|
Propositional Truncation
The vertical bar, , is a glyph with various uses in mathematics, computing, and typography. It has many names, often related to particular meanings: Sheffer stroke (in logic), pipe, bar, or (literally the word "or"), vbar, and others. Usage Mathematics The vertical bar is used as a mathematical symbol in numerous ways: * absolute value: , x, , read "the ''absolute value'' of ''x''" * cardinality: , S, , read "the ''cardinality'' of the set ''S''" * conditional probability: P(X, Y), reads "the probability of ''X'' ''given'' ''Y''" * determinant: , A, , read "the ''determinant'' of the matrix ''A''". When the matrix entries are written out, the determinant is denoted by surrounding the matrix entries by vertical bars instead of the usual brackets or parentheses of the matrix, as in \begin a & b \\ c & d\end. * distance: P, ab, denoting the shortest ''distance'' between point P to line ab, so line P, ab is perpendicular to line ab * divisibility: a \mid b, read "''a'' ''divid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chōonpu
The , also known as , , , or Katakana-Hiragana Prolonged Sound Mark by the Unicode Consortium, is a Japanese symbol that indicates a ''chōon'', or a long vowel of two morae in length. Its form is a horizontal or vertical line in the center of the text with the width of one kanji or kana character. It is written horizontally in horizontal text and vertically in vertical text (). The chōonpu is usually used to indicate a long vowel sound in katakana writing, rarely in hiragana writing, and never in romanized Japanese. The ''chōonpu'' is a distinct mark from the dash, and in most Japanese typefaces it can easily be distinguished. In horizontal writing it is similar in appearance to, but should not be confused with, the kanji character ("one"). The symbol is sometimes used with hiragana, for example in the signs of ramen restaurants, which are normally written /らあめん in hiragana, and ラーメン in katakana. Usually, however, hiragana does not use the ''chōonpu'' bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matrix (mathematics)
In mathematics, a matrix (plural matrices) is a rectangular array or table of numbers, symbols, or expressions, arranged in rows and columns, which is used to represent a mathematical object or a property of such an object. For example, \begin1 & 9 & -13 \\20 & 5 & -6 \end is a matrix with two rows and three columns. This is often referred to as a "two by three matrix", a "-matrix", or a matrix of dimension . Without further specifications, matrices represent linear maps, and allow explicit computations in linear algebra. Therefore, the study of matrices is a large part of linear algebra, and most properties and operations of abstract linear algebra can be expressed in terms of matrices. For example, matrix multiplication represents composition of linear maps. Not all matrices are related to linear algebra. This is, in particular, the case in graph theory, of incidence matrices, and adjacency matrices. ''This article focuses on matrices related to linear algebra, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Logic
Logic is the study of correct reasoning. It includes both formal and informal logic. Formal logic is the science of deductively valid inferences or of logical truths. It is a formal science investigating how conclusions follow from premises in a topic-neutral way. When used as a countable noun, the term "a logic" refers to a logical formal system that articulates a proof system. Formal logic contrasts with informal logic, which is associated with informal fallacies, critical thinking, and argumentation theory. While there is no general agreement on how formal and informal logic are to be distinguished, one prominent approach associates their difference with whether the studied arguments are expressed in formal or informal languages. Logic plays a central role in multiple fields, such as philosophy, mathematics, computer science, and linguistics. Logic studies arguments, which consist of a set of premises together with a conclusion. Premises and conclusions are usual ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colon (punctuation)
The colon is a punctuation mark consisting of two equally sized dots aligned vertically. A colon often precedes an explanation, a list, or a quoted sentence. It is also used between hours and minutes in time, between certain elements in medical journal citations, chapter and verse in Bible citations, and, in the US, for salutations in business letters and other formal letter writing. History In Ancient Greek, in rhetoric and prosody, the term (', 'limb, member of a body') did not refer to punctuation, but to a member or section of a complete thought or passage; see also '' Colon (rhetoric)''. From this usage, in palaeography, a colon is a clause or group of clauses written as a line in a manuscript.''Oxford English Dictionary'', 1st ed. "colon, ''n.²''" Oxford University Press (Oxford), 1891. In the 3rd century BC, Aristophanes of Byzantium is alleged to have devised a punctuation system, in which the end of such a was thought to occasion a medium-length breath, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Less Than
In mathematics, an inequality is a relation which makes a non-equal comparison between two numbers or other mathematical expressions. It is used most often to compare two numbers on the number line by their size. There are several different notations used to represent different kinds of inequalities: * The notation ''a'' ''b'' means that ''a'' is greater than ''b''. In either case, ''a'' is not equal to ''b''. These relations are known as strict inequalities, meaning that ''a'' is strictly less than or strictly greater than ''b''. Equivalence is excluded. In contrast to strict inequalities, there are two types of inequality relations that are not strict: * The notation ''a'' ≤ ''b'' or ''a'' ⩽ ''b'' means that ''a'' is less than or equal to ''b'' (or, equivalently, at most ''b'', or not greater than ''b''). * The notation ''a'' ≥ ''b'' or ''a'' ⩾ ''b'' means that ''a'' is greater than or equal to ''b'' (or, equivalently, at least ''b'', or not less than ''b''). The r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Set-builder Notation
In set theory and its applications to logic, mathematics, and computer science, set-builder notation is a mathematical notation for describing a set by enumerating its elements, or stating the properties that its members must satisfy. Defining sets by properties is also known as set comprehension, set abstraction or as defining a set's intension. Sets defined by enumeration A set can be described directly by enumerating all of its elements between curly brackets, as in the following two examples: * \ is the set containing the four numbers 3, 7, 15, and 31, and nothing else. * \=\ is the set containing , , and , and nothing else (there is no order among the elements of a set). This is sometimes called the "roster method" for specifying a set. When it is desired to denote a set that contains elements from a regular sequence, an ellipses notation may be employed, as shown in the next examples: * \ is the set of integers between 1 and 100 inclusive. * \ is the set of natu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Restriction (mathematics)
In mathematics, the restriction of a function f is a new function, denoted f\vert_A or f , obtained by choosing a smaller domain A for the original function f. The function f is then said to extend f\vert_A. Formal definition Let f : E \to F be a function from a set E to a set F. If a set A is a subset of E, then the restriction of f to A is the function _A : A \to F given by _A(x) = f(x) for x \in A. Informally, the restriction of f to A is the same function as f, but is only defined on A. If the function f is thought of as a relation (x,f(x)) on the Cartesian product E \times F, then the restriction of f to A can be represented by its graph where the pairs (x,f(x)) represent ordered pairs in the graph G. Extensions A function F is said to be an ' of another function f if whenever x is in the domain of f then x is also in the domain of F and f(x) = F(x). That is, if \operatorname f \subseteq \operatorname F and F\big\vert_ = f. A '' '' (respectively, '' '', etc.) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Group (mathematics)
In mathematics, a group is a set and an operation that combines any two elements of the set to produce a third element of the set, in such a way that the operation is associative, an identity element exists and every element has an inverse. These three axioms hold for number systems and many other mathematical structures. For example, the integers together with the addition operation form a group. The concept of a group and the axioms that define it were elaborated for handling, in a unified way, essential structural properties of very different mathematical entities such as numbers, geometric shapes and polynomial roots. Because the concept of groups is ubiquitous in numerous areas both within and outside mathematics, some authors consider it as a central organizing principle of contemporary mathematics. In geometry groups arise naturally in the study of symmetries and geometric transformations: The symmetries of an object form a group, called the symmetry group of the ob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Order (group Theory)
In mathematics, the order of a finite group is the number of its elements. If a group is not finite, one says that its order is ''infinite''. The ''order'' of an element of a group (also called period length or period) is the order of the subgroup generated by the element. If the group operation is denoted as a multiplication, the order of an element of a group, is thus the smallest positive integer such that , where denotes the identity element of the group, and denotes the product of copies of . If no such exists, the order of is infinite. The order of a group is denoted by or , and the order of an element is denoted by or , instead of \operatorname(\langle a\rangle), where the brackets denote the generated group. Lagrange's theorem states that for any subgroup of a finite group , the order of the subgroup divides the order of the group; that is, is a divisor of . In particular, the order of any element is a divisor of . Example The symmetric group S3 ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norm (mathematics)
In mathematics, a norm is a function from a real or complex vector space to the non-negative real numbers that behaves in certain ways like the distance from the origin: it commutes with scaling, obeys a form of the triangle inequality, and is zero only at the origin. In particular, the Euclidean distance of a vector from the origin is a norm, called the Euclidean norm, or 2-norm, which may also be defined as the square root of the inner product of a vector with itself. A seminorm satisfies the first two properties of a norm, but may be zero for vectors other than the origin. A vector space with a specified norm is called a normed vector space. In a similar manner, a vector space with a seminorm is called a ''seminormed vector space''. The term pseudonorm has been used for several related meanings. It may be a synonym of "seminorm". A pseudonorm may satisfy the same axioms as a norm, with the equality replaced by an inequality "\,\leq\," in the homogeneity axiom. It ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
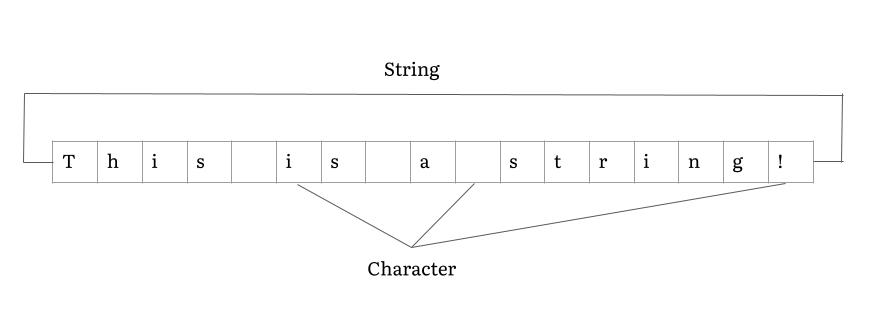
String (computer Science)
In computer programming, a string is traditionally a sequence of characters, either as a literal constant or as some kind of variable. The latter may allow its elements to be mutated and the length changed, or it may be fixed (after creation). A string is generally considered as a data type and is often implemented as an array data structure of bytes (or words) that stores a sequence of elements, typically characters, using some character encoding. ''String'' may also denote more general arrays or other sequence (or list) data types and structures. Depending on the programming language and precise data type used, a variable declared to be a string may either cause storage in memory to be statically allocated for a predetermined maximum length or employ dynamic allocation to allow it to hold a variable number of elements. When a string appears literally in source code, it is known as a string literal or an anonymous string. In formal languages, which are used in mathemati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



%2C_15th_century_(The_S.S._Teacher's_Edition-The_Holy_Bible_-_Plate_XII%2C_1).jpg)