|
Process Mining
Process mining is a family of techniques for analyzing event data to understand and improve operational processes. Part of the fields of data science and Business_process_management, process management, process mining is generally built on Logging (computing), logs that contain case id, a unique identifier for a particular process instance; an activity, a description of the event that is occurring; a timestamp; and sometimes other information such as resources, costs, and so on. There are three main classes of process mining techniques: ''process discovery'', ''conformance checking'', and ''process enhancement''. In the past, terms like ''workflow mining'' and ''automated business process discovery'' (ABPD) were used. Overview Process mining techniques are often used when no formal description of the process can be obtained by other approaches, or when the quality of existing documentation is questionable. For example, application of process mining methodology to the audit trails o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Data Science
Data science is an interdisciplinary academic field that uses statistics, scientific computing, scientific methods, processing, scientific visualization, algorithms and systems to extract or extrapolate knowledge from potentially noisy, structured, or unstructured data. Data science also integrates domain knowledge from the underlying application domain (e.g., natural sciences, information technology, and medicine). Data science is multifaceted and can be described as a science, a research paradigm, a research method, a discipline, a workflow, and a profession. Data science is "a concept to unify statistics, data analysis, informatics, and their related methods" to "understand and analyze actual phenomena" with data. It uses techniques and theories drawn from many fields within the context of mathematics, statistics, computer science, information science, and domain knowledge. However, data science is different from computer science and information science. Turing Awar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eindhoven University Of Technology
The Eindhoven University of Technology (), Abbreviation, abbr. TU/e, is a public university, public technical university in the Netherlands, situated in Eindhoven. In 2020–21, around 14,000 students were enrolled in its Bachelor of Science, BSc and Master of Science, MSc programs and around 1350 students were enrolled in its Doctor of Philosophy, PhD and EngD programs. In 2021, the TU/e employed around 3900 people. TU/e is the Dutch member of the EuroTech Universities Alliance, a partnership of European universities of science & technology. The other members are Technical University of Denmark (DTU), École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL), École Polytechnique (L’X), The Technion, and Technical University of Munich (TUM). History The Eindhoven University of Technology was founded as the ''Technische Hogeschool Eindhoven'' (THE) on 23 June 1956 by the Dutch government. It was the second institute of its kind in the Netherlands, after the Delft University of Tech ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
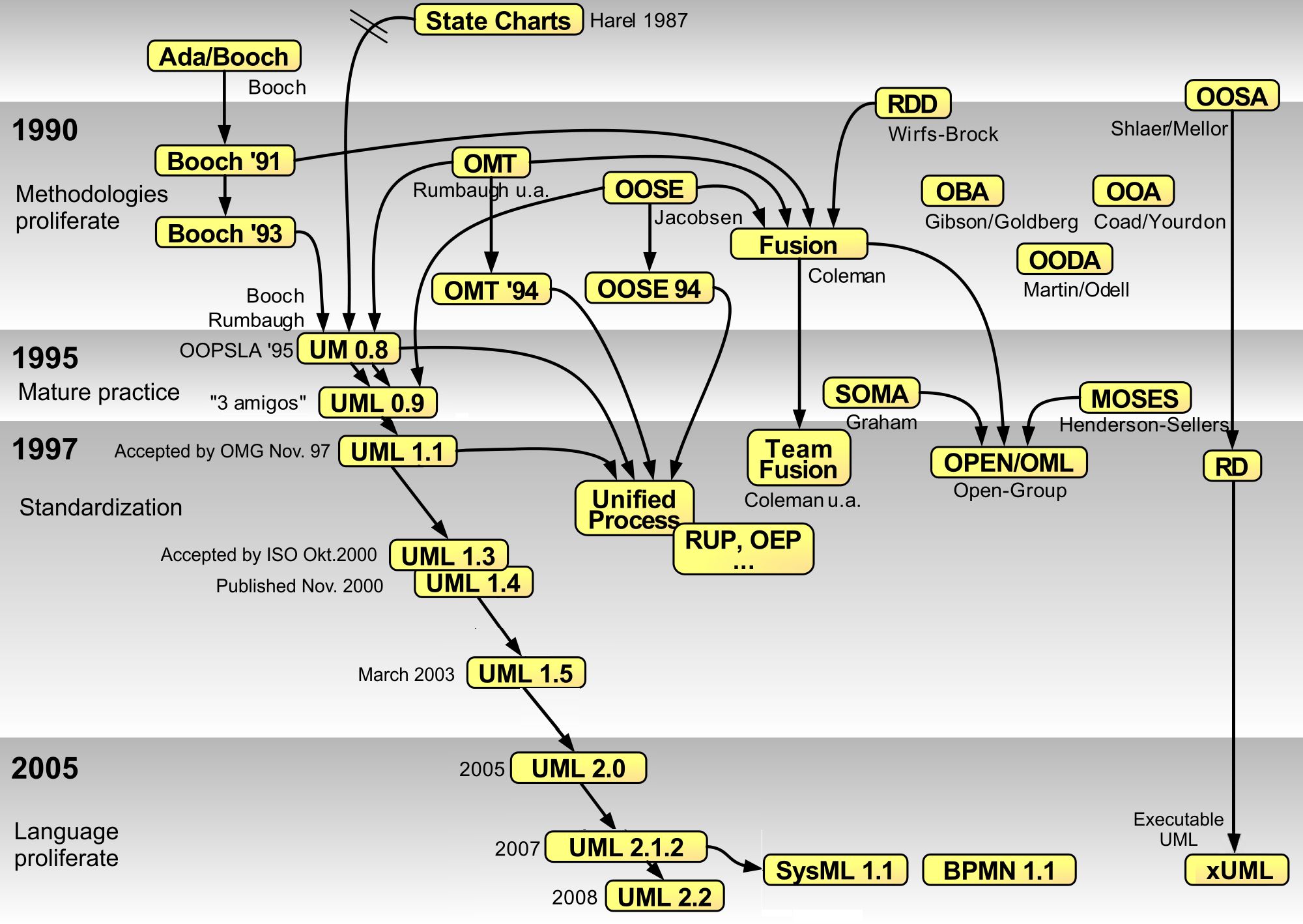
State Diagram
A state diagram is used in computer science and related fields to describe the behavior of systems. State diagrams require that the system is composed of a finite number of states. Sometimes, this is indeed the case, while at other times this is a reasonable abstraction. Many forms of state diagrams exist, which differ slightly and have different semantics. Overview State diagrams provide an abstract description of a system's behavior. This behavior is analyzed and represented by a series of events that can occur in one or more possible states. Hereby "each diagram usually represents objects of a single class and track the different states of its objects through the system". State diagrams can be used to graphically represent finite-state machines (also called finite automata). This was introduced by Claude Shannon and Warren Weaver in their 1949 book ''The Mathematical Theory of Communication''. Another source is Taylor Booth in his 1967 book ''Sequential Machines and Aut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Activity Diagram
Activity diagrams are graphical representations of workflows of stepwise activities and actions with support for choice, iteration, and concurrency. In the Unified Modeling Language, activity diagrams are intended to model both computational and organizational processes (i.e., workflows), as well as the data flows intersecting with the related activities. "Object nodes hold data that is input to and output from executable nodes, and moves across object flow edges. Control nodes specify sequencing of executable nodes via control flow edges." In other words, although activity diagrams primarily show the overall control flow, they can also include elements showing the data flow between activities through one or more data stores. Construction Activity diagrams are constructed from a limited number of shapes, connected with arrows. The most important shape types are as follows: * '' stadia'' represent ''actions''; * ''diamonds'' represent ''decisions''; * ''bars'' represent the start ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Business Process Model And Notation
Business Process Model and Notation (BPMN) is a graphical representation for specifying business processes in a business process model. Originally developed by the Business Process Management Initiative (BPMI), BPMN has been maintained by the Object Management Group (OMG) since the two organizations merged in 2005. Version 2.0 of BPMN was released in January 2011, at which point the name was amended to Business Process Model ''and'' Notation to reflect the introduction of execution semantics, which were introduced alongside the existing notational and diagramming elements. Though it is an OMG specification, BPMN is also ratified as ISO 19510. The latest version is BPMN 2.0.2, published in January 2014. Overview Business Process Model and Notation (BPMN) is a standard for business process modeling that provides a graphical notation for specifying business processes in a ''Business Process Diagram'' (BPD), based on a flowcharting technique very similar to activity diagrams from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
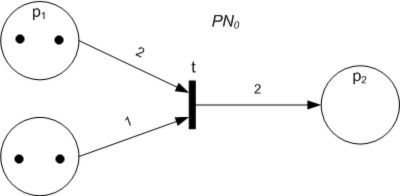
Petri Net
A Petri net, also known as a place/transition net (PT net), is one of several mathematical modeling languages for the description of distributed systems. It is a class of discrete event dynamic system. A Petri net is a directed bipartite graph that has two types of elements: places and transitions. Place elements are depicted as white circles and transition elements are depicted as rectangles. A place can contain any number of tokens, depicted as black circles. A transition is enabled if all places connected to it as inputs contain at least one token. Some sources state that Petri nets were invented in August 1939 by Carl Adam Petri — at the age of 13 — for the purpose of describing chemical processes. Like industry standards such as UML activity diagrams, Business Process Model and Notation, and event-driven process chains, Petri nets offer a graphical notation for stepwise processes that include choice, iteration, and concurrent execution. Unlike these standards, Pet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alpha Algorithm
The α-algorithm or α-miner is an algorithm used in process mining Process mining is a family of techniques for analyzing event data to understand and improve operational processes. Part of the fields of data science and Business_process_management, process management, process mining is generally built on Logging ..., aimed at reconstructing causality from a set of sequences of events. It was first put forward by Wil van der Aalst, van der Aalst, Weijters and Măruşter. The goal of Alpha miner is to convert the event log into a workflow-net based on the relations between various activities in the event log. An event log is a multi-set of traces, and a trace is a sequence of activity names. Several extensions or modifications of it have since been presented, which will be listed below. Alpha miner was the first Business process discovery, process discovery algorithm ever proposed, and it gives a good overview of the aim of process discovery and how various activities within the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Business Process Discovery
Business process discovery (BPD) related to business process management and process mining is a set of techniques that manually or automatically construct a representation of an organisations' current business processes and their major process variations. These techniques use data recorded in the existing organisational methods of work, documentations, and technology systems that run business processes within an organisation. The type of data required for process discovery is called an event log. Any record of data that contains the case id (a unique identifier that is helpful in grouping activities belonging to the same case), activity name (description of the activity taking place), and timestamp. Such a record qualifies for an event log and can be used to discover the underlying process model. The event log can contain additional information related to the process, such as the resources executing the activity, the type or nature of the events, or any other relevant details. Process ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organisational Mining
