|
Process Tomography
Process tomography consists of tomographic imaging of systems, such as process pipes in industry. In tomography the 3D distribution of some physical quantity in the object is determined. There is a widespread need to get tomographic information about process. This information can be used, for example, in the design and control of processes. Tomography involves taking measurements around the periphery of an object (e.g. process vessel or patient) to determine what is going on inside. The best known technique is CT scanning in medicine; however, process tomography instrumentation needs to be cheaper, faster and more robust. Many different imaging methods are used in process tomography, e.g. ultrasonic imaging, positron emission tomography (PET), electrical resistance tomography (ERT) and electrical impedance tomography (EIT), electrical capacitance tomography (ECT), magnetic induction tomography (MIT). In all cases external sensors are used to detect signals from boundary of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tomography
Tomography is imaging by sections or sectioning that uses any kind of penetrating wave. The method is used in radiology, archaeology, biology, atmospheric science, geophysics, oceanography, plasma physics, materials science, cosmochemistry, astrophysics, quantum information, and other areas of science. The word ''tomography'' is derived from Ancient Greek τόμος ''tomos'', "slice, section" and γράφω ''graphō'', "to write" or, in this context as well, "to describe." A device used in tomography is called a tomograph, while the image produced is a tomogram. In many cases, the production of these images is based on the mathematical procedure tomographic reconstruction, such as X-ray computed tomography technically being produced from multiple projectional radiographs. Many different reconstruction algorithms exist. Most algorithms fall into one of two categories: filtered back projection (FBP) and iterative reconstruction (IR). These procedures give inexact results: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
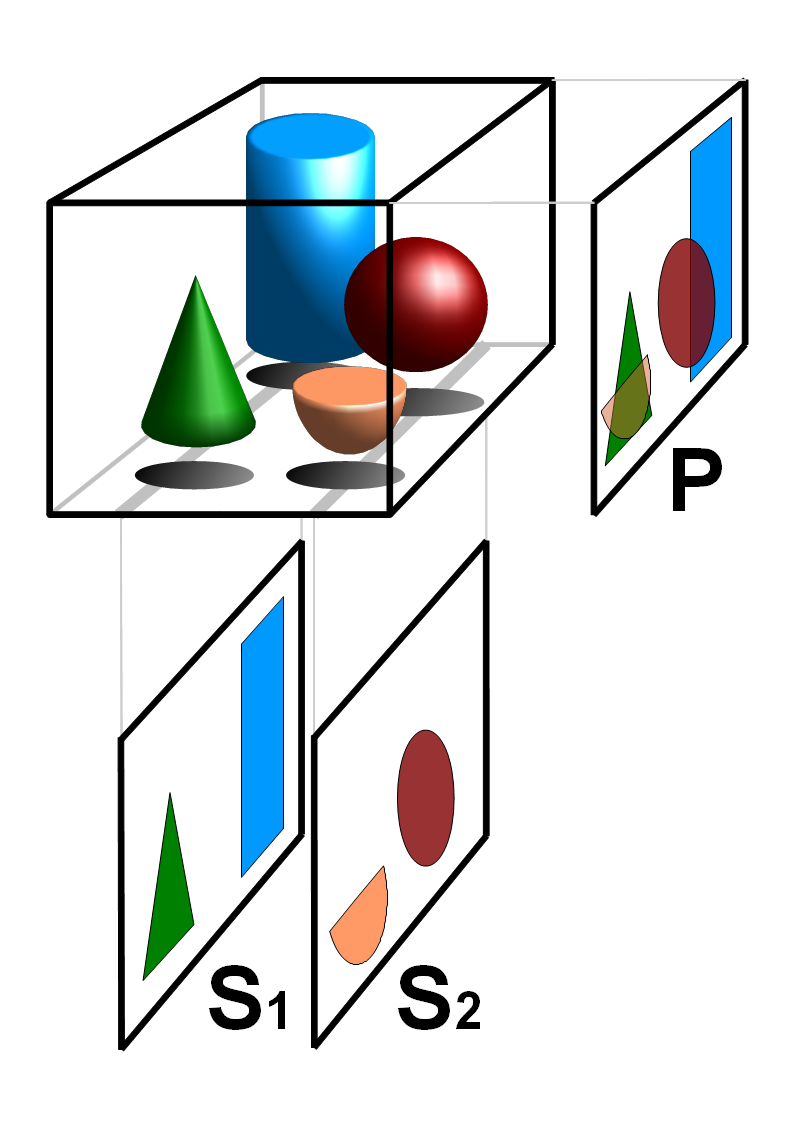
Three-dimensional Space
Three-dimensional space (also: 3D space, 3-space or, rarely, tri-dimensional space) is a geometric setting in which three values (called ''parameters'') are required to determine the position of an element (i.e., point). This is the informal meaning of the term dimension. In mathematics, a tuple of numbers can be understood as the Cartesian coordinates of a location in a -dimensional Euclidean space. The set of these -tuples is commonly denoted \R^n, and can be identified to the -dimensional Euclidean space. When , this space is called three-dimensional Euclidean space (or simply Euclidean space when the context is clear). It serves as a model of the physical universe (when relativity theory is not considered), in which all known matter exists. While this space remains the most compelling and useful way to model the world as it is experienced, it is only one example of a large variety of spaces in three dimensions called 3-manifolds. In this classical example, when the t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computed Axial Tomography
A computed tomography scan (CT scan; formerly called computed axial tomography scan or CAT scan) is a medical imaging technique used to obtain detailed internal images of the body. The personnel that perform CT scans are called radiographers or radiology technologists. CT scanners use a rotating X-ray tube and a row of detectors placed in a gantry to measure X-ray attenuations by different tissues inside the body. The multiple X-ray measurements taken from different angles are then processed on a computer using tomographic reconstruction algorithms to produce tomographic (cross-sectional) images (virtual "slices") of a body. CT scans can be used in patients with metallic implants or pacemakers, for whom magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is contraindicated. Since its development in the 1970s, CT scanning has proven to be a versatile imaging technique. While CT is most prominently used in medical diagnosis, it can also be used to form images of non-living objects. The 1979 N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medicine
Medicine is the science and Praxis (process), practice of caring for a patient, managing the diagnosis, prognosis, Preventive medicine, prevention, therapy, treatment, Palliative care, palliation of their injury or disease, and Health promotion, promoting their health. Medicine encompasses a variety of health care practices evolved to maintain and restore health by the prevention (medical), prevention and therapy, treatment of illness. Contemporary medicine applies biomedical sciences, biomedical research, medical genetics, genetics, and medical technology to diagnosis (medical), diagnose, treat, and prevent injury and disease, typically through pharmaceuticals or surgery, but also through therapies as diverse as psychotherapy, splint (medicine), external splints and traction, medical devices, biologic medical product, biologics, and Radiation (medicine), ionizing radiation, amongst others. Medicine has been practiced since Prehistoric medicine, prehistoric times, and for most o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medical Ultrasonography
Medical ultrasound includes diagnostic techniques (mainly imaging techniques) using ultrasound, as well as therapeutic applications of ultrasound. In diagnosis, it is used to create an image of internal body structures such as tendons, muscles, joints, blood vessels, and internal organs, to measure some characteristics (e.g. distances and velocities) or to generate an informative audible sound. Its aim is usually to find a source of disease or to exclude pathology. The usage of ultrasound to produce visual images for medicine is called medical ultrasonography or simply sonography. The practice of examining pregnant women using ultrasound is called obstetric ultrasonography, and was an early development of clinical ultrasonography. Ultrasound is composed of sound waves with frequencies which are significantly higher than the range of human hearing (>20,000 Hz). Ultrasonic images, also known as sonograms, are created by sending pulses of ultrasound into tissue usin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Positron Emission Tomography
Positron emission tomography (PET) is a functional imaging technique that uses radioactive substances known as radiotracers to visualize and measure changes in metabolic processes, and in other physiological activities including blood flow, regional chemical composition, and absorption. Different tracers are used for various imaging purposes, depending on the target process within the body. For example: * Fluorodeoxyglucose ( 18F">sup>18FDG or FDG) is commonly used to detect cancer; * 18Fodium fluoride">sup>18Fodium fluoride (Na18F) is widely used for detecting bone formation; * Oxygen-15 (15O) is sometimes used to measure blood flow. PET is a common imaging technique, a medical scintillography technique used in nuclear medicine. A radiopharmaceutical – a radioisotope attached to a drug – is injected into the body as a radioactive tracer, tracer. When the radiopharmaceutical undergoes beta plus decay, a positron is emitted, and when the positron interacts with an or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrical Resistance Tomography
Electrical impedance tomography (EIT) is a noninvasive type of medical imaging in which the electrical conductivity, permittivity, and impedance of a part of the body is inferred from surface electrode measurements and used to form a tomographic image of that part. Electrical conductivity varies considerably among various biological tissues (absolute EIT) or the movement of fluids and gases within tissues (difference EIT). The majority of EIT systems apply small alternating currents at a single frequency, however, some EIT systems use multiple frequencies to better differentiate between normal and suspected abnormal tissue within the same organ (multifrequency-EIT or electrical impedance spectroscopy). Typically, conducting surface electrodes are attached to the skin around the body part being examined. Small alternating currents will be applied to some or all of the electrodes, the resulting equi-potentials being recorded from the other electrodes (figures 1 and 2). This proc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrical Impedance Tomography
Electrical impedance tomography (EIT) is a noninvasive type of medical imaging in which the electrical conductivity, permittivity, and impedance of a part of the body is inferred from surface electrode measurements and used to form a tomographic image of that part. Electrical conductivity varies considerably among various biological tissues (absolute EIT) or the movement of fluids and gases within tissues (difference EIT). The majority of EIT systems apply small alternating currents at a single frequency, however, some EIT systems use multiple frequencies to better differentiate between normal and suspected abnormal tissue within the same organ (multifrequency-EIT or electrical impedance spectroscopy). Typically, conducting surface electrodes are attached to the skin around the body part being examined. Small alternating currents will be applied to some or all of the electrodes, the resulting equi-potentials being recorded from the other electrodes (figures 1 and 2). This proc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrical Capacitance Tomography
Electrical capacitance tomography (ECT) is a method for determination of the dielectric permittivity distribution in the interior of an object from external capacitance measurements. It is a close relative of electrical impedance tomography and is proposed as a method for industrial process monitoring. Although capacitance sensing methods were in widespread use the idea of using capacitance measurement to form images is attributed to Maurice Beck and co-workers at UMIST in the 1980s. Although usually called tomography, the technique differs from conventional tomographic methods, in which high resolution images are formed of slices of a material. The measurement electrodes, which are metallic plates, must be sufficiently large to give a measureable change in capacitance. This means that very few electrodes are used, typically eight to sixteen electrodes. An N-electrode system can only provide N(N−1)/2 independent measurements. This means that the technique is limited to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Induction Tomography
Magnetic induction tomography is an imaging technique used to image electromagnetic properties of an object by using the eddy current effect. It is also called electromagnetic induction tomography, electromagnetic tomography (EMT), eddy current tomography, and eddy current testing. Applications The method is used in nondestructive testing and geophysics, and has potential applications in medicine. It is also used to generate 3D images of passive electromagnetic properties, which has applications in brain imaging, cryosurgery Cryosurgery is the use of extreme cold in surgery to destroy abnormal or diseased tissue; thus, it is the surgical application of cryoablation. The term comes from the Greek words cryo (κρύο) ("icy cold") and surgery (''cheirourgiki'' – � ... monitoring in medical imaging, and metal flow visualization in metalworking processes. References * * Peyton, A. J., et al. "An overview of electromagnetic inductance tomography: description of three different ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrical Capacitance Volume Tomography
Electrical capacitance volume tomography (ECVT) is a non-invasive 3D imaging technology applied primarily to multiphase flows. It was first introduced by W. Warsito, Q. Marashdeh, and L.-S. Fan as an extension of the conventional electrical capacitance tomography (ECT). In conventional ECT, sensor plates are distributed around a surface of interest. Measured capacitance between plate combinations is used to reconstruct 2D images (tomograms) of material distribution. In ECT, the fringing field from the edges of the plates is viewed as a source of distortion to the final reconstructed image and is thus mitigated by guard electrodes. ECVT exploits this fringing field and expands it through 3D sensor designs that deliberately establish an electric field variation in all three dimensions. The image reconstruction algorithms are similar in nature to ECT; nevertheless, the reconstruction problem in ECVT is more complicated. The sensitivity matrix of an ECVT sensor is more ill-conditioned an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrical Impedance Tomography
Electrical impedance tomography (EIT) is a noninvasive type of medical imaging in which the electrical conductivity, permittivity, and impedance of a part of the body is inferred from surface electrode measurements and used to form a tomographic image of that part. Electrical conductivity varies considerably among various biological tissues (absolute EIT) or the movement of fluids and gases within tissues (difference EIT). The majority of EIT systems apply small alternating currents at a single frequency, however, some EIT systems use multiple frequencies to better differentiate between normal and suspected abnormal tissue within the same organ (multifrequency-EIT or electrical impedance spectroscopy). Typically, conducting surface electrodes are attached to the skin around the body part being examined. Small alternating currents will be applied to some or all of the electrodes, the resulting equi-potentials being recorded from the other electrodes (figures 1 and 2). This proc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




%2C_1987._(9663810916).jpg)

