|
Pringle Maneuver
The Pringle manoeuvre is a surgical technique used in some abdominal operations and in liver trauma. The hepatoduodenal ligament is clamped either with a surgical tool called a haemostat, an umbilical tape or by hand. This limits blood inflow through the hepatic artery and the portal vein, controlling bleeding from the liver. Uses The Pringle manoeuvre is used during liver surgery and in some cases of severe liver trauma to minimize blood loss. For short durations of use, it is very effective at reducing intraoperative blood loss. The Pringle manoeuvre is applied during closure of a vena cava injury when an atriocaval shunt is placed. Limits The Pringle manoeuvre is more effective in preventing blood loss during liver surgery if central venous pressure is maintained at 5 mmHg or lower. This is due to the fact that Pringle manoeuver technique aims at controlling the blood inflow into the liver, having no effect on the outflow. In case of using Pringle manoeuver during liv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abdominal Surgery
The term abdominal surgery broadly covers surgical procedures that involve opening the abdomen (laparotomy). Surgery of each abdominal organ is dealt with separately in connection with the description of that organ (see stomach, kidney, liver, etc.) Diseases affecting the abdominal cavity are dealt with generally under their own names (e.g. appendicitis). Types The most common abdominal surgeries are described below. * Appendectomy: surgical opening of the abdominal cavity and removal of the appendix. Typically performed as definitive treatment for appendicitis, although sometimes the appendix is prophylactically removed incidental to another abdominal procedure. * Caesarean section (also known as C-section): a surgical procedure in which one or more incisions are made through a mother's abdomen (laparotomy) and uterus (hysterotomy) to deliver one or more babies, or, rarely, to remove a dead fetus. * Inguinal hernia surgery: the repair of an inguinal hernia. *Exploratory lapa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atriocaval Shunt
An atriocaval shunt (ACS) is an intraoperative surgical shunt between the atrium of the heart and the inferior vena cava. It is used during the repair of larger juxtahepatic (next to the liver) vascular injuries such as an injury to the local vena cava. Injuries to the inferior vena cava are challenging, those behind the liver being the most difficult to repair. __TOC__ Procedure and results Injury to the vena cava adjacent to the liver and/or connected hepatic veins leads to often fatal bleeding. Patients may be admitted already in hemorrhagic shock with death occurring even before the bleeding area is localized. Surgically, the area is difficult to access as it is largely covered by the liver. In 1968 Schrock et al. reported on the first use of the ACS. They devised this approach after observing that above the renal veins only the right adrenal vein, the hepatic veins, and the inferior phrenic veins enter the inferior vena cava. The placement of the shunt allowed venous return to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Hogarth Pringle
James Hogarth Pringle (born 26 January 1863 in Parramatta, Australia – died 24 April 1941 in Killearn, Scotland) was an Australian-born British surgeon in Glasgow, who made a number of important contributions to surgical practice. He is most famous for the development of the Pringle manoeuvre, a technique still used in surgery today. Early life He was the only son of George Hogarth Pringle (1830–1871) a well known surgeon in Parramatta, New South Wales, Australia. Before emigrating to Australia George Hogarth Pringle had worked in Edinburgh with Joseph Lister and had been responsible for the introduction of antiseptic surgical practice into Australia. After his father died in 1872, James returned to Britain to school at Sedbergh in Cumberland and from there entered the University of Edinburgh Medical School to study medicine, graduating in 1885. After graduation he was able travel to Europe to study surgical practice at Hamburg, Berlin and Vienna. This visit to European cen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
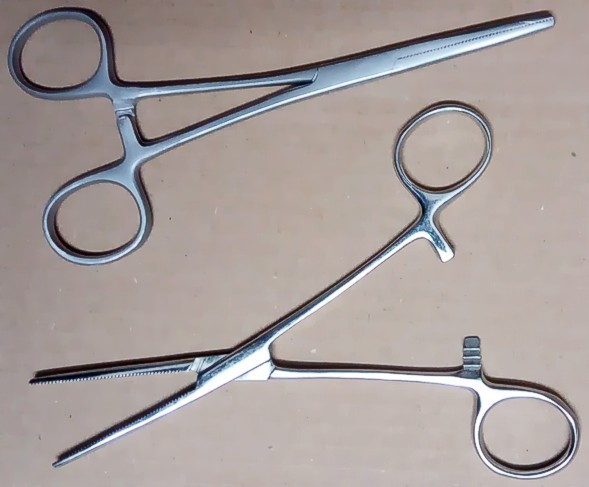
Hemostat
A hemostat (also called a hemostatic clamp, arterial forceps, or pean after Jules-Émile Péan) is a surgical tool used in many surgical procedures to control bleeding. For this reason, it is common in the initial phases of surgery for the initial incision to be lined with hemostats which close blood vessels awaiting ligation. Hemostats belong to a group of instruments that pivot (similar to scissors, and including needle holders, tissue holders and various clamps) where the structure of the tip determines its function. The hemostat has handles that can be held in place by their locking mechanism. The locking mechanism is typically a series of interlocking teeth, a few on each handle, that allow the user to adjust the clamping force of the pliers. When locked together, the force between the tips is approximately 40 N (9 lbf). History The earliest known drawing of a pivoting surgical instrument dates back to 1500 BC on a tomb at Thebes, Egypt. Later Roman bronze and steel piv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blood
Blood is a body fluid in the circulatory system of humans and other vertebrates that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells, and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells. Blood in the circulatory system is also known as ''peripheral blood'', and the blood cells it carries, ''peripheral blood cells''. Blood is composed of blood cells suspended in blood plasma. Plasma, which constitutes 55% of blood fluid, is mostly water (92% by volume), and contains proteins, glucose, mineral ions, hormones, carbon dioxide (plasma being the main medium for excretory product transportation), and blood cells themselves. Albumin is the main protein in plasma, and it functions to regulate the colloidal osmotic pressure of blood. The blood cells are mainly red blood cells (also called RBCs or erythrocytes), white blood cells (also called WBCs or leukocytes) and platelets (also called thrombocytes). The most abundant cells in vertebrate blood a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lesser Omentum
The lesser omentum (small omentum or gastrohepatic omentum) is the double layer of peritoneum that extends from the liver to the lesser curvature of the stomach, and to the first part of the duodenum. The lesser omentum is usually divided into these two connecting parts: the hepatogastric ligament, and the hepatoduodenal ligament. Structure The lesser omentum is extremely thin, and is continuous with the two layers of peritoneum which cover respectively the antero-superior and postero-inferior surfaces of the stomach and first part of the duodenum. When these two layers reach the lesser curvature of the stomach and the upper border of the duodenum, they join and ascend as a double fold to the porta hepatis. To the left of the porta, the fold is attached to the bottom of the fossa for the ductus venosus, along which it is carried to the diaphragm, where the two layers separate to embrace the end of the esophagus. At the right border of the lesser omentum, the two layers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reperfusion Injury
Reperfusion injury, sometimes called ischemia-reperfusion injury (IRI) or reoxygenation injury, is the tissue damage caused when blood supply returns to tissue ('' re-'' + ''perfusion'') after a period of ischemia or lack of oxygen (anoxia or hypoxia). The absence of oxygen and nutrients from blood during the ischemic period creates a condition in which the restoration of circulation results in inflammation and oxidative damage through the induction of oxidative stress rather than (or along with) restoration of normal function. Reperfusion injury is distinct from cerebral hyperperfusion syndrome (sometimes called "Reperfusion syndrome"), a state of abnormal cerebral vasodilation. Mechanisms Reperfusion of ischemic tissues is often associated with microvascular injury, particularly due to increased permeability of capillaries and arterioles that lead to an increase of diffusion and fluid filtration across the tissues. Activated endothelial cells produce more reactive oxygen sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hepatic Vein
In human anatomy, the hepatic veins are the veins that drain venous blood from the liver into the inferior vena cava (as opposed to the hepatic portal vein which conveys blood from the gastrointestinal organs to the liver). There are usually three large upper hepatic veins draining from the left, middle, and right parts of the liver, as well as a number (6-20) of lower hepatic veins. All hepatic veins are valveless. Structure All the hepatic veins drain into the inferior vena cava. The hepatic veins are divided into an upper and a lower group. Upper group The upper group consists of three hepatic veins - the right, middle, and left hepatic veins - draining the central veins from the right, middle, and left regions of the liver and are larger than the lower group of veins. The veins of the upper group drain into the suprahepatic part of the inferior vena cava (i.e. part superior to the liver). Right hepatic vein The right hepatic vein is the longest and largest of all the he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inferior Vena Cava
The inferior vena cava is a large vein that carries the deoxygenated blood from the lower and middle body into the right atrium of the heart. It is formed by the joining of the right and the left common iliac veins, usually at the level of the fifth lumbar vertebra. The inferior vena cava is the lower (" inferior") of the two venae cavae, the two large veins that carry deoxygenated blood from the body to the right atrium of the heart: the inferior vena cava carries blood from the lower half of the body whilst the superior vena cava carries blood from the upper half of the body. Together, the venae cavae (in addition to the coronary sinus, which carries blood from the muscle of the heart itself) form the venous counterparts of the aorta. It is a large retroperitoneal vein that lies posterior to the abdominal cavity and runs along the right side of the vertebral column. It enters the right auricle at the lower right, back side of the heart. The name derives from la, ve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Millimetre Of Mercury
A millimetre of mercury is a manometric unit of pressure, formerly defined as the extra pressure generated by a column of mercury one millimetre high, and currently defined as exactly pascals. It is denoted mmHg or mm Hg. Although not an SI unit, the millimetre of mercury is still routinely used in medicine, meteorology, aviation, and many other scientific fields. One millimetre of mercury is approximately 1 Torr, which is of standard atmospheric pressure ( ≈ ). Although the two units are not equal, the relative difference (less than ) is negligible for most practical uses. History For much of human history, the pressure of gases like air was ignored, denied, or taken for granted, but as early as the 6th century BC, Greek philosopher Anaximenes of Miletus claimed that all things are made of air that is simply changed by varying levels of pressure. He could observe water evaporating, changing to a gas, and felt that this applied even to solid matter. More ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bleeding
Bleeding, hemorrhage, haemorrhage or blood loss, is blood escaping from the circulatory system from damaged blood vessels. Bleeding can occur internally, or externally either through a natural opening such as the mouth, nose, ear, urethra, vagina or anus, or through a puncture in the skin. Hypovolemia is a massive decrease in blood volume, and death by excessive loss of blood is referred to as exsanguination. Typically, a healthy person can endure a loss of 10–15% of the total blood volume without serious medical difficulties (by comparison, blood donation typically takes 8–10% of the donor's blood volume). The stopping or controlling of bleeding is called hemostasis and is an important part of both first aid and surgery. Types * Upper head ** Intracranial hemorrhage – bleeding in the skull. ** Cerebral hemorrhage – a type of intracranial hemorrhage, bleeding within the brain tissue itself. ** Intracerebral hemorrhage – bleeding in the brain caused by the rupture of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chronic Venous Insufficiency
Chronic venous insufficiency (CVI) is a medical condition in which blood pools in the veins, straining the walls of the vein. The most common cause of CVI is superficial venous reflux which is a treatable condition. As functional venous valves are required to provide for efficient blood return from the lower extremities, this condition typically affects the legs. If the impaired vein function causes significant symptoms, such as swelling and ulcer formation, it is referred to as chronic venous disease. It is sometimes called ''chronic peripheral venous insufficiency'' and should not be confused with post-thrombotic syndrome in which the deep veins have been damaged by previous deep vein thrombosis. Most cases of CVI can be improved with treatments to the superficial venous system or stenting the deep system. Varicose veins for example can now be treated by local anesthetic endovenous surgery. Rates of CVI are higher in women than in men. Other risk factors include genetics, sm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |