|
Prophetic Perfect Tense
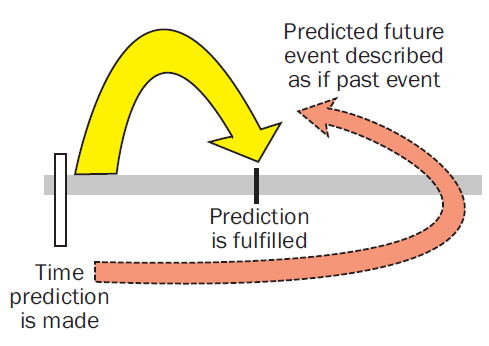
The prophetic perfect tense is a literary technique used in the Bible that describes future events that are so certain to happen that they are referred to in the past tense as if they had already happened. History The category of "prophetic perfect" was already suggested by medieval Hebrew grammarians,Max F. Rogland, ''Alleged Non-past Uses of «qatal» in Classical Hebrew'' (Assen: Royal Van Gorcum, 2003), pp. 53-56. such as David Kimhi: "The matter is as clear as though it had already passed,"Bruce Waltke & M. O’Connor, ''An Introduction to Biblical Hebrew Syntax'' (Winona Lake, IN: Eisenbrauns, 1990), p. 464, n. 45 or Isaac ben Yedaiah: " he rabbisof blessed memory followed, in these words of theirs, in the paths of the prophets who speak of something which will happen in the future in the language of the past. Since they saw in prophetic vision that which was to occur in the future, they spoke about it in the past tense and testified firmly that it had happened, to teach the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diagram Of The Prophetic Perfect
A diagram is a symbolic Depiction, representation of information using Visualization (graphics), visualization techniques. Diagrams have been used since prehistoric times on Cave painting, walls of caves, but became more prevalent during the Age of Enlightenment, Enlightenment. Sometimes, the technique uses a Three-dimensional space, three-dimensional visualization which is then graphical projection, projected onto a two-dimensional surface. The word ''graphics, graph'' is sometimes used as a synonym for diagram. Overview The term "diagram" in its commonly used sense can have a general or specific meaning: * ''visual information device'' : Like the term "illustration", "diagram" is used as a collective term standing for the whole class of technical genres, including graphics, graphs, technical drawings and tables. * ''specific kind of visual display'' : This is the genre that shows qualitative data with shapes that are connected by lines, arrows, or other visual links. In sci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bible
The Bible (from Koine Greek , , 'the books') is a collection of religious texts or scriptures that are held to be sacred in Christianity, Judaism, Samaritanism, and many other religions. The Bible is an anthologya compilation of texts of a variety of forms originally written in Hebrew, Aramaic, and Koine Greek. These texts include instructions, stories, poetry, and prophecies, among other genres. The collection of materials that are accepted as part of the Bible by a particular religious tradition or community is called a biblical canon. Believers in the Bible generally consider it to be a product of divine inspiration, but the way they understand what that means and interpret the text can vary. The religious texts were compiled by different religious communities into various official collections. The earliest contained the first five books of the Bible. It is called the Torah in Hebrew and the Pentateuch (meaning ''five books'') in Greek; the second oldest part was a coll ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Past Tense
The past tense is a grammatical tense whose function is to place an action or situation in the past. Examples of verbs in the past tense include the English verbs ''sang'', ''went'' and ''washed''. Most languages have a past tense, with some having several types in order to indicate how far back the action took place. Some languages have a compound past tense which uses auxiliary verbs as well as an imperfect tense which expresses continuous or repetitive events or actions. Some languages inflect the verb, which changes the ending to indicate the past tense, while non-inflected languages may use other words, such as "yesterday" or "last week" etc to indicate that something took place in the past. Introduction In some languages, the grammatical expression of past tense is combined with the expression of other categories such as grammatical aspect (see tense–aspect). Thus a language may have several types of past tense form, their use depending on what aspectual or other addi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David Kimhi
''Cervera Bible'', David Qimhi's Grammar Treatise David Kimhi ( he, ר׳ דָּוִד קִמְחִי, also Kimchi or Qimḥi) (1160–1235), also known by the Hebrew acronym as the RaDaK () (Rabbi David Kimhi), was a medieval rabbi, biblical commentator, philosopher, and grammarian. Early life Kimhi was born in Narbonne, a city in southern France in the Occitania region, the youngest son of Rabbi Joseph Kimhi and the brother of Rabbi Moses Kimhi, both also biblical commentators and grammarians. Kimhi was raised by his older brother Moses following the untimely death of their father. Later, he supported himself by teaching Talmud to the young. He was well versed in the whole range of Hebrew literature, and became the most illustrious representative of his name. Works of the Kimhi family were underwritten by the Ibn Yahya family of Lisbon, Portugal. Rabbinic career and scholarship Kimhi saw himself primarily as a compiler and summarizer. As a noted Hebrew grammarian, his book ''Mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wilhelm Gesenius
Heinrich Friedrich Wilhelm Gesenius (3 February 178623 October 1842) was a German orientalist, lexicographer, Christian Hebraist, Lutheran theologian, Biblical scholar and critic. Biography Gesenius was born at Nordhausen. In 1803 he became a student of philosophy and theology at the University of Helmstedt, where Heinrich Henke was his most influential teacher; but the latter part of his university course was taken at Göttingen, where Johann Gottfried Eichhorn and Thomas Christian Tychsen were then at the height of their popularity. In 1806, shortly after graduation, he became ''Repetent'' and ''Privatdozent'' (or ''Magister legens'') at Göttingen; and, as he was later proud to say, had August Neander for his first pupil in Hebrew language. On 8 February 1810 he became ''professor extraordinarius'' in theology, and on 16 June 1811 was promoted to ''ordinarius'', at the University of Halle, where, in spite of many offers of high preferment elsewhere, he spent the rest of his l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Figures Of Speech
A figure of speech or rhetorical figure is a word or phrase that intentionally deviates from ordinary language use in order to produce a rhetorical effect. Figures of speech are traditionally classified into '' schemes,'' which vary the ordinary sequence of words, and '' tropes,'' where words carry a meaning other than what they ordinarily signify. An example of a scheme is a polysyndeton: the repetition of a conjunction before every element in a list, whereas the conjunction typically would appear only before the last element, as in "Lions and tigers and bears, oh my!"—emphasizing the danger and number of animals more than the prosaic wording with only the second "and". An example of a trope is the metaphor, describing one thing as something that it clearly is not in order to lead the mind to compare them, in "All the world's a stage." Four rhetorical operations Classical rhetoricians classified figures of speech into four categories or :Jansen, Jeroen (2008) Imitatio'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biblical Exegesis
Biblical criticism is the use of critical analysis to understand and explain the Bible. During the eighteenth century, when it began as ''historical-biblical criticism,'' it was based on two distinguishing characteristics: (1) the concern to avoid dogma and bias by applying a neutral, non-sectarian, reason-based judgment to the study of the Bible, and (2) the belief that the reconstruction of the historical events behind the texts, as well as the history of how the texts themselves developed, would lead to a correct understanding of the Bible. This sets it apart from earlier, pre-critical methods; from the anti-critical methods of those who oppose criticism-based study; from later post-critical orientation, and from the many different types of criticism which biblical criticism transformed into in the late twentieth and early twenty-first centuries. Most scholars believe the German Enlightenment () led to the creation of biblical criticism, although some assert that its roots ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)