price, which is the market price of the underlying security or commodity on the day an option is taken out. Alternatively, the strike price may be fixed at a discount or premium. The strike price is a key variable in a derivatives contract between two parties. Where the contract requires delivery of the underlying instrument, the trade will be at the strike price, regardless of the market price of the underlying instrument at that time. Moneyness Moneyness is the value of a financial contract if the contract settlement is financial. More specifically, it is the difference between the strike price of the option and the current trading price of its underlying security. In options trading, terms such as ''in-the- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Retracement (finance)
Retracement in finance is a complete or partial reversal of the price of a security or a derivative from its current trend A fad, trend, or craze is any form of collective behavior that develops within a culture, a generation, or social group in which a group of people enthusiastically follow an impulse for a short time period. Fads are objects or behaviors th ..., thereby creating a temporary counter-trend. Not to be confused with Fibonacci Retracement, market correction and/or market reversal, which are the most popular types of retracements. References As used by journalists: *http://www.marketwatch.com/story/trust-the-streak-this-is-more-than-just-some-bear-market-rally-2016-03-21 *http://www.chicagotribune.com/news/sns-wp-blm-currency-comment-8c2c2374-f0ff-11e5-a2a3-d4e9697917d1-20160323-story.html *https://www.cnbc.com/2016/03/21/is-the-pain-trade-still-higher.html {{finance-stub Financial markets ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
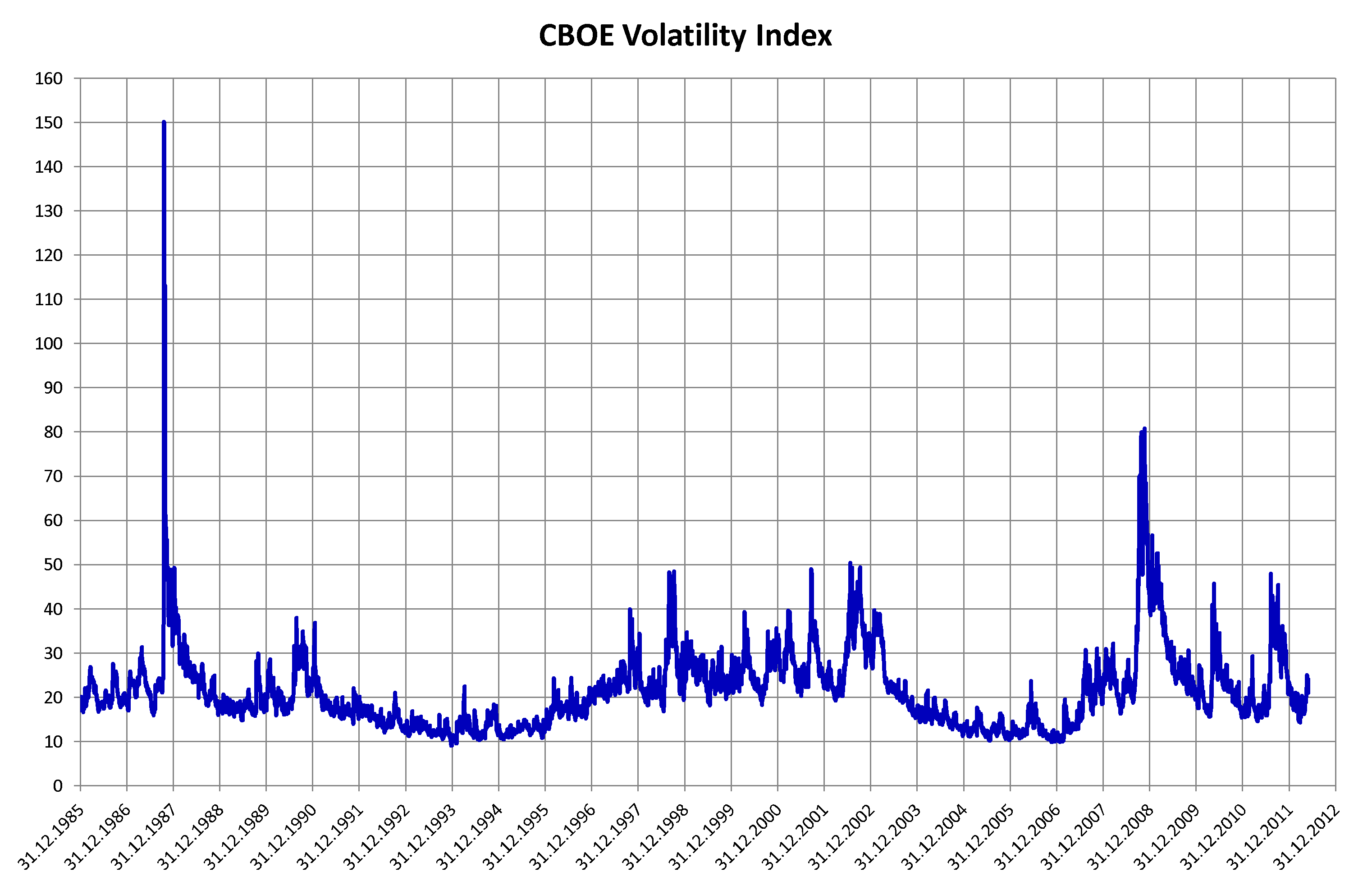
Volatility (finance)
In finance, volatility (usually denoted by "sigma, σ") is the Variability (statistics), degree of variation of a trading price series over time, usually measured by the standard deviation of logarithmic returns. Historic volatility measures a time series of past market prices. Implied volatility looks forward in time, being derived from the market price of a market-traded derivative (in particular, an option). Volatility terminology Volatility as described here refers to the actual volatility, more specifically: * actual current volatility of a financial instrument for a specified period (for example 30 days or 90 days), based on historical prices over the specified period with the last observation the most recent price. * actual historical volatility which refers to the volatility of a financial instrument over a specified period but with the last observation on a date in the past **near synonymous is realized volatility, the square root of the realized variance, in turn c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Covered Option
A covered option is a financial transaction in which the holder of securities sells (or "writes") a type of financial options contract known as a "call" or a " put" against stock that they own or are shorting. The seller of a covered option receives compensation, or "premium", for this transaction, which can limit losses; however, the act of selling a covered option also limits their profit potential to the upside. One covered option is sold for every hundred shares the seller wishes to cover. A covered option constructed with a call is called a "covered call", while one constructed with a put is a "covered put". This strategy is generally considered conservative because the seller of a covered option reduces both their risk and their return. Characteristics Covered calls are bullish by nature, while covered puts are bearish. The payoff from selling a covered call is identical to selling a short naked put. Both variants are a short implied volatility strategy. Covered cal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |