|
Prima BioMed
Immutep Ltd (formerly Prima Biomed) is a biotechnology company working primarily in the field of cancer immunotherapy using the LAG3 immune control mechanism. The company was originally built on CVac, a therapeutic cancer vaccine. In late 2014 the privately held French immunotherapy company Immutep SA was purchased by Prima Biotech. Prima currently has three main products in its pipeline, all acquired with Immutep: Eftilagimod alpha, (lab name: IMP321) which is recombinant soluble LAG-3, used as an activator of antigen presenting cells. This product has completed a Phase IIa clinical study, where it doubled the expected response rate in HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer. IMP731, a depleting monoclonal antibody for autoimmune diseases, targeting LAG-3+ activated T cells. This antibody has been licensed to GlaxoSmithKline. IMP701, an antagonist monoclonal antibody to LAG3 for use in cancer. This product has been licensed to Novartis History Immutep (formerly Prima B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Public Company
A public company is a company whose ownership is organized via shares of stock which are intended to be freely traded on a stock exchange or in over-the-counter markets. A public (publicly traded) company can be listed on a stock exchange (listed company), which facilitates the trade of shares, or not (unlisted public company). In some jurisdictions, public companies over a certain size must be listed on an exchange. In most cases, public companies are ''private'' enterprises in the ''private'' sector, and "public" emphasizes their reporting and trading on the public markets. Public companies are formed within the legal systems of particular states, and therefore have associations and formal designations which are distinct and separate in the polity in which they reside. In the United States, for example, a public company is usually a type of corporation (though a corporation need not be a public company), in the United Kingdom it is usually a public limited company (plc), i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HER2
Receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbB-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''ERBB2'' gene. ERBB is abbreviated from erythroblastic oncogene B, a gene originally isolated from the avian genome. The human protein is also frequently referred to as ''HER2'' (human epidermal growth factor receptor 2) or CD340 (cluster of differentiation 340). HER2 is a member of the human epidermal growth factor receptor (HER/EGFR/ERBB) family. But contrary to other member of the ERBB family, HER2 does not directly bind ligand. HER2 activation results from heterodimerization with another ERBB member or by homodimerization when HER2 concentration are high, for instance in cancer. Amplification or over-expression of this oncogene has been shown to play an important role in the development and progression of certain aggressive types of breast cancer. In recent years the protein has become an important biomarker and target of therapy for approximately 30% of breast cancer patients. Name ''H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Institut Gustave Roussy
Gustave Roussy is the first leader cancer-research hospital in Europe and ranked among the top 3 best specialized hospitals in the world . It is a centre for high quality patient care, research and teaching. It is highly-known for the treatment of (among others): skin cancers like melanoma, breast cancer, and lung cancer. It provides access to care with many expert doctors who have historically revolutionized the treatment of cancer and contributed to the surge of new molecules in the treatment of cancers and tumors. It is located in the Parisian area. It is named after Gustave Roussy, a Swiss-French neuropathologist. In April 2019, three new interventional radiology rooms were inaugurated, making it the largest platform of this type in Europe, entirely dedicated to oncology. Interventional radiology is a so-called "minimally invasive" diagnostic and treatment technique, which uses images to guide access to deep-lying organs, without having to "open up" patients. Gustave Roussy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immune Checkpoint
Immune checkpoints are regulators of the immune system. These pathways are crucial for self-tolerance, which prevents the immune system from attacking cells indiscriminately. However, some cancers can protect themselves from attack by stimulating immune checkpoint targets. Inhibitory checkpoint molecules are targets for cancer immunotherapy due to their potential for use in multiple types of cancers. Currently approved checkpoint inhibitors block CTLA4 and PD-1 and PD-L1. For the related basic science discoveries, James P. Allison and Tasuku Honjo won the Tang Prize in Biopharmaceutical Science and the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 2018. Stimulatory checkpoint molecules Four stimulatory checkpoint molecules are members of the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor superfamily—CD27, CD40, OX40, GITR and CD137. Another two stimulatory checkpoint molecules belong to the B7-CD28 superfamily—CD28 itself and ICOS. * CD27: This molecule supports antigen-specific ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
P Value
In null-hypothesis significance testing, the ''p''-value is the probability of obtaining test results at least as extreme as the result actually observed, under the assumption that the null hypothesis is correct. A very small ''p''-value means that such an extreme observed outcome would be very unlikely under the null hypothesis. Reporting ''p''-values of statistical tests is common practice in academic publications of many quantitative fields. Since the precise meaning of ''p''-value is hard to grasp, misuse is widespread and has been a major topic in metascience. Basic concepts In statistics, every conjecture concerning the unknown probability distribution of a collection of random variables representing the observed data X in some study is called a ''statistical hypothesis''. If we state one hypothesis only and the aim of the statistical test is to see whether this hypothesis is tenable, but not to investigate other specific hypotheses, then such a test is called a null ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
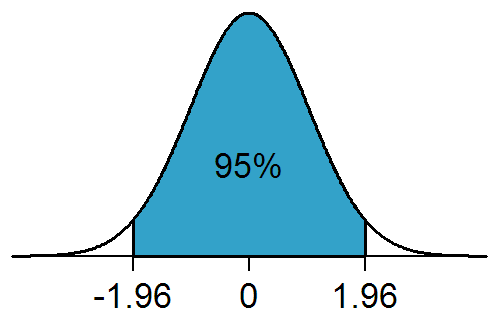
Statistical Significance
In statistical hypothesis testing, a result has statistical significance when it is very unlikely to have occurred given the null hypothesis (simply by chance alone). More precisely, a study's defined significance level, denoted by \alpha, is the probability of the study rejecting the null hypothesis, given that the null hypothesis is true; and the ''p''-value of a result, ''p'', is the probability of obtaining a result at least as extreme, given that the null hypothesis is true. The result is statistically significant, by the standards of the study, when p \le \alpha. The significance level for a study is chosen before data collection, and is typically set to 5% or much lower—depending on the field of study. In any experiment or observation that involves drawing a sample from a population, there is always the possibility that an observed effect would have occurred due to sampling error alone. But if the ''p''-value of an observed effect is less than (or equal to) the significanc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Progression-free Survival
Progression-free survival (PFS) is "the length of time during and after the treatment of a disease, such as cancer, that a patient lives with the disease but it does not get worse". In oncology, PFS usually refers to situations in which a tumor is present, as demonstrated by laboratory testing, radiologic testing, or clinically. Similarly, "disease-free survival" is the length of time after patients have received treatment and have no detectable disease. Time to progression (TTP) does not count patients who die from other causes but is otherwise a close equivalent to PFS (unless there are many such events). The FDA gives separate definitions and prefers PFS. Background PFS is widely used as a surrogate endpoint in oncology. The definition of "progression" generally involves imaging techniques (plain radiograms, CT scans, MRI, PET scans, ultrasounds) or other aspects: biochemical progression may be defined on the basis of an increase in a tumor marker (such as CA125 for epithelial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ovarian Cancer
Ovarian cancer is a cancerous tumor of an ovary. It may originate from the ovary itself or more commonly from communicating nearby structures such as fallopian tubes or the inner lining of the abdomen. The ovary is made up of three different cell types including epithelial cells, germ cells, and stromal cells. When these cells become abnormal, they have the ability to divide and form tumors. These cells can also invade or spread to other parts of the body. When this process begins, there may be no or only vague symptoms. Symptoms become more noticeable as the cancer progresses. These symptoms may include bloating, vaginal bleeding, pelvic pain, abdominal swelling, constipation, and loss of appetite, among others. Common areas to which the cancer may spread include the lining of the abdomen, lymph nodes, lungs, and liver. The risk of ovarian cancer increases with age. Most cases of ovarian cancer develop after menopause. It is also more common in women who have ovulated m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epithelial
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is one of the four basic types of animal tissue, along with connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. It is a thin, continuous, protective layer of compactly packed cells with a little intercellular matrix. Epithelial tissues line the outer surfaces of organs and blood vessels throughout the body, as well as the inner surfaces of cavities in many internal organs. An example is the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. There are three principal shapes of epithelial cell: squamous (scaly), columnar, and cuboidal. These can be arranged in a singular layer of cells as simple epithelium, either squamous, columnar, or cuboidal, or in layers of two or more cells deep as stratified (layered), or ''compound'', either squamous, columnar or cuboidal. In some tissues, a layer of columnar cells may appear to be stratified due to the placement of the nuclei. This sort of tissue is called pseudostratified. All glands are made up of epitheli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reverse Takeover
A reverse takeover (RTO), reverse merger, or reverse IPO is the acquisition of a public company by a private company so that the private company can bypass the lengthy and complex process of going public. Sometimes, conversely, the public company is bought by the private company through an asset swap and share issue. The transaction typically requires reorganization of capitalization of the acquiring company. Process In a reverse takeover, shareholders of the private company purchase control of the public shell company/ SPAC and then merge it with the private company. The publicly traded corporation is called a "shell" since all that exists of the original company is its organizational structure. The private company shareholders receive a substantial majority of the shares of the public company and control of its board of directors. The transaction can be accomplished within weeks. The transaction involves the private and shell company exchanging information on each other, neg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burnet Institute
The Burnet Institute is an Australian medical institute that combines medical research in the laboratory and the field, with public health action to address major health issues affecting disadvantaged communities in Australia, and internationally. As of 2011, the institute was home to more than 450 medical researchers, working across six main themes: infectious diseases; maternal and child health; sexual and reproductive health; alcohol and other drugs harm reduction; immunity, vaccines and immunisation; and the health of young people. With a head office located in Commercial Road, Prahran, Victoria, the institute delivers public health programs across four continents including Africa, Oceania, and Asia and is led by its director and chief executive officer, Professor Brendan Crabb , an immunologist. Current research Burnet Institute has particular expertise in infectious diseases (especially HIV, hepatitis viruses, influenza and malaria) and in understanding the immune resp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Austin Hospital, Melbourne
The Austin Hospital is a public teaching hospital in Melbourne's north-eastern suburb of Heidelberg, and is administered by Austin Health, along with the Heidelberg Repatriation Hospital and the Royal Talbot Rehabilitation Centre. History The Austin Hospital was founded in 1882 as a charitable institution for incurables by Elizabeth Austin, the widow of Thomas Austin. It had several name changes before becoming the Austin Hospital.History Austin Hospital, retrieved 2009-03-03. War and post-war During World War II, two s were located at the site - the 115th Australian General Hospital, operated by the |