|
Proazaphosphatrane
In chemistry, a Verkade base (or Verkade superbase) is a superbase with the formula P(MeNCH2CH2)3N. A colorless oil, it is an aminophosphine although its inventor John Verkade called it proazaphosphatrane. The trimethyl derivative or 2,5,8,9-tetraza-1-phosphabicyclo .3.3ndecane is the simplest. Diverse analogues of the Verkade base are known, e.g. with isopropyl groups in place of methyl. Synthesis and reactions The Verkade base is generated by the reaction of N,N,N-trimethyl tren with tris(dimethylamino)phosphine: :P(NMe2)3 + (MeNHCH2CH2)3N → P(MeNCH2CH2)3N + 3 Me2NH The principal reaction of the Verkade base is protonation. The proton is attacked by the Verkade base at phosphorus, which induces the formation of a transannular P-N bond. The product exemplifies the structure of an atrane. 290 px, left, Protonation of Verkade base. The conjugate acid P(MeNCH2CH2)3Nsup>+ has a pKa of 32.9 in acetonitrile. For comparison, the conjugate acid of triethylamine has a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atrane
Atranes are a class of tricyclic molecules with three five-membered rings. It is a heterocyclic structure similar to the propellanes. It has a transannular dative bond from a nitrogen at one bridgehead to a Lewis acidic atom such as silicon or boron at the other bridgehead.Voronkov, Mikhail G.; Baryshok, Viktor P. "Atranes - a new generation of biologically active substances" (in Russian) Vestnik Rossiiskoi Akademii Nauk 2010, volume 80, 985-992. The name "atrane" was first proposed by . Nomenclature Various atranes are named depending on the central element, e.g. "silatrane" (E = silicon); "boratrane" (E = boron); "phosphatrane" (E = phosphorus), etc. It is also proposed that when Y = nitrogen, the prefix "aza" be inserted before ''element'' + "atrane" (azasilatrane, for example) because atranes wherein E = silicon and Y = oxygen have been referred to as just "silatranes". Structure and properties Silatranes exhibit unusual properties as well as biological activity in w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superbases
A superbase is a compound that has a particularly high affinity for protons. Superbases are of theoretical interest and potentially valuable in organic synthesis. Superbases have been described and used since the 1850s.''Superbases for Organic Synthesis'' Ed. Ishikawa, T., John Wiley and Sons, Ltd.: West Sussex, UK. 2009. Definitions Generically IUPAC defines a superbase as a "compound having a very high basicity, such as lithium diisopropylamide." Superbases are often defined in two broad categories, organic and organometallic. Organic superbases are charge-neutral compounds with basicities greater than that of proton sponge (pKBH+ = 18.6 in MeCN)." In a related definition: any species with a higher absolute proton affinity (APA = 245.3 kcal/mol) and intrinsic gas phase basicity (GB = 239 kcal/mol) than proton sponge. Common superbases of this variety feature amidine, guanidine, and phosphazene functional groups. Strong superbases can be designed by utilizing multiple intram ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transannular
In organic chemistry annulation (from the Latin ''anellus'' for "little ring"; occasionally annelation) is a chemical reaction in which a new ring is constructed on a molecule. : Examples are the Robinson annulation, Danheiser annulation and certain cycloadditions. Annular molecules are constructed from side-on condensed cyclic segments, for example helicenes and acenes. In transannulation a bicyclic molecule is created by intramolecular carbon-carbon bond formation in a large monocyclic ring. An example is the samarium(II) iodide induced ketone - alkene cyclization of ''5-methylenecyclooctanone'' which proceeds through a ketyl intermediate: : Benzannulation The term benzannulated compounds refers to derivatives of cyclic compounds (usually aromatic) which are fused to a benzene ring. Examples are listed in the table below: In contemporary chemical literature, the term benzannulation also means "construction of benzene rings from acyclic precursors". upright=1.4, Protonation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superbase
A superbase is a compound that has a particularly high affinity for protons. Superbases are of theoretical interest and potentially valuable in organic synthesis. Superbases have been described and used since the 1850s.''Superbases for Organic Synthesis'' Ed. Ishikawa, T., John Wiley and Sons, Ltd.: West Sussex, UK. 2009. Definitions Generically IUPAC defines a superbase as a "compound having a very high basicity, such as lithium diisopropylamide." Superbases are often defined in two broad categories, organic and organometallic. Organic superbases are charge-neutral compounds with basicities greater than that of proton sponge (pKBH+ = 18.6 in MeCN)." In a related definition: any species with a higher absolute proton affinity (APA = 245.3 kcal/mol) and intrinsic gas phase basicity (GB = 239 kcal/mol) than proton sponge. Common superbases of this variety feature amidine, guanidine, and phosphazene functional groups. Strong superbases can be designed by utilizing multiple intram ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triethylamine
Triethylamine is the chemical compound with the formula N(CH2CH3)3, commonly abbreviated Et3N. It is also abbreviated TEA, yet this abbreviation must be used carefully to avoid confusion with triethanolamine or tetraethylammonium, for which TEA is also a common abbreviation. It is a colourless volatile liquid with a strong fishy odor reminiscent of ammonia. Like diisopropylethylamine (Hünig's base), triethylamine is commonly employed in organic synthesis, usually as a base. Synthesis and properties Triethylamine is prepared by the alkylation of ammonia with ethanol: :NH3 + 3 C2H5OH → N(C2H5)3 + 3 H2O The pKa of protonated triethylamine is 10.75,David Evans Research Group and it can be used to prepare buffer solutions at that pH. The |
Quaternary Ammonium Compounds
In chemistry, quaternary ammonium cations, also known as quats, are positively charged polyatomic ions of the structure , R being an alkyl group or an aryl group. Unlike the ammonium ion () and the primary, secondary, or tertiary ammonium cations, the quaternary ammonium cations are permanently charged, independent of the pH of their solution. Quaternary ammonium salts or quaternary ammonium compounds (called quaternary amines in oilfield parlance) are salts of quaternary ammonium cations. Polyquats are a variety of engineered polymer forms which provide multiple quat molecules within a larger molecule. Quats are used in consumer applications including as antimicrobials (such as detergents and disinfectants), fabric softeners, and hair conditioners. As an antimicrobial, they are able to inactivate enveloped viruses (such as SARS-CoV-2). Quats tend to be gentler on surfaces than bleach-based disinfectants, and are generally fabric-safe. Synthesis Quaternary ammonium compou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amides
In organic chemistry, an amide, also known as an organic amide or a carboxamide, is a compound with the general formula , where R, R', and R″ represent organic groups or hydrogen atoms. The amide group is called a peptide bond when it is part of the main chain of a protein, and an isopeptide bond when it occurs in a side chain, such as in the amino acids asparagine and glutamine. It can be viewed as a derivative of a carboxylic acid () with the hydroxyl group () replaced by an amine group (); or, equivalently, an acyl (alkanoyl) group () joined to an amine group. Common examples of amides are acetamide (), benzamide (), and dimethylformamide (). Amides are qualified as primary, secondary, and tertiary according to whether the amine subgroup has the form , , or , where R and R' are groups other than hydrogen. The core of amides is called the amide group (specifically, carboxamide group). Amides are pervasive in nature and technology. Proteins and important plastics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphazenes
Phosphazenes refer to classes of organophosphorus compounds featuring phosphorus(V) with a double bond between P and N. One class of phosphazenes have the formula . These phosphazenes are also known as iminophosphoranes and phosphine imides. They are superbases. Another class of compounds called phosphazenes are represented with the formula , where X = halogen, alkoxy group, amide and other organyl groups. One example is hexachlorocyclotriphosphazene . Bis(triphenylphosphine)iminium chloride is also referred to as a phosphazene, where Ph = phenyl group. This article focuses on those phosphazenes with the formula . Phosphazene bases Phosphazene bases are strong non-metallic non-ionic and low-nucleophilic bases. They are stronger bases than regular amine or amidine bases. Protonation takes place at a doubly bonded nitrogen atom. Related to phosphazene bases are the Verkade bases, which feature P(III) with three amido substituents and a transannular amine. The p''K''a's of , where R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Condensation Reaction
In organic chemistry, a condensation reaction is a type of chemical reaction in which two molecules are combined to form a single molecule, usually with the loss of a small molecule such as water. If water is lost, the reaction is also known as a dehydration synthesis. However other molecules can also be lost, such as ammonia, ethanol, acetic acid and hydrogen sulfide. The addition of the two molecules typically proceeds in a step-wise fashion to the addition product, usually in equilibrium, and with loss of a water molecule (hence the name condensation). The reaction may otherwise involve the functional groups of the molecule, and is a versatile class of reactions that can occur in acidic or basic conditions or in the presence of a catalyst. This class of reactions is a vital part of life as it is essential to the formation of peptide bonds between amino acids and to the biosynthesis of fatty acids. Many variations of condensation reactions exist. Common examples include the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
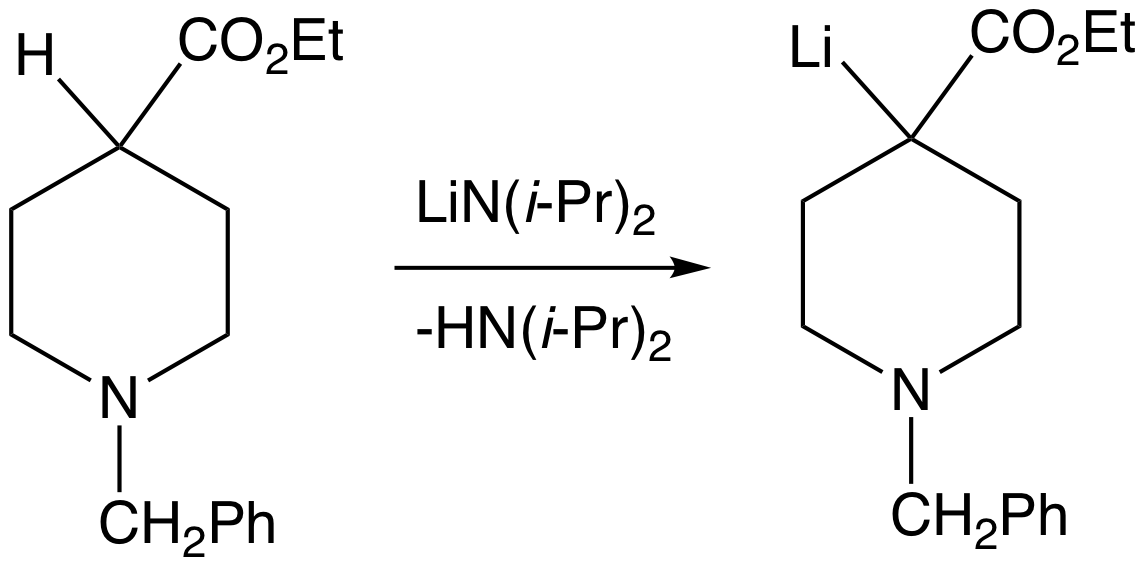
Deprotonate
Deprotonation (or dehydronation) is the removal (transfer) of a proton (or hydron, or hydrogen cation), (H+) from a Brønsted–Lowry acid in an acid–base reaction.Henry Jakubowski, Biochemistry Online Chapter 2A3, https://employees.csbsju.edu/hjakubowski/classes/ch331/protstructure/PS_2A3_AA_Charges.html, accessed 12/2/2020 The species formed is the conjugate base of that acid. The complementary process, when a proton is added (transferred) to a Brønsted–Lowry base, is protonation (or hydronation). The species formed is the conjugate acid of that base. A species that can either accept or donate a proton is referred to as amphiprotic. An example is the H2O (water) molecule, which can gain a proton to form the hydronium ion, H3O+, or lose a proton, leaving the hydroxide ion, OH−. The relative ability of a molecule to give up a proton is measured by its p''K''a value. A low p''K''a value indicates that the compound is acidic and will easily give up its proton to a base. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemistry
Chemistry is the science, scientific study of the properties and behavior of matter. It is a natural science that covers the Chemical element, elements that make up matter to the chemical compound, compounds made of atoms, molecules and ions: their composition, structure, properties, behavior and the changes they undergo during a Chemical reaction, reaction with other Chemical substance, substances. Chemistry also addresses the nature of chemical bonds in chemical compounds. In the scope of its subject, chemistry occupies an intermediate position between physics and biology. It is sometimes called the central science because it provides a foundation for understanding both Basic research, basic and Applied science, applied scientific disciplines at a fundamental level. For example, chemistry explains aspects of plant growth (botany), the formation of igneous rocks (geology), how atmospheric ozone is formed and how environmental pollutants are degraded (ecology), the properties ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |