|
Pro (linguistics)
In generative linguistics, PRO (called "big PRO", distinct from ''pro'', "small pro" or " little pro") is a pronominal determiner phrase (DP) without phonological content. As such, it is part of the set of empty categories. The null pronoun PRO is postulated in the subject position of non-finite clauses. One property of PRO is that, when it occurs in a non-finite complement clause, it can be bound by the main clause subject ("subject control") or the main clause object ("object control"). The presence of PRO in non-finite clauses lacking overt subjects allows a principled solution for problems relating to binding theory. Within government and binding theory, the existence and distribution of PRO followed from the PRO theorem, which states that PRO may not be governed. More recent analyses have abandoned the PRO theorem. Instead, PRO is taken to be in complementary distribution with overt subjects because it is the only item that is able to carry ''null case'' which is checked for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Generative Linguistics
Generative grammar, or generativism , is a linguistic theory that regards linguistics as the study of a hypothesised innate grammatical structure. It is a biological or biologistic modification of earlier structuralist theories of linguistics, deriving ultimately from glossematics. Generative grammar considers grammar as a system of rules that generates exactly those combinations of words that form grammatical sentences in a given language. It is a system of explicit rules that may apply repeatedly to generate an indefinite number of sentences which can be as long as one wants them to be. The difference from structural and functional models is that the object is base-generated within the verb phrase in generative grammar. This purportedly cognitive structure is thought of as being a part of a universal grammar, a syntactic structure which is caused by a genetic mutation in humans. Generativists have created numerous theories to make the NP VP (NP) analysis work in natural lan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
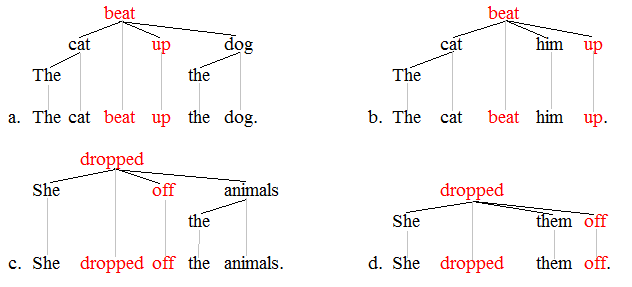
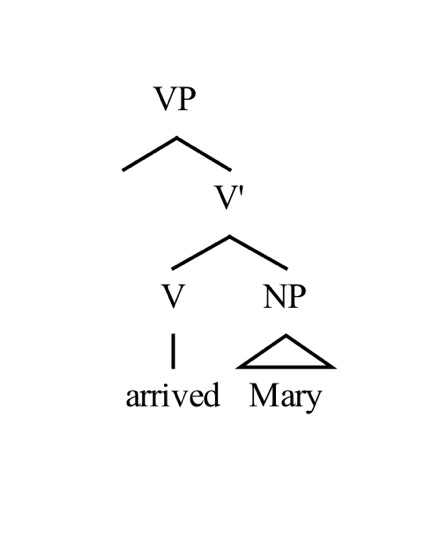
Syntactic Trees
In linguistics, syntax () is the study of how words and morphemes combine to form larger units such as phrases and sentences. Central concerns of syntax include word order, grammatical relations, hierarchical sentence structure (constituency), agreement, the nature of crosslinguistic variation, and the relationship between form and meaning (semantics). There are numerous approaches to syntax that differ in their central assumptions and goals. Etymology The word ''syntax'' comes from Ancient Greek roots: "coordination", which consists of ''syn'', "together", and ''táxis'', "ordering". Topics The field of syntax contains a number of various topics that a syntactic theory is often designed to handle. The relation between the topics is treated differently in different theories, and some of them may not be considered to be distinct but instead to be derived from one another (i.e. word order can be seen as the result of movement rules derived from grammatical relations). Seq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syntactic Tree Diagram,'They Want To Become Millionaires'
In linguistics, syntax () is the study of how words and morphemes combine to form larger units such as phrases and sentences. Central concerns of syntax include word order, grammatical relations, hierarchical sentence structure (constituency), agreement, the nature of crosslinguistic variation, and the relationship between form and meaning (semantics). There are numerous approaches to syntax that differ in their central assumptions and goals. Etymology The word ''syntax'' comes from Ancient Greek roots: "coordination", which consists of ''syn'', "together", and ''táxis'', "ordering". Topics The field of syntax contains a number of various topics that a syntactic theory is often designed to handle. The relation between the topics is treated differently in different theories, and some of them may not be considered to be distinct but instead to be derived from one another (i.e. word order can be seen as the result of movement rules derived from grammatical relations). Seq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syntactic Tree Diagram,'They Want Their Son To Become A Millionaire'
In linguistics, syntax () is the study of how words and morphemes combine to form larger units such as phrases and sentences. Central concerns of syntax include word order, grammatical relations, hierarchical sentence structure (constituency), agreement, the nature of crosslinguistic variation, and the relationship between form and meaning (semantics). There are numerous approaches to syntax that differ in their central assumptions and goals. Etymology The word ''syntax'' comes from Ancient Greek roots: "coordination", which consists of ''syn'', "together", and ''táxis'', "ordering". Topics The field of syntax contains a number of various topics that a syntactic theory is often designed to handle. The relation between the topics is treated differently in different theories, and some of them may not be considered to be distinct but instead to be derived from one another (i.e. word order can be seen as the result of movement rules derived from grammatical relations). Seq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
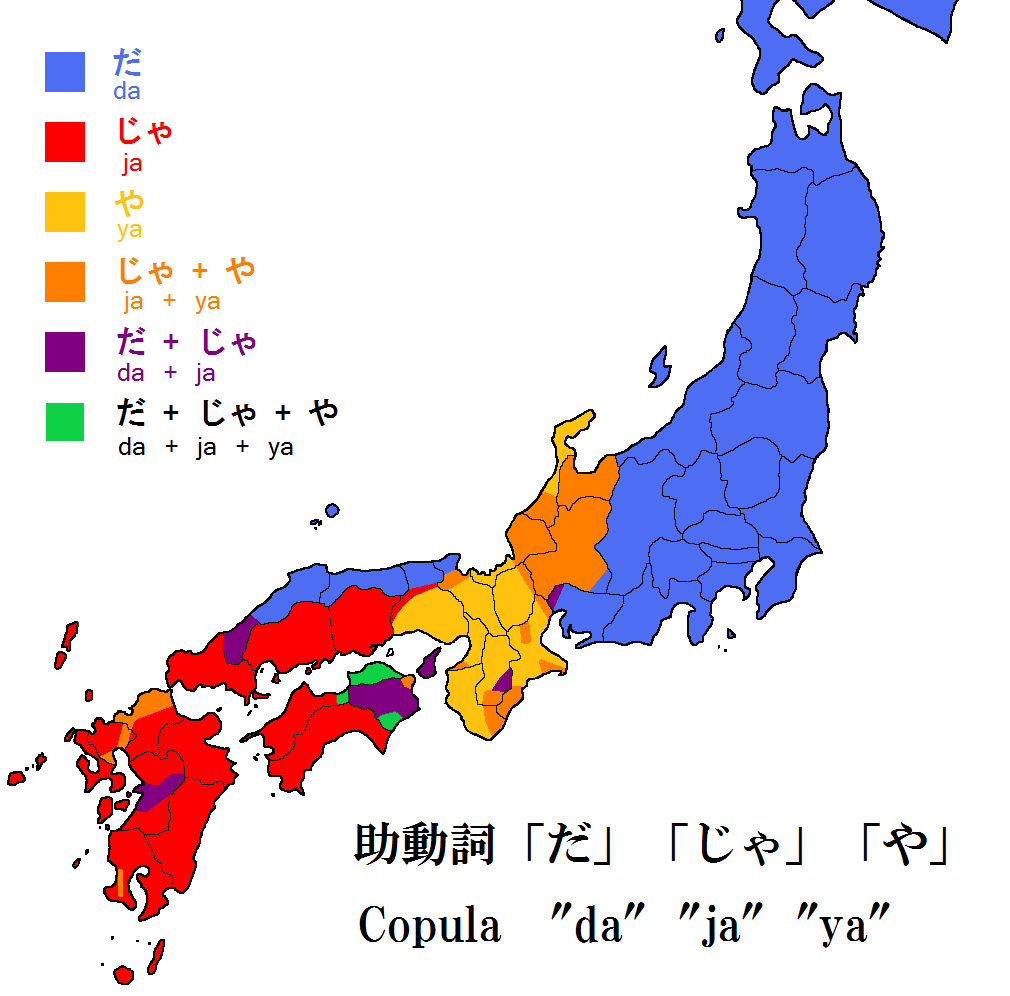
Copula (linguistics)
In linguistics, a copula (plural: copulas or copulae; abbreviated ) is a word or phrase that links the subject of a sentence to a subject complement, such as the word ''is'' in the sentence "The sky is blue" or the phrase ''was not being'' in the sentence "It was not being co-operative." The word ''copula'' derives from the Latin noun for a "link" or "tie" that connects two different things. A copula is often a verb or a verb-like word, though this is not universally the case. A verb that is a copula is sometimes called a copulative or copular verb. In English primary education grammar courses, a copula is often called a linking verb. In other languages, copulas show more resemblances to pronouns, as in Classical Chinese and Guarani, or may take the form of suffixes attached to a noun, as in Korean, Beja, and Inuit languages. Most languages have one main copula, although some (like Spanish, Portuguese and Thai) have more than one, while others have none. In the case of Eng ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agreement (linguistics)
In linguistics, agreement or concord ( abbreviated ) occurs when a word changes form depending on the other words to which it relates. It is an instance of inflection, and usually involves making the value of some grammatical category (such as gender or person) "agree" between varied words or parts of the sentence. For example, in Standard English, one may say ''I am'' or ''he is'', but not "I is" or "he am". This is because English grammar requires that the verb and its subject agree in ''person''. The pronouns ''I'' and ''he'' are first and third person respectively, as are the verb forms ''am'' and ''is''. The verb form must be selected so that it has the same person as the subject in contrast to notional agreement, which is based on meaning. By category Agreement generally involves matching the value of some grammatical category between different constituents of a sentence (or sometimes between sentences, as in some cases where a pronoun is required to agree with its ante ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subject Complement
In grammar, a subject complement or predicative of the subject is a predicative expression that follows a linking verb ( copula) and that complements the subject of the sentence by either (1) renaming it or (2) describing it. It completes the meaning of the subject. In the former case, a renaming noun phrase such as a noun or pronoun is called a predicative nominal. An adjective following the copula and describing the subject is called a predicative adjective. In either case the predicative complement in effect mirrors the subject. Subject complements are used with a small class of verbs called linking verbs or copulas, of which ''be'' is the most common. Since linking verbs are intransitive, subject complements are not affected by any action of the verb. Subject complements are typically neither clause arguments nor adjuncts. A predicative complement can be either a subject complement or an object complement. A predicate nominative does not determine the verb. When there is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reflexive Pronoun
A reflexive pronoun is a pronoun that refers to another noun or pronoun (its antecedent) within the same sentence. In the English language specifically, a reflexive pronoun will end in ''-self'' or ''-selves'', and refer to a previously named noun or pronoun (''myself'', ''yourself'', ''ourselves'', ''themselves'', etc.). English intensive pronouns, used for emphasis, take the same form. In generative grammar, a reflexive pronoun is an anaphor that must be bound by its antecedent (see binding). In a general sense, it is a noun phrase that obligatorily gets its meaning from another noun phrase in the sentence. Different languages have different binding domains for reflexive pronouns, according to their structure. Origins and usage In Indo-European languages, the reflexive pronoun has its origins in Proto-Indo-European. In some languages, some distinction exists between normal object and reflexive pronouns, mainly in the third person: whether one says "I like me" or "I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syntactic Tree Diagram,'It Is Important To Prepare Myself (or) Oneself For The Exam'
In linguistics, syntax () is the study of how words and morphemes combine to form larger units such as phrases and sentences. Central concerns of syntax include word order, grammatical relations, hierarchical sentence structure (constituency), agreement, the nature of crosslinguistic variation, and the relationship between form and meaning (semantics). There are numerous approaches to syntax that differ in their central assumptions and goals. Etymology The word ''syntax'' comes from Ancient Greek roots: "coordination", which consists of ''syn'', "together", and ''táxis'', "ordering". Topics The field of syntax contains a number of various topics that a syntactic theory is often designed to handle. The relation between the topics is treated differently in different theories, and some of them may not be considered to be distinct but instead to be derived from one another (i.e. word order can be seen as the result of movement rules derived from grammatical relations). Seq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lexical Entry
In lexicography, a lexical item is a single word, a part of a word, or a chain of words (catena) that forms the basic elements of a language's lexicon (≈ vocabulary). Examples are ''cat'', ''traffic light'', ''take care of'', ''by the way'', and ''it's raining cats and dogs''. Lexical items can be generally understood to convey a single meaning, much as a lexeme, but are not limited to single words. Lexical items are like semes in that they are "natural units" translating between languages, or in learning a new language. In this last sense, it is sometimes said that language consists of grammaticalized lexis, and not lexicalized grammar. The entire store of lexical items in a language is called its lexis. Lexical items composed of more than one word are also sometimes called ''lexical chunks'', ''gambits'', ''lexical phrases'', ''lexicalized stems'', or ''speech formulae''. The term ''polyword listemes'' is also sometimes used. Types Common types of lexical items/chunks i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theta Criterion
The theta-criterion (also named θ-criterion) is a constraint on x-bar theory that was first proposed by as a rule within the system of principles of the government and binding theory, called theta-theory (θ-theory). As theta-theory is concerned with the distribution and assignment of theta-roles (a.k.a. thematic roles), the theta-criterion describes the specific match between arguments and theta-roles (θ-roles) in logical form (LF): Being a constraint on x-bar theory, the criterion aims to parse out ill-formed sentences. Thus, if the number or categories of arguments in a sentence does not meet the theta-role assigner's requirement in any given sentence, that sentence will be deemed ungrammatical. . In other words, theta-criterion sorts sentences into grammatical and ungrammatical bins based on c-selection and s-selection. Applied Theta grid A theta-role is a status of thematic relation . In other words, a theta-role describes the connection of meaning between a predi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theta Roles
In generative grammar, a theta role or θ-role is the formal device for representing syntactic verb argument, argument structure—the number and type of noun phrases—required syntactically by a particular verb. For example, the verb ''put'' requires three arguments (i.e., it is Valency (linguistics), trivalent). The formal mechanism for implementing a verb's argument structure is codified as theta roles. The verb ''put'' is said to "assign" three theta roles. This is coded in a theta grid associated with the lexical entry for the verb. The correspondence between the theta grid and the actual sentence is accomplished by means of a bijective filter on the grammar known as the theta criterion. Early conceptions of theta roles include (Fillmore called theta roles "cases") and . Theta roles are prominent in government and binding theory and the standard theory of transformational grammar. Thematic relations The term "theta role" is often used interchangeably with the term the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |