|
Principle
A principle may relate to a fundamental truth or proposition that serves as the foundation for a system of beliefs or behavior or a chain of reasoning. They provide a guide for behavior or evaluation. A principle can make values explicit, so they are expressed in the form of rules and standards. Principles unpack the values underlying them more concretely so that the values can be more easily operationalized in policy statements and actions. In law, higher order, overarching principles establish rules to be followed, modified by sentencing guidelines relating to context and proportionality. In science and nature, a principle may define the essential characteristics of the system, or reflect the system's designed purpose. The effective operation would be impossible if any one of the principles was to be ignored. A system may be explicitly based on and implemented from a document of principles as was done in IBM's 360/370 ''Principles of Operation''. It is important to differe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Precautionary Principle
The precautionary principle (or precautionary approach) is a broad epistemological, philosophical and legal approach to innovations with potential for causing harm when extensive scientific knowledge on the matter is lacking. It emphasizes caution, pausing and review before leaping into new innovations that may prove disastrous. Critics argue that it is vague, self-cancelling, unscientific and an obstacle to progress. In an engineering context, the precautionary principle manifests itself as the factor of safety. It was apparently suggested, in civil engineering, by Belidorde Bélidor, Bernard Forest, La science des ingénieurs, dans la conduite des travaux de fortification et d'architecture civile, Paris: Chez Claude Jombert 1729 in 1729. Interrelation between safety factor and reliability is extensively studied by engineers and philosophers. The principle is often used by policy makers in situations where there is the possibility of harm from making a certain decision (e.g. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anthropic Principle
In cosmology, the anthropic principle, also known as the observation selection effect, is the proposition that the range of possible observations that could be made about the universe is limited by the fact that observations are only possible in the type of universe that is capable of developing observers in the first place. Proponents of the anthropic principle argue that it explains why the universe has the age and the fundamental physical constants necessary to accommodate intelligent life. If either had been significantly different, no one would have been around to make observations. Anthropic reasoning has been used to address the question as to why certain measured physical constants take the values that they do, rather than some other arbitrary values, and to explain a perception that the universe appears to be finely tuned for the existence of life. There are many different formulations of the anthropic principle. Philosopher Nick Bostrom counts thirty, but the underlying ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reality Principle
In Freudian psychology and psychoanalysis, the reality principle () is the ability of the mind to assess the reality of the external world, and to act upon it accordingly, as opposed to acting according to the pleasure principle. The reality principle is the governing principle of the actions taken by the ego, after its slow development from a "pleasure-ego" into a "reality-ego". History Freud argued that "an ego thus educated has become 'reasonable'; it no longer lets itself be governed by the pleasure principle, but obeys the reality principle, which also, at bottom, seeks to obtain pleasure, but pleasure which is assured through taking account of reality, even though it is pleasure postponed and diminished". In his introductory lectures of 1915, at the University of Vienna, Freud popularized the concept of the unconscious as the largest and most influential part of the mind, including those drives, instincts and motives humans are often forced to deny except in disguised f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Principle Of Relativity
In physics, the principle of relativity is the requirement that the equations describing the laws of physics have the same form in all admissible frames of reference. For example, in the framework of special relativity, the Maxwell equations have the same form in all inertial frames of reference. In the framework of general relativity, the Maxwell equations or the Einstein field equations have the same form in arbitrary frames of reference. Several principles of relativity have been successfully applied throughout science, whether implicitly (as in Newtonian mechanics) or explicitly (as in Albert Einstein's special relativity and general relativity). Basic concepts Certain principles of relativity have been widely assumed in most scientific disciplines. One of the most widespread is the belief that any law of nature should be the same at all times; and scientific investigations generally assume that laws of nature are the same regardless of the person measuring them. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
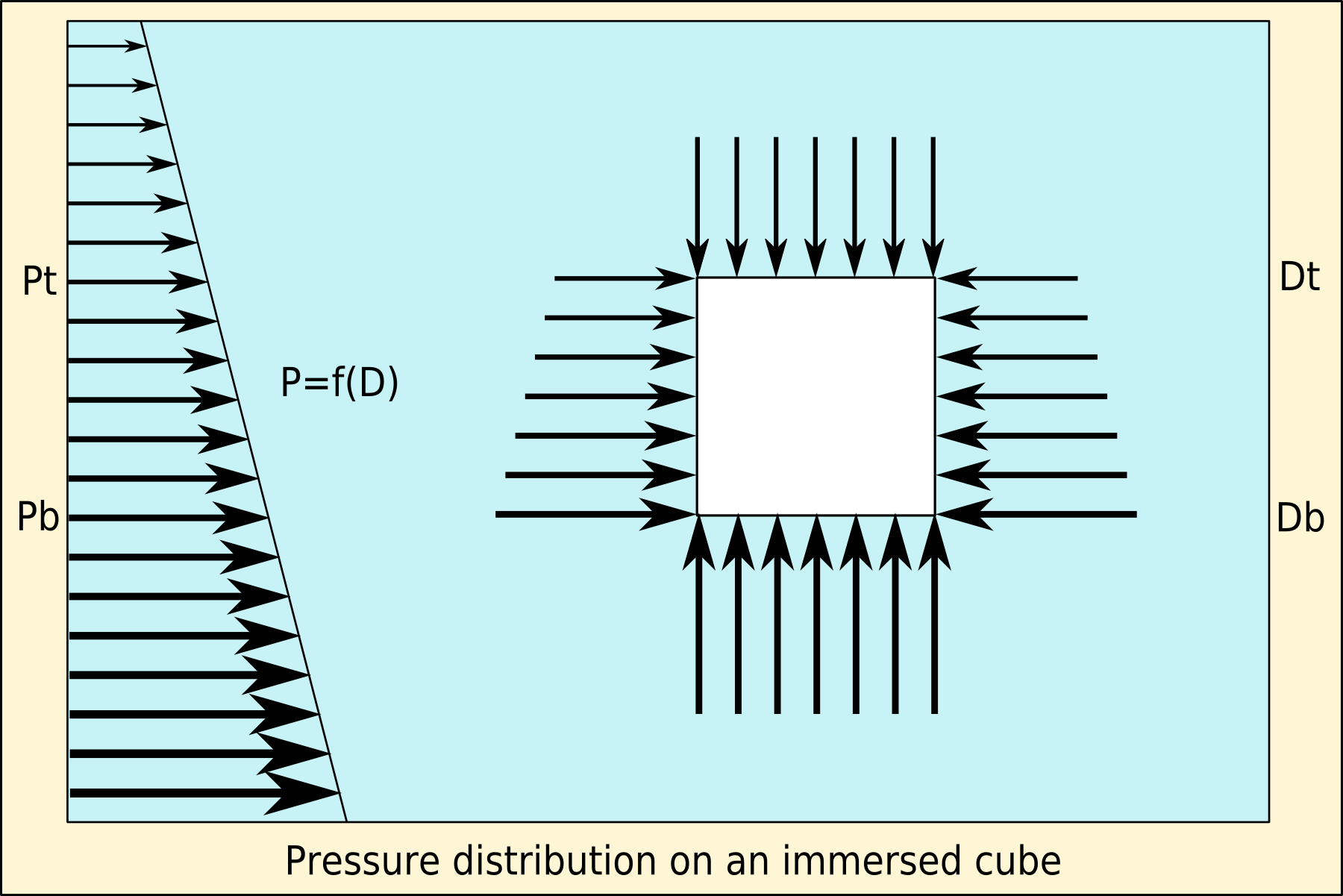
Archimedes' Principle
Archimedes' principle states that the upward buoyant force that is exerted on a body immersed in a fluid, whether fully or partially, is equal to the weight of the fluid that the body displaces. Archimedes' principle is a law of physics fundamental to fluid mechanics. It was formulated by Archimedes of Syracuse. Explanation In '' On Floating Bodies'', Archimedes suggested that (c. 246 BC): Archimedes' principle allows the buoyancy of any floating object partially or fully immersed in a fluid to be calculated. The downward force on the object is simply its weight. The upward, or buoyant, force on the object is that stated by Archimedes' principle above. Thus, the net force on the object is the difference between the magnitudes of the buoyant force and its weight. If this net force is positive, the object rises; if negative, the object sinks; and if zero, the object is neutrally buoyant—that is, it remains in place without either rising or sinking. In simple words, Archim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cosmological Principle
In modern physical cosmology, the cosmological principle is the notion that the spatial distribution of matter in the universe is uniformly isotropic and homogeneous when viewed on a large enough scale, since the forces are expected to act equally throughout the universe on a large scale, and should, therefore, produce no observable inequalities in the large-scale structuring over the course of evolution of the matter field that was initially laid down by the Big Bang. Definition Astronomer William Keel explains: The cosmological principle is usually stated formally as 'Viewed on a sufficiently large scale, the properties of the universe are the same for all observers.' This amounts to the strongly philosophical statement that the part of the universe which we can see is a fair sample, and that the same physical laws apply throughout. In essence, this in a sense says that the universe is knowable and is playing fair with scientists. As Andrew Liddle puts it, "the cosmologic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pleasure Principle (psychology)
In Freudian psychoanalysis, the pleasure principle () is the instinctive seeking of pleasure and avoiding of pain to satisfy biological and psychological needs. Specifically, the pleasure principle is the animating force behind the id. Precursors Epicurus in the ancient world, and later Jeremy Bentham, laid stress upon the role of pleasure in directing human life, the latter stating: "Nature has placed mankind under the governance of two sovereign masters, ''pain'' and ''pleasure''". Freud's most immediate predecessor and guide however was Gustav Theodor Fechner and his psychophysics. Freudian developments Freud used the idea that the mind seeks pleasure and avoids pain in his ''Project for a Scientific Psychology'' of 1895, as well as in the theoretical portion of '' The Interpretation of Dreams'' of 1900, where he termed it the 'unpleasure principle'.''On Metapsychology'', p. 36. In the ''Two Principles of Mental Functioning'' of 1911, contrasting it with the reality prin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mediocrity Principle
The mediocrity principle is the philosophical notion that "if an item is drawn at random from one of several sets or categories, it's more likely to come from the most numerous category than from any one of the less numerous categories". The principle has been taken to suggest that there is nothing very unusual about the evolution of the Solar System, Earth's history, the evolution of biological complexity, human evolution, or any one nation. It is a heuristic in the vein of the Copernican principle, and is sometimes used as a philosophical statement about the place of humanity. The idea is to assume mediocrity, rather than starting with the assumption that a phenomenon is special, privileged, exceptional, or even superior. David Bates ascribed the mediocrity principle to Sebastian von Hoerner, who as early as 1961 wrote the following:In a footnote, von Hoerner thanked F. D. Drake for his input on the subject. Extraterrestrial life The mediocrity principle suggests, given ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homestead Principle
The homestead principle is the principle by which one gains ownership of an unowned natural resource by performing an act of original appropriation. Appropriation could be enacted by putting an unowned resource to active use (as with using it to produce some product), joining it with previously acquired property, or by marking it as owned (as with livestock branding). Homesteading is one of the foundations of Rothbardian anarcho-capitalism and right-libertarianism. In political philosophy Mohammad In Islam, a "dead" land (not previously owned or under use by the public) can be owned by "reviving" it, as per the prophetic saying: "If anyone revives dead land, it belongs to him, and the unjust root has no right." This principle, however, does not deprive the community from some common rights in the land, including the right to pass water through it to the neighbor's land, for example. John Locke In his 1690 work '' Second Treatise of Government'', Enlightenment ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Golden Rule
The Golden Rule is the principle of treating others as one would want to be treated by them. It is sometimes called an ethics of reciprocity, meaning that one should reciprocate to others how one would like them to treat the person (not necessarily how they actually treat them). Various expressions of this rule can be found in the tenets of most religions and creeds through the ages. The Maxim (philosophy), maxim may appear as a Affirmation and negation, positive or negative injunction governing conduct: * Treat others as one would like others to treat them (positive or directive form) * Do ''not'' treat others in ways that one would ''not'' like to be treated (negative or prohibitive form) * What one wishes upon others, they wish upon themselves (empathetic or responsive form) Etymology The Terminology, term "Golden Rule", or "Golden law", began to be used widely in the early 17th century in Britain by Anglicanism, Anglican theologians and preachers; the earliest known usage ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Separation Of Church And State
The separation of church and state is a philosophical and Jurisprudence, jurisprudential concept for defining political distance in the relationship between religious organizations and the State (polity), state. Conceptually, the term refers to the creation of a secular state (with or without legally explicit church-state separation) and to disestablishment, the changing of an existing, formal relationship between the church and the state. The concept originated among early Baptists in America. In 1644, Roger Williams, a Baptist minister and founder of the Rhode Island, state of Rhode Island and the First Baptist Church in America, was the first public official to call for "a wall or hedge of separation" between "the wilderness of the world" and "the garden of the church." Although the concept is older, the exact phrase "separation of church and state" is derived from "wall of separation between Church & State," a term coined by Thomas Jefferson in his 1802 letter to members of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Principle Of Priority
Priority is a principle in Taxonomy (biology), biological taxonomy by which a valid scientific name is established based on the oldest available name. It is a decisive rule in Botanical nomenclature, botanical and zoological nomenclature to recognise the first Binomial nomenclature, binomial name (also called ''binominal name'' in zoology) given to an organism as the correct and acceptable name. The purpose is to select one scientific name as a stable one out of two or more alternate names that often exist for a single species. The ''International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants'' (ICN) defines it as: "A right to precedence established by the date of valid publication of a legitimate name or of an earlier homonym, or by the date of designation of a type." Basically, it is a scientific procedure to eliminate duplicate or multiple names for a species, for which Lucien Marcus Underwood called it "the principle of outlaw in nomenclature". History The principle of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |