|
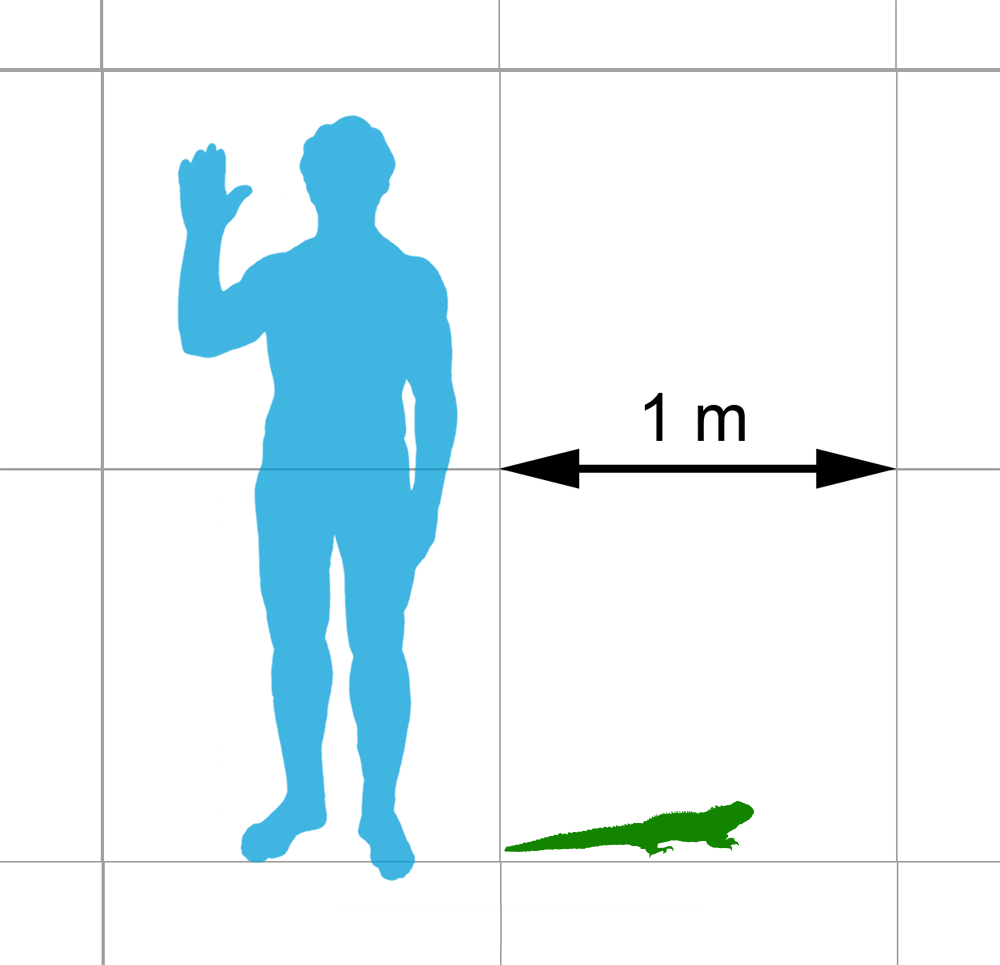
Priosphenodon Avelesi
''Priosphenodon'' is an extinct rhynchocephalian known from the early Late Cretaceous of Argentina. It is believed to have been a fairly large herbivore, having a longer snout than modern tuatara, with teeth specialised for shearing plant matter, like other members of Eilenodontinae. The teeth are densely packed with a cone-in-cone structure, and have prismatic enamel structure similar to those of mammals and the lizard ''Uromastyx,'' which was likely an adaptation to wear resistance in the absence of tooth replacement. Two species are known, ''P. avelesi'' and ''P. minimus''. The latter has also been considered a part of the separate genus ''Kaikaifilusaurus.'' Fossils of the genus have been found in the Candeleros and Cerro Barcino Formation The Cerro Barcino Formation (also known as the Gorro Frigio Formation) is a geological formation in South America whose strata span the Early Cretaceous to the earliest Late Cretaceous. The top age for the formation has been estimated to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cenomanian
The Cenomanian is, in the ICS' geological timescale, the oldest or earliest age of the Late Cretaceous Epoch or the lowest stage of the Upper Cretaceous Series. An age is a unit of geochronology; it is a unit of time; the stage is a unit in the stratigraphic column deposited during the corresponding age. Both age and stage bear the same name. As a unit of geologic time measure, the Cenomanian Age spans the time between 100.5 and 93.9 million years ago (Mya). In the geologic timescale, it is preceded by the Albian and is followed by the Turonian. The Upper Cenomanian starts around at 95 Mya. The Cenomanian is coeval with the Woodbinian of the regional timescale of the Gulf of Mexico and the early part of the Eaglefordian of the regional timescale of the East Coast of the United States. At the end of the Cenomanian, an anoxic event took place, called the Cenomanian-Turonian boundary event or the "Bonarelli event", that is associated with a minor extinction event for marine spec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tuatara
Tuatara (''Sphenodon punctatus'') are reptiles endemic to New Zealand. Despite their close resemblance to lizards, they are part of a distinct lineage, the order Rhynchocephalia. The name ''tuatara'' is derived from the Māori language and means "peaks on the back". The single extant species of tuatara is the only surviving member of its order. Rhynchocephalians originated during the Triassic (~250 million years ago), reached worldwide distribution and peak diversity during the Jurassic and, with the exception of tuatara, were extinct by 60 million years ago. Their closest living relatives are squamates (lizards and snakes). For this reason, tuatara are of interest in the study of the evolution of lizards and snakes, and for the reconstruction of the appearance and habits of the earliest diapsids, a group of amniote tetrapods that also includes dinosaurs (including birds) and crocodilians. Tuatara are greenish brown and grey, and measure up to from head to tail-tip and wei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fossils Of Argentina
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved in amber, hair, petrified wood and DNA remnants. The totality of fossils is known as the ''fossil record''. Paleontology is the study of fossils: their age, method of formation, and evolutionary significance. Specimens are usually considered to be fossils if they are over 10,000 years old. The oldest fossils are around 3.48 billion years old to 4.1 billion years old. Early edition, published online before print. The observation in the 19th century that certain fossils were associated with certain rock strata led to the recognition of a geological timescale and the relative ages of different fossils. The development of radiometric dating techniques in the early 20th century allowed scientists to quantitatively measure the absolute ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cretaceous Argentina
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 145 to 66 million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era, as well as the longest. At around 79 million years, it is the longest geological period of the entire Phanerozoic. The name is derived from the Latin ''creta'', "chalk", which is abundant in the latter half of the period. It is usually abbreviated K, for its German translation ''Kreide''. The Cretaceous was a period with a relatively warm climate, resulting in high eustatic sea levels that created numerous shallow inland seas. These oceans and seas were populated with now-extinct marine reptiles, ammonites, and rudists, while dinosaurs continued to dominate on land. The world was ice free, and forests extended to the poles. During this time, new groups of mammals and birds appeared. During the Early Cretaceous, flowering plants appeared and began to rapidly diversify, becoming the dominant group of plants across the Earth by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Cretaceous Reptiles Of South America
Late may refer to: * LATE, an acronym which could stand for: ** Limbic-predominant age-related TDP-43 encephalopathy, a proposed form of dementia ** Local-authority trading enterprise, a New Zealand business law ** Local average treatment effect, a concept in econometrics Music * ''Late'' (album), a 2000 album by The 77s * Late!, a pseudonym used by Dave Grohl on his ''Pocketwatch'' album * Late (rapper), an underground rapper from Wolverhampton * "Late" (song), a song by Blue Angel * "Late", a song by Kanye West from ''Late Registration'' Other * Late (Tonga), an uninhabited volcanic island southwest of Vavau in the kingdom of Tonga * "Late" (''The Handmaid's Tale''), a television episode * LaTe, Oy Laivateollisuus Ab, a defunct shipbuilding company * Late may refer to a person who is Dead See also * * * ''Lates'', a genus of fish in the lates perch family * Later (other) * Tardiness * Tardiness (scheduling) In scheduling, tardiness is a measure of a delay in exe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turonian Life
The Turonian is, in the ICS' geologic timescale, the second age in the Late Cretaceous Epoch, or a stage in the Upper Cretaceous Series. It spans the time between 93.9 ± 0.8 Ma and 89.8 ± 1 Ma (million years ago). The Turonian is preceded by the Cenomanian Stage and underlies the Coniacian Stage. At the beginning of the Turonian an oceanic anoxic event (OAE 2) took place, also referred to as the Cenomanian-Turonian boundary event or the "Bonarelli Event". Stratigraphic definition The Turonian (French: ''Turonien'') was defined by the French paleontologist Alcide d'Orbigny (1802–1857) in 1842. Orbigny named it after the French city of Tours in the region of Touraine (department Indre-et-Loire), which is the original type locality. The base of the Turonian Stage is defined as the place where the ammonite species '' Watinoceras devonense'' first appears in the stratigraphic column. The official reference profile (the GSSP) for the base of the Turonian is located in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cenomanian Life
The Cenomanian is, in the ICS' geological timescale, the oldest or earliest age of the Late Cretaceous Epoch or the lowest stage of the Upper Cretaceous Series. An age is a unit of geochronology; it is a unit of time; the stage is a unit in the stratigraphic column deposited during the corresponding age. Both age and stage bear the same name. As a unit of geologic time measure, the Cenomanian Age spans the time between 100.5 and 93.9 million years ago (Mya). In the geologic timescale, it is preceded by the Albian and is followed by the Turonian. The Upper Cenomanian starts around at 95 Mya. The Cenomanian is coeval with the Woodbinian of the regional timescale of the Gulf of Mexico and the early part of the Eaglefordian of the regional timescale of the East Coast of the United States. At the end of the Cenomanian, an anoxic event took place, called the Cenomanian-Turonian boundary event or the "Bonarelli event", that is associated with a minor extinction event for marine speci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prehistoric Reptile Genera
Prehistory, also known as pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the use of the first stone tools by hominins 3.3 million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The use of symbols, marks, and images appears very early among humans, but the earliest known writing systems appeared 5000 years ago. It took thousands of years for writing systems to be widely adopted, with writing spreading to almost all cultures by the 19th century. The end of prehistory therefore came at very different times in different places, and the term is less often used in discussing societies where prehistory ended relatively recently. In the early Bronze Age, Sumer in Mesopotamia, the Indus Valley Civilisation, and ancient Egypt were the first civilizations to develop their own scripts and to keep historical records, with their neighbors following. Most other civilizations reached the end of prehistory during the following Iron Age. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prehistoric Lepidosaurs
Prehistory, also known as pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the use of the first stone tools by hominins 3.3 million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The use of symbols, marks, and images appears very early among humans, but the earliest known writing systems appeared 5000 years ago. It took thousands of years for writing systems to be widely adopted, with writing spreading to almost all cultures by the 19th century. The end of prehistory therefore came at very different times in different places, and the term is less often used in discussing societies where prehistory ended relatively recently. In the early Bronze Age, Sumer in Mesopotamia, the Indus Valley Civilisation, and ancient Egypt were the first civilizations to develop their own scripts and to keep historical records, with their neighbors following. Most other civilizations reached the end of prehistory during the following Iron Age. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Priosphenodon NT Small
''Priosphenodon'' is an extinct rhynchocephalian known from the early Late Cretaceous of Argentina. It is believed to have been a fairly large herbivore, having a longer snout than modern tuatara, with teeth specialised for shearing plant matter, like other members of Eilenodontinae. The teeth are densely packed with a cone-in-cone structure, and have prismatic enamel structure similar to those of mammals and the lizard ''Uromastyx,'' which was likely an adaptation to wear resistance in the absence of tooth replacement. Two species are known, ''P. avelesi'' and ''P. minimus''. The latter has also been considered a part of the separate genus ''Kaikaifilusaurus.'' Fossils of the genus have been found in the Candeleros and Cerro Barcino Formation The Cerro Barcino Formation (also known as the Gorro Frigio Formation) is a geological formation in South America whose strata span the Early Cretaceous to the earliest Late Cretaceous. The top age for the formation has been estimated to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cerro Barcino Formation
The Cerro Barcino Formation (also known as the Gorro Frigio Formation) is a geological formation in South America whose strata span the Early Cretaceous to the earliest Late Cretaceous. The top age for the formation has been estimated to be Cenomanian. Earlier estimates placed the formation until the Campanian. The formation was deposited in the Cañadón Asfalto Basin, a rift basin that started forming in the earliest Jurassic. Dinosaur remains are among the fossils that have been recovered from the formation. The Cerro Barcino Formation is the second-youngest unit of the Chubut Group, which also includes the older Los Adobes Formation. Both formations cover a vast area in Chubut Province, Argentina. The two formations are distinguished by geological features suggesting a distinct change in climate, from a wetter, flood plain environment in the Los Adobes to a much more arid, desert-like environment in the Cerro Barcino.Rauhut et al., 2003 The Cerro Barcino Formation is subdiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Candeleros Formation
The Candeleros Formation (formerly known as the Candeleros Member of the "Río Limay Formation") is a geologic formation that crops out in the Río Negro, Neuquén, and Mendoza provinces of northern Patagonia, Argentina. It is the oldest formation in the Neuquén Group and belongs to the Rio Limay Subgroup. Formerly that subgroup was treated as a formation, and the Candeleros Formation was known as the Candeleros Member.Sánchez ''et al.'', 2006 Description The type locality of the Candeleros Formation is Candeleros Hill in Neuquén Province, after which the formation was named by Wichmann in 1929.Wichmann, 1929 This formation unconformably overlies the Lohan Cura Formation, and it is in turn overlain by the Huincul Formation, also a unit of the Neuquén Group. The sediments of the latter are of lighter greenish and yellow colors and the boundary between the Candeleros and Huincul formations is easily recognizable.Leanza ''et al.'', 2004 The Candeleros Formation is almost th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |