|
Prosthecobacter
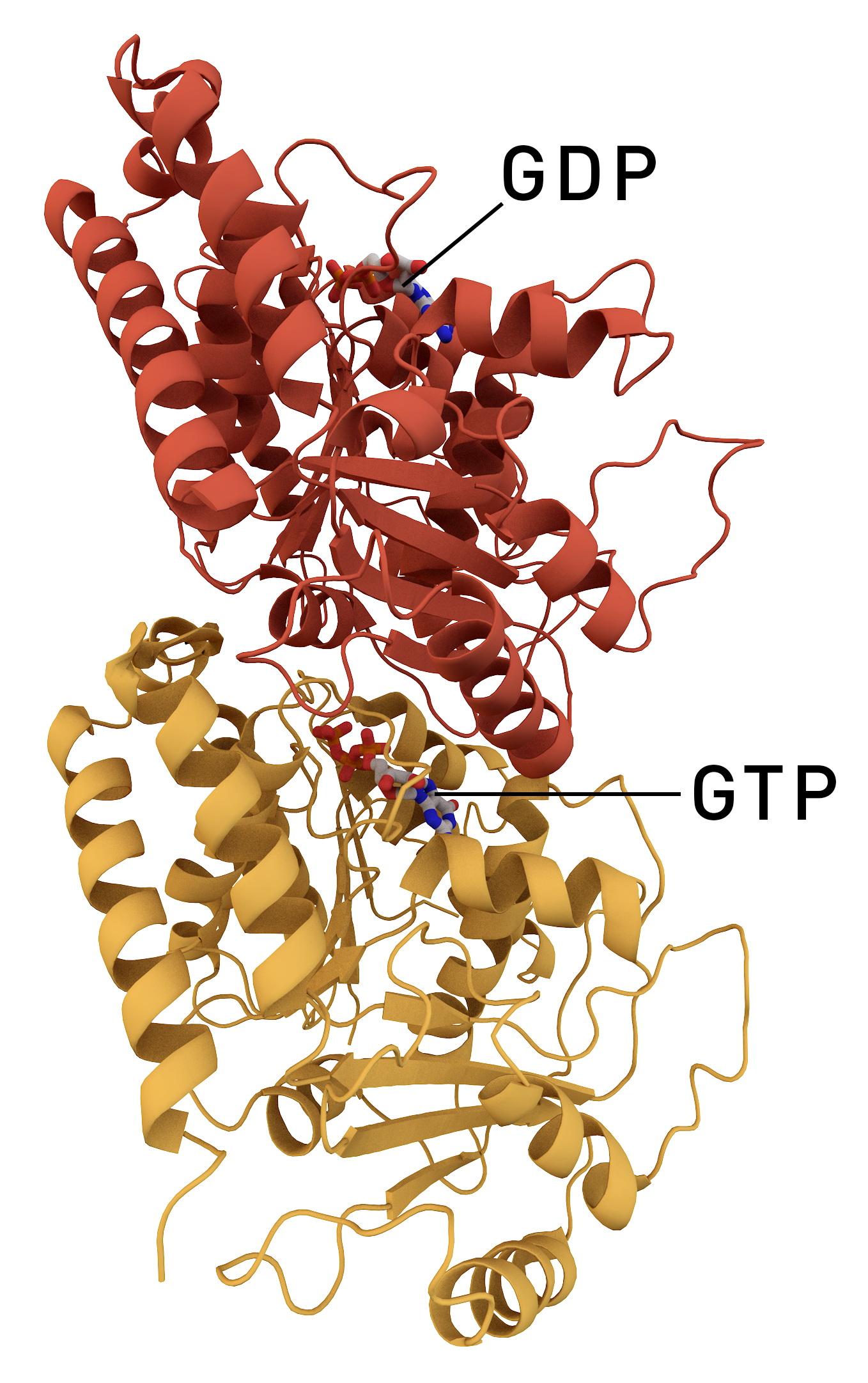
''Prosthecobacter'' is a genus of bacteria from the phylum Verrucomicrobiota with a distinctive characteristic; the presence of tubulin-like genes. Tubulins, which are components of the microtubule, have never been observed in Gracilicutes before. Tubulin was long thought to be specific to eukaryotes. More recently, however, several prokaryotic proteins have been shown to be related to tubulin. Most bacteria have a homologous structure, FtsZ. ''Prosthecobacter'' are the exception to this, containing genes that have higher sequence homology to eukaryotic tubulin than FtsZ. These genes are called bacterial tubulin a (BtubA) and bacterial tubulin b (BtubB). The properties are not exactly same. However, surface loops and microtubules are extremely similar. Phylogeny The currently accepted taxonomy is based on the List of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature (LPSN) and National Center for Biotechnology Information The National Center for Biotechnology Informa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prosthecobacter Debontii
''Prosthecobacter'' is a genus of bacteria from the phylum Verrucomicrobiota with a distinctive characteristic; the presence of tubulin-like genes. Tubulins, which are components of the microtubule, have never been observed in Gracilicutes before. Tubulin was long thought to be specific to eukaryotes. More recently, however, several prokaryotic proteins have been shown to be related to tubulin. Most bacteria have a homologous structure, FtsZ. ''Prosthecobacter'' are the exception to this, containing genes that have higher sequence homology to eukaryotic tubulin than FtsZ. These genes are called bacterial tubulin a (BtubA) and bacterial tubulin b (BtubB). The properties are not exactly same. However, surface loops and microtubules are extremely similar. Phylogeny The currently accepted taxonomy is based on the List of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature (LPSN) and National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) See also * List of bacterial orders * List o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prosthecobacter Fluviatilis
''Prosthecobacter fluviatilis'' is a bacterium from the genus ''Prosthecobacter ''Prosthecobacter'' is a genus of bacteria from the phylum Verrucomicrobiota with a distinctive characteristic; the presence of tubulin-like genes. Tubulins, which are components of the microtubule, have never been observed in Gracilicutes ...''. References Verrucomicrobiota Bacteria described in 2008 {{Bacteria-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prosthecobacter Algae
''Prosthecobacter algae'' is a Gram-negative, facultatively anaerobic and fusiform-shaped bacterium from the genus ''Prosthecobacter'' which has been isolated from activated sludge The activated sludge process is a type of biological wastewater treatment process for treating sewage or industrial wastewaters using aeration and a biological floc composed of bacteria and protozoa. It uses air (or oxygen) and microorganisms .... References Verrucomicrobiota Bacteria described in 2014 {{Bacteria-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tubulin
Tubulin in molecular biology can refer either to the tubulin protein superfamily of globular proteins, or one of the member proteins of that superfamily. α- and β-tubulins polymerize into microtubules, a major component of the eukaryotic cytoskeleton. Microtubules function in many essential cellular processes, including mitosis. Tubulin-binding drugs kill cancerous cells by inhibiting microtubule dynamics, which are required for DNA segregation and therefore cell division. In eukaryotes, there are six members of the tubulin superfamily, although not all are present in all species.Turk E, Wills AA, Kwon T, Sedzinski J, Wallingford JB, Stearns "Zeta-Tubulin Is a Member of a Conserved Tubulin Module and Is a Component of the Centriolar Basal Foot in Multiciliated Cells"Current Biology (2015) 25:2177-2183. Both α and β tubulins have a mass of around 50 kDa and are thus in a similar range compared to actin (with a mass of ~42 kDa). In contrast, tubulin polymers (microtubules) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Bacteria Genera
This article lists the genera of the bacteria. The currently accepted taxonomy is based on the List of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature (LPSN) and National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI). However many taxonomic names are taken from the GTDB release 07-RS207 (8th April 2022). Phyla {, border="0" style="width: 100%;" ! , - , style="border:0px" valign="top", {, class="wikitable sortable" style="width: 100%; font-size: 95%;" !Syperphylum !Phylum !Authority !Synonyms , - , Parakaryota , , , Myojin parakaryote , - , , " Canglongiota" , Zhang et al. 2022 , , - , , " Fervidibacteria" , , OctSpa1-106 , - , , " Heilongiota" , Zhang et al. 2022 , , - , , " Qinglongiota" , Zhang et al. 2022 , , - , , " Salinosulfoleibacteria" , Tazi et al. 2006 , , - , , " Teskebacteria" , Dojka 1998 , WS1 , - , , " Tharpellota" , Speth et al. 2022 , , - , Terrabacteria , Chloroflexota , Whitman et al. 2018 , " Thermomicrobiota" , - , Terrabacteria , " Dormibacter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Verrucomicrobiota
Verrucomicrobiota is a phylum of Gram-negative bacteria that contains only a few described species. The species identified have been isolated from fresh water, marine and soil environments and human faeces. A number of as-yet uncultivated species have been identified in association with eukaryotic hosts including extrusive explosive ectosymbionts of protists and endosymbionts of nematodes residing in their gametes. Verrucomicrobiota are abundant within the environment, though relatively inactive. This phylum is considered to have two sister phyla: Chlamydiota (formerly Chlamydiae) and Lentisphaerota (formerly Lentisphaerae) within the PVC superphylum. The Verrucomicrobiota phylum can be distinguished from neighbouring phyla within the PVC group by the presence of several conserved signature indels (CSIs). These CSIs represent unique, synapomorphic characteristics that suggest common ancestry within Verrucomicrobiota and an independent lineage amidst other bacteria. CSIs hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microtubule
Microtubules are polymers of tubulin that form part of the cytoskeleton and provide structure and shape to eukaryotic cells. Microtubules can be as long as 50 micrometres, as wide as 23 to 27 nm and have an inner diameter between 11 and 15 nm. They are formed by the polymerization of a dimer of two globular proteins, alpha and beta tubulin into protofilaments that can then associate laterally to form a hollow tube, the microtubule. The most common form of a microtubule consists of 13 protofilaments in the tubular arrangement. Microtubules play an important role in a number of cellular processes. They are involved in maintaining the structure of the cell and, together with microfilaments and intermediate filaments, they form the cytoskeleton. They also make up the internal structure of cilia and flagella. They provide platforms for intracellular transport and are involved in a variety of cellular processes, including the movement of secretory vesicles, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gracilicutes
Gracilicutes (Latin: ''gracilis'', slender, and ''cutis'', skin, referring to the cell wall) is a clade in bacterial phylogeny. Traditionally gram staining results were most commonly used as a classification tool, consequently until the advent of molecular phylogeny, the Kingdom Monera (as the domains Bacteria and Archaea were known then) was divided into four phyla, * Gracilicutes (gram-negative, it is split in many groups, but some authors still use it in a narrower sense) * Firmacutes ic(gram-positive, subsequently corrected to Firmicutes, today it excludes the Actinomycetota) * Mollicutes (gram variable, later renamed Tenericutes and now Mycoplasmatota, e.g. ''Mycoplasma'') * Mendosicutes (uneven gram stain, "methanogenic bacteria" now known as methanogens and classed as Archaea) This classification system was abandoned in favour of the three-domain system based on molecular phylogeny started by C. Woese. Using hand-drawn schematics rather than standard molecular phylog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |