|
Prosperity Bonus
Alberta's Prosperity Bonus, nicknamed Ralph bucks after then-premier Ralph Klein, was a one-time $400 payment paid out to almost 3 million Albertan residents in 2006. The Government of Alberta paid a dividend to residents of Alberta due to a massive oil-fuelled provincial budget surplus. Background - 2004 general election Notice for Klein's prosperity bonus would come less than a year following the 2004 Alberta general election which saw the Progressive Conservative Party of Alberta elected for the tenth consecutive majority government, and Klein continuing as Premier for the fourth straight term. Despite retaining power in Alberta, the election revealed weakness in the popularity of Premier Klein and the Progressive Conservative Party. Their share of the popular vote dropped from 61.9% in 2001 to 46.8%. Prosperity bonus announcement In September 2005, Alberta Premier Ralph Klein announced in an open letter to Albertans that the province was expecting significant higher than e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ralph Klein
Ralph Philip Klein (November 1, 1942 – March 29, 2013) was a Canadian politician and journalist who served as the 12th premier of Alberta and leader of the Progressive Conservative Association of Alberta from 1992 until his retirement in 2006. Klein also served as the 32nd mayor of Calgary from 1980 to 1989. Ralph was born and mostly grew up in Calgary, Alberta. After dropping out of High School in grade 11, Klein joined the Royal Canadian Air Force reserves for one year and then attended the Calgary Business College. Klein later worked as a teacher and principal at the Calgary Business College, and later public relations with non-profits. After that, Klein became a prominent local journalist in Calgary where he reported on the challenges of the working class, social outcasts and First Nations, endearing himself to those groups. In 1980, Klein turned his attention to politics and as an underdog was elected Mayor of Calgary, where he oversaw the boom and bust of the oil indu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tax Return (Canada)
A tax return is the completion of documentation that calculates an entity or individual's income earned and the amount of taxes to be paid to the government or government organizations or, potentially, back to the taxpayer. Taxation is one of the biggest sources of income for the government. There are two types of taxes—Direct tax, direct and Indirect tax, indirect—which are both parts of the tax revenue. Tax revenue is the income gained by government from taxes that are levied on income, profit, goods and services, land revenue, ownership, and transfer of property, and other taxes. Total tax revenue calculated as a percentage of GDP shows the share of the country’s output collected by the government through taxes. Tax revenue is used by governments to grant sums of money to communities, the military, education, hospitals, and infrastructure. In the United States the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) administers federal tax laws. It is a government entity that fulfils thre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Credit
Social credit is a distributive philosophy of political economy developed by C. H. Douglas. Douglas attributed economic downturns to discrepancies between the cost of goods and the compensation of the workers who made them. To combat what he saw as a chronic deficiency of purchasing power in the economy, Douglas prescribed government intervention in the form of the issuance of debt free money directly to consumers or producers (if they sold their product below cost to consumers) in order to combat such discrepancy. In defence of his ideas, Douglas wrote that "Systems were made for men, and not men for systems, and the interest of man which is self-development, is above all systems, whether theological, political or economic." Douglas said that Social Crediters want to build a new civilization based upon " absolute economic security" for the individual, where "they shall sit every man under his vine and under his fig tree; and none shall make them afraid." In his words, "what ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prosperity Certificate
In 1936, the Alberta Social Credit Party-led government of the Province of Alberta, Canada, introduced prosperity certificates in an attempt to alleviate the effects of the Great Depression. Premier William Aberhart's government had won power in the 1935 provincial election partly on the scheme. The certificates were not issued to the general public as Aberhart had promised in his election platform but instead were used to pay relief workers on provincial public works projects and were put into circulation via special agreements with municipalities. Although not technically money, each certificate was marked with a value of one dollar, and redeemable for $1 Canadian at the end of its life or on certain dates during the course of the program. Other certificates were in the amount of $5. $239,000 worth of scrip was issued in August 1936. A goal of the program was to encourage spending and circulation of the spending power. To achieve this, hoarding of the certificates was discou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alberta Heritage Savings Trust Fund
The Alberta Heritage Savings Trust Fund (HSTF) is a sovereign wealth fund established in 1976 by the Government of Alberta under then-Premier Peter Lougheed. The Heritage Savings Trust Fund was created with three objectives: "to save for the future, to strengthen or diversify the economy, and to improve the quality of life of Albertans." The operations of the Heritage Savings Trust Fund are subject to the ''Alberta Heritage Savings Trust Fund Act'' and with the goal of providing "prudent stewardship of the savings from Alberta's non-renewable resources by providing the greatest financial returns on those savings for current and future generations of Albertans." Between 1976 and 1983 the Government of Alberta deposited a portion of oil revenue into the fund. The Heritage Savings Trust Fund used oil revenues to invest for the long term in such areas as health care, education and research and as a way of ensuring that the development of non-renewable resources would be of long-term ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ATB Financial
ATB Financial is a financial institution and Crown corporation wholly owned by the province of Alberta, the only province in Canada with such a financial institution under its exclusive ownership. Originally established as Alberta Treasury Branches in 1938, ATB Financial operates only in Alberta and provides financial services to over 800,000 Albertan residents and businesses. It is the largest public bank in North America and Alberta’s largest financial institution based in the province. Headquartered in Edmonton, ATB Financial has over 5000 team members. ATB is not a chartered bank, meaning it is not regulated by the Canadian federal government under the ''Bank Act'' and associated regulations. ATB is instead regulated entirely by the Government of Alberta under the authority of the ''ATB Financial Act'' and associated regulations; the legislation is modeled on the statutes, regulations, and guidelines which govern banks and other federally chartered financial institutio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deficit Spending
Within the budgetary process, deficit spending is the amount by which spending exceeds revenue over a particular period of time, also called simply deficit, or budget deficit; the opposite of budget surplus. The term may be applied to the budget of a government, private company, or individual. Government deficit spending was first identified as a necessary economic tool by John Maynard Keynes in the wake of the Great Depression. It is a central point of controversy in economics, as discussed below. Controversy Government deficit spending is a central point of controversy in economics, with prominent economists holding differing views. The mainstream economics position is that deficit spending is desirable and necessary as part of countercyclical fiscal policy, but that there should not be a structural deficit (i.e., permanent deficit): The government should run deficits during recessions to compensate for the shortfall in aggregate demand, but should run surpluses in boom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2010s Oil Glut
The 2010s oil glut is a significant surplus of crude oil that started in 2014–2015 and accelerated in 2016, with multiple causes. They include general oversupply as unconventional US and Canadian tight oil (shale oil) production reached critical volumes, geopolitical rivalries among oil-producing nations, falling demand across commodities markets due to the deceleration of the Chinese economy, and possible restraint of long-term demand as environmental policy promotes fuel efficiency and steers an increasing share of energy consumption away from fossil fuels. The world price of oil was above US in 2012, and remained relatively strong above $100 until September 2014, after which it entered a sharp downward spiral, falling below $30 by January 2016. OPEC production was poised to rise further with the lifting of international sanctions against Iran, at a time when markets already appeared to be oversupplied by at least per day. In December 2015, ''The Telegraph'' quoted a maj ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2000s Energy Crisis
From the mid-1980s to September 2003, the inflation-adjusted price of a barrel of crude oil on NYMEX was generally under US$25/barrel in 2008 dollars. During 2003, the price rose above $30, reached $60 by 11 August 2005, and peaked at $147.30 in July 2008. Commentators attributed these price increases to many factors, including Middle East tension, soaring demand from China, the falling value of the U.S. dollar, reports showing a decline in petroleum reserves, worries over peak oil, and financial speculation. For a time, geopolitical events and natural disasters had strong short-term effects on oil prices, such as North Korean missile tests, the 2006 conflict between Israel and Lebanon, worries over Iranian nuclear plans in 2006, Hurricane Katrina, and various other factors. By 2008, such pressures appeared to have an insignificant impact on oil prices given the onset of the global recession. The recession caused demand for energy to shrink in late 2008, with oil prices c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canadian Taxpayers Federation
The Canadian Taxpayers Federation (CTF; french: Fédération canadienne des contribuables, link=no) is a federally incorporated, non-profit organization in Canada. It claimed 30,517 donors and 215,009 supporters in 2018–19. Voting membership, however, is restricted to the board of directors. According to its by-laws, the board "can have as few as three and as many as 20" members. In 2017, it reportedly had a voting membership of six board members, and in 2020 it had four.https://www.taxpayer.com/about/board/ It describes itself as a taxpayers advocacy group, and the organization advocates lower taxes, less waste, and an increase in government accountability. It was founded in Saskatchewan in 1990 through a merger of the Association of Saskatchewan Taxpayers and the Resolution One Association of Alberta. The CTF maintains a federal office in Ottawa, and has staff based in Calgary, Vancouver, Victoria, Edmonton, Regina, Toronto, Montreal and Halifax. Provincial offices conduct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
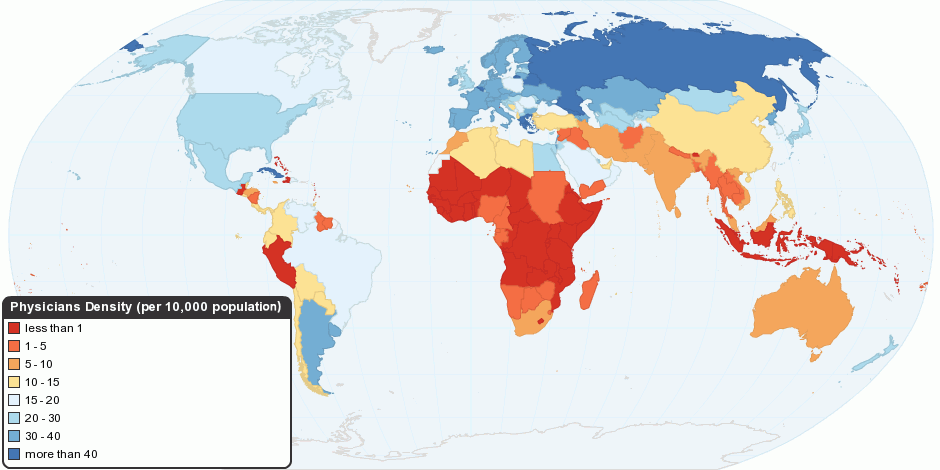
Health Care
Health care or healthcare is the improvement of health via the prevention, diagnosis, treatment, amelioration or cure of disease, illness, injury, and other physical and mental impairments in people. Health care is delivered by health professionals and allied health fields. Medicine, dentistry, pharmacy, midwifery, nursing, optometry, audiology, psychology, occupational therapy, physical therapy, athletic training, and other health professions all constitute health care. It includes work done in providing primary care, secondary care, and tertiary care, as well as in public health. Access to health care may vary across countries, communities, and individuals, influenced by social and economic conditions as well as health policies. Providing health care services means "the timely use of personal health services to achieve the best possible health outcomes". Factors to consider in terms of health care access include financial limitations (such as insurance coverage), geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tax Cut
A tax cut represents a decrease in the amount of money taken from taxpayers to go towards government revenue. Tax cuts decrease the revenue of the government and increase the disposable income of taxpayers. Tax cuts usually refer to reductions in the percentage of tax paid on income, goods and services. As they leave consumers with more disposable income, tax cuts are an example of an expansionary fiscal policy. Tax cuts also include reduction in tax in other ways, such as tax credit, deductions and loopholes. How a tax cut affects the economy depends on which tax is cut. Policies that increase disposable income for lower- and middle-income households are more likely to increase overall consumption and "hence stimulate the economy". Tax cuts in isolation boost the economy because they increase government borrowing. However, they are often accompanied by spending cuts or changes in monetary policy that can offset their stimulative effects. Types Tax cuts are typically cuts in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.png)