An organization or organisation (Commonwealth English; see spelling differences) is an entity—such as a company, or corporation or an institution (formal organization), or an association—comprising one or more people and having a particular purpose. Organizations may also operate secretly or illegally in the case of secret societies, criminal organizations, and resistance movements. And in some cases may have obstacles from other organizations (e.g.: MLK's organization). What makes an organization recognized by the government is either filling out incorporation or recognition in the form of either societal pressure (e.g.: Advocacy group), causing concerns (e.g.: Resistance movement) or being considered the spokesperson of a group of people subject to negotiation (e.g.: the Polisario Front being recognized as the sole representative of the Sahrawi people and forming a partially recognized state.) Compare the concept of social groups, which may include non-organiza ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Performance Analysis In Process Mining
A performance is an act or process of staging or presenting a play, concert, or other form of entertainment. It is also defined as the action or process of carrying out or accomplishing an action, task, or function. Performance has evolved globally, from ancient rituals to modern artistic expressions. Expanding the article with historical and cultural perspectives would improve its scope. Ancient & Classical Theater: Rooted in rituals (Egyptian passion plays, Indigenous storytelling), early performances led to Greek tragedy, Sanskrit drama, and Chinese opera. Medieval & Early Modern Performance: Includes mystery plays in Europe, Commedia dell’arte in Italy, and Kabuki & Noh in Japan. Contemporary & Political Performance: Modern forms include agitprop theater, Forum Theater, and performance art as activism. By highlighting global traditions, the article would better reflect performance as a universal human expression shaped by history and culture. Management science In the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conformance Checking
Business process conformance checking (a.k.a. conformance checking for short) is a family of process mining techniques to compare a Process modeling, process model with an event log of the same process. It is used to check if the actual execution of a business process, as recorded in the event log, conforms to the model and vice versa. For instance, there may be a process model indicating that purchase orders of more than one million euros require two checks. Analysis of the event log will show whether this rule is followed or not. Another example is the checking of the so-called “Four-eyes principle, four-eyes” principle stating that particular activities should not be executed by one and the same person. By scanning the event log using a model specifying these requirements, one can discover potential cases of fraud. Hence, conformance checking may be used to detect, locate and explain deviations, and to measure the severity of these deviations. Overview Conformance checking ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Token-based Replay
Token-based replay technique is a conformance checking algorithm that checks how well a process conforms with its model by replaying each trace on the model (in Petri net, Petri net notation ). Using the four counters ''produced tokens, consumed tokens, missing tokens, and remaining tokens,'' it records the situations where a transition is forced to fire and the remaining tokens after the replay ends. Based on the count at each counter, we can compute the ''fitness value'' between the trace and the model. The algorithm The token-replay technique uses four counters to keep track of a trace during the replaying: * : Produced tokens * : Consumed tokens * : Missing tokens (consumed while not there) * : Remaining tokens (produced but not consumed) Invariants: * At any time: p+m \ge c \ge m * At the end: r = p + m - c At the beginning, a token is produced for the source place (p = 1) and at the end, a token is consumed from the sink place (c' = c + 1). When the replay ends, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |