|
Proline Racemase
In enzymology, a proline racemase () is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction :L-proline \rightleftharpoons D-proline Hence, this enzyme has two substrates, L- and D-proline, and two products, D- and L- proline. This enzyme belongs to the family of proline racemases acting on free amino acids. The systematic name of this enzyme class is proline racemase. This enzyme participates in arginine and proline metabolism. These enzymes catalyse the interconversion of L- and D-proline in bacteria. Species distribution This first eukaryotic proline racemase was identified in ''Trypanosoma cruzi'' and fully characterized . The parasite enzyme, ''Tc''PRAC, is as a co-factor-independent proline racemase and displays B-cell mitogenic properties when released by ''T. cruzi'' upon infection, contributing to parasite escape. Novel proline racemases of medical and veterinary importance were described respectively in '' Clostridium difficile'' () and ''Trypanosoma vivax'' (). These ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzymology
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. Almost all metabolic processes in the cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts are catalytic RNA molecules, called ribozymes. Enzymes' specificity comes from their unique three-dimensional structures. Like all catalysts, enzymes increase the reaction ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
4-hydroxyproline Epimerase
In enzymology, a 4-hydroxyproline epimerase () is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction :''trans''-4-hydroxy-L-proline \rightleftharpoons ''cis''-4-hydroxy-D-proline Hence, this enzyme has one substrate, trans-4-hydroxy-L-proline, and one product, cis-4-hydroxy-D-proline. This enzyme belongs to the family of isomerases, specifically those racemases and epimerases acting on amino acids and derivatives. The systematic name of this enzyme class is 4-hydroxyproline 2-epimerase. Other names in common use include hydroxyproline epimerase, hydroxyproline 2-epimerase, and L-hydroxyproline epimerase. This enzyme participates in arginine and proline metabolism Arginine and proline metabolism is one of the central pathways for the biosynthesis of the amino acids arginine and proline from glutamate. The pathways linking arginine, glutamate, and proline are bidirectional. Thus, the net utilization or prod .... References * EC 5.1.1 Enzymes of unknown structure< ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homodimer
In biochemistry, a protein dimer is a macromolecular complex formed by two protein monomers, or single proteins, which are usually non-covalently bound. Many macromolecules, such as proteins or nucleic acids, form dimers. The word ''dimer'' has roots meaning "two parts", '' di-'' + '' -mer''. A protein dimer is a type of protein quaternary structure. A protein homodimer is formed by two identical proteins. A protein heterodimer is formed by two different proteins. Most protein dimers in biochemistry are not connected by covalent bonds. An example of a non-covalent heterodimer is the enzyme reverse transcriptase, which is composed of two different amino acid chains. An exception is dimers that are linked by disulfide bridges such as the homodimeric protein NEMO. Some proteins contain specialized domains to ensure dimerization (dimerization domains) and specificity. The G protein-coupled cannabinoid receptors have the ability to form both homo- and heterodimers with several ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isothermal Titration Calorimetry
Isothermal titration calorimetry (ITC) is a physical technique used to determine the thermodynamic parameters of interactions in solution. It is most often used to study the binding of small molecules (such as medicinal compounds) to larger macromolecules (proteins, DNA etc.). It consists of two cells which are enclosed in an adiabatic jacket. The compounds to be studied are placed in the sample cell, while the other cell, the reference cell, is used as a control and contains the buffer in which the sample is dissolved. Thermodynamic measurements ITC is a quantitative technique that can determine the binding affinity (K_a), enthalpy changes (\Delta H), and binding stoichiometry (n) of the interaction between two or more molecules in solution. From these initial measurements, Gibbs free energy changes (\Delta G) and entropy changes (\Delta S) can be determined using the relationship: :::\Delta G = -RT\ln = \Delta H -T\Delta S (where R is the gas constant and T is the absolute ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Racemase
Epimerases and racemases are isomerase enzymes that catalyze the inversion of stereochemistry in biological molecules. Racemases catalyze the stereochemical inversion around the asymmetric carbon atom in a substrate having only one center of asymmetry. Epimerases catalyze the stereochemical inversion of the configuration about an asymmetric carbon atom in a substrate having more than one center of asymmetry, thus interconverting epimers. Human epimerases include methylmalonyl-CoA epimerase, involved in the metabolic breakdown of the amino acids alanine, isoleucine, methionine and valine, and UDP-glucose 4-epimerase, which is used in the final step of galactose metabolism - catalyzing the reversible conversion of UDP-galactose to UDP-glucose. See also * Galactose epimerase deficiency Galactose epimerase deficiency, also known as GALE deficiency, Galactosemia III and UDP-galactose-4-epimerase deficiency, is a rare, autosomal recessive form of galactosemia associated with a def ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clostridium Sticklandii
''Acetoanaerobium sticklandii'' is an anaerobic, motile, gram-positive bacterium. It was first isolated in 1954 from the black mud of the San Francisco Bay Area by T.C. Stadtman, who also named the species. ''A. sticklandii'' is not pathogenic in humans. Biology and biochemistry ''Acetoanaerobium sticklandii'' ferment amino acids by using the Stickland reaction, which couples the oxidation of one amino acid and the reduction of another. L.H. Stickland described this process in 1934. The enzymes in the Stickland reaction are D-proline reductase (an electron acceptor) and Glycine reductase. ''A. sticklandii'' preferentially utilize threonine, arginine, serine, cysteine, proline, and glycine during the growth phase and lysine during the stationary phase, while excreting glutamate, aspartate and alanine. Selenoproteins can be found in the genome of ''A. sticklandii''. One such selenoprotein, glycine reductase A was first identified in ''A. sticklandii''. ''A. sticklandii'' uses a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brucella Melitensis
''Brucella melitensis'' is a Gram-negative coccobacillus bacterium from the Brucellaceae family. The bacterium causes ovine brucellosis, along with '' Brucella ovis''. It affects primarily sheep and goats, but cases have also been observed in cattle, yaks, water buffalo, Bactrian and dromedary camels, alpacas, dogs, horses and pigs. Humans can become infected if they have contact with an infected animal or its byproducts. Animals acquire ''B. melitensis'' by venereal transmission and contact with the placenta, fetus, fetal fluids, and vaginal discharges from infected animals. The organism is found in blood, urine, milk, and semen. It is zoonotic, unlike ''B. ovis'', causing Malta fever or localized brucellosis in humans. Clinical manifestation The bacterium causes severe inflammation of the epididymis, with formation of spermatocoeles and fibrinous adhesions. This disease is known as ovine brucellosis, and is a reportable disease in the USA. In goats and sheep, ''B. melit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brucella Suis
''Brucella suis'' is a bacterium that causes swine brucellosis, a zoonosis that affects pigs. The disease typically causes chronic inflammatory lesions in the reproductive organs of susceptible animals or orchitis, and may even affect joints and other organs. The most common symptom is abortion in pregnant susceptible sows at any stage of gestation. Other manifestations are temporary or permanent sterility, lameness, posterior paralysis, spondylitis, and abscess formation. It is transmitted mainly by ingestion of infected tissues or fluids, semen during breeding, and suckling infected animals. Since brucellosis threatens the food supply and causes undulant fever, ''Brucella suis'' and other ''Brucella'' species (''B. melitensis, B. abortus, B. ovis, B. canis'') are recognized as potential agricultural, civilian, and military bioterrorism agents. Symptoms and signs The most frequent clinical sign following ''B. suis'' infection is abortion in pregnant females, reduced milk produ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brucella Abortus
''Brucella abortus'' is a Gram-negative bacterium in the family Brucellaceae and is one of the causative agents of brucellosis. The rod-shaped pathogen is classified under the domain Bacteria. The prokaryotic ''B. abortus'' is non-spore-forming, non-motile and aerobic. Transmission ''Brucella abortus'' enters phagocytes that invade human and animal innate defenses which in turn, cause chronic disease in the host. The liver and spleen are the mainly affected areas of the body. Farm workers and veterinarians are the highest risk individuals for acquiring the disease due to their close proximity to the animals. Swine, goats, sheep, and cattle are a few of the reservoirs for the disease. ''B. abortus'' causes abortion and infertility in adult cattle and is a zoonosis which is present worldwide. Humans are commonly infected after drinking unpasteurized milk from affected animals or, less commonly, when coming into contact with infected tissues and liquids (afterbirth, etc.). The i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burkholderia Pseudomallei
''Burkholderia pseudomallei'' (also known as ''Pseudomonas pseudomallei'') is a Gram-negative, bipolar, aerobic, motile rod-shaped bacterium. It is a soil-dwelling bacterium endemic in tropical and subtropical regions worldwide, particularly in Thailand and northern Australia. It was reported in 2008 that there had been an expansion of the affected regions due to significant natural disasters, and it could be found in Southern China, Hong Kong, and countries in America. ''B. pseudomallei'', amongst other pathogens, has been found in monkeys imported into the United States from Asia for laboratory use, posing a risk that the pathogen could be introduced into the country. Although it is mainly a soil-dwelling bacteria, a study performed by Apinya Pumpuang and others showed that ''Burkholderia pseudomallei'' survived in distilled water for 16 years, demonstrating that it is capable of living in water if a specific environment is provided. It is resistant to a variety of harsh condit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
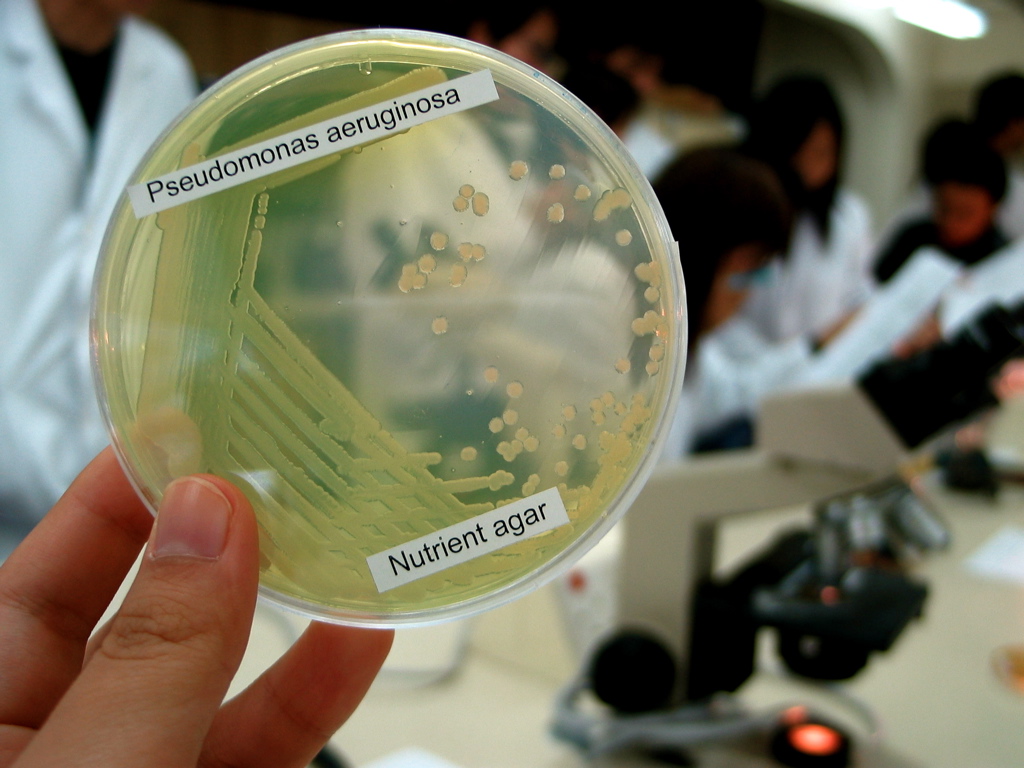
Pseudomonas Aeruginosa
''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'' is a common encapsulated, gram-negative, aerobic–facultatively anaerobic, rod-shaped bacterium that can cause disease in plants and animals, including humans. A species of considerable medical importance, ''P. aeruginosa'' is a multidrug resistant pathogen recognized for its ubiquity, its intrinsically advanced antibiotic resistance mechanisms, and its association with serious illnesses – hospital-acquired infections such as ventilator-associated pneumonia and various sepsis syndromes. The organism is considered opportunistic insofar as serious infection often occurs during existing diseases or conditions – most notably cystic fibrosis and traumatic burns. It generally affects the immunocompromised but can also infect the immunocompetent as in hot tub folliculitis. Treatment of ''P. aeruginosa'' infections can be difficult due to its natural resistance to antibiotics. When more advanced antibiotic drug regimens are needed adverse effects may re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trypanosoma Vivax
''Trypanosoma vivax'' is a parasite species in the genus ''Trypanosoma''. It causes the disease Animal trypanosomiasis, nagana, affecting cattle or wild mammals. It is mainly occurs in West Africa, although it has spread to South America. Range Historically restricted to sub-Saharan Africa especially West Africa, it has spread to 13 countries of South America. This has been made easier by its mechanical transmission route, see #Life cycle, Life cycle below. Hosts Hosts include, cattle farming, Cattle, horse husbandry, horses, sheep farming, sheep, and camel herding, camels. in South America it is an emerging agricultural pathogen, emerging pathogen of cattle, and sometimes horses and other ruminants. Life cycle Unusual for a trypanosome, ''T. vivax'' does not infect the ''Glossina'' vector midgut. Instead it infects and completes an abbreviated life cycle only in the vector's proboscis. Thus it is entirely mechanically transmitted. For this reason it has had a relatively easy t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |