|
Price Township, Pennsylvania
Price Township is a township in Monroe County, Pennsylvania, United States. The population was 3,675 at the 2020 census. Geography According to the United States Census Bureau, the township has a total area of 25.2 square miles (65.2 km2), of which 25.0 square miles (64.8 km2) is land and 0.2 square mile (0.4 km2) (0.64%) is water. Demographics As of the census of 2000, there were 2,649 people, 925 households, and 703 families residing in the township. The population density was . There were 1,270 housing units at an average density of . The racial makeup of the township was 91.09% White, 5.21% African American, 0.15% Native American, 1.17% Asian, 1.02% from other races, and 1.36% from two or more races. Hispanic or Latino of any race were 3.89% of the population. There were 925 households, out of which 41.9% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 65.3% were married couples living together, 6.6% had a female householder with no h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PA 447
Pennsylvania Route 447 (PA 447) is a north–south state route located in northeast Pennsylvania in The Poconos. The southern terminus of the route is at U.S. Route 209 (US 209) near an interchange with Interstate 80 (I-80) in Smithfield Township. The northern terminus is at PA 191 and PA 507 in Dreher Township. The route heads northwest from US 209 in Monroe County and forms a brief concurrency with US 209 Business (US 209 Bus.) in the northern part of East Stroudsburg. PA 447 continues and forms a concurrency with PA 191 in Analomink before winding north through rural areas. The route bends northwest and crosses PA 390 in Canadensis. PA 447 passes through a section of Pike County before entering Wayne County and reaching its northern terminus. In 1928, the road was designated as PA 190 between US 209 (now US 209 Bus.) in East Stroudsburg and PA 90 (now PA 191) south of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marriage
Marriage, also called matrimony or wedlock, is a culturally and often legally recognized union between people called spouses. It establishes rights and obligations between them, as well as between them and their children, and between them and their in-laws. It is considered a cultural universal, but the definition of marriage varies between cultures and religions, and over time. Typically, it is an institution in which interpersonal relationships, usually sexual, are acknowledged or sanctioned. In some cultures, marriage is recommended or considered to be compulsory before pursuing any sexual activity. A marriage ceremony is called a wedding. Individuals may marry for several reasons, including legal, social, libidinal, emotional, financial, spiritual, and religious purposes. Whom they marry may be influenced by gender, socially determined rules of incest, prescriptive marriage rules, parental choice, and individual desire. In some areas of the world, arrang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NorŌĆÖeaster
A nor'easter (also northeaster; see below), or an East Coast low is a synoptic-scale extratropical cyclone in the western North Atlantic Ocean. The name derives from the direction of the winds that blow from the northeast. The original use of the term in North America is associated with storms that impact the upper north Atlantic coast of the United States and the Atlantic Provinces of Canada. Typically, such storms originate as a low-pressure area that forms within of the shore between North Carolina and Massachusetts. The precipitation pattern is similar to that of other extratropical storms. Nor'easters are usually accompanied by heavy rain or snow, and can cause severe coastal flooding, coastal erosion, hurricane-force winds, or blizzard conditions. Nor'easters are usually most intense during winter in New England and Atlantic Canada. They thrive on converging air massesŌĆöthe cold polar air mass and the warmer air over the waterŌĆöand are more severe in winter when t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ice Storm
An ice storm, also known as a glaze event or a silver storm is a type of winter storm characterized by freezing rain. The U.S. National Weather Service defines an ice storm as a storm which results in the accumulation of at least of ice on exposed surfaces. They are generally not violent storms but instead are commonly perceived as gentle rains occurring at temperatures just below freezing. Formation The formation of ice begins with a layer of above-freezing air above a layer of sub-freezing temperatures closer to the surface. Frozen precipitation melts to rain while falling into the warm air layer, and then begins to refreeze in the cold layer below. If the precipitate refreezes while still in the air, it will land on the ground as sleet. Alternatively, the liquid droplets can continue to fall without freezing, passing through the cold air just above the surface. This thin layer of air then cools the rain to a temperature below freezing (). However, the drops themselves ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wind Chill
Wind chill or windchill (popularly wind chill factor) is the lowering of body temperature due to the passing-flow of lower-temperature air. Wind chill numbers are always lower than the air temperature for values where the formula is valid. When the apparent temperature is higher than the air temperature, the heat index is used instead. Explanation A surface loses heat through conduction, evaporation, convection, and radiation. The rate of convection depends on both the difference in temperature between the surface and the fluid surrounding it and the velocity of that fluid with respect to the surface. As convection from a warm surface heats the air around it, an insulating boundary layer of warm air forms against the surface. Moving air disrupts this boundary layer, or epiclimate, allowing for cooler air to replace the warm air against the surface. The faster the wind speed, the more readily the surface cools. Alternative approaches Many formulas exist for wind chill beca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Department Of Agriculture
The United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) is the United States federal executive departments, federal executive department responsible for developing and executing federal laws related to farming, forestry, rural economic development, and food. It aims to meet the needs of commercial farming and livestock food production, promotes agricultural trade and production, works to assure food safety, protects natural resources, fosters rural communities and works to end hunger in the United States and internationally. It is headed by the United States Secretary of Agriculture, Secretary of Agriculture, who reports directly to the President of the United States and is a member of the president's Cabinet of the United States, Cabinet. The current secretary is Tom Vilsack, who has served since February 24, 2021. Approximately 80% of the USDA's $141 billion budget goes to the Food and Nutrition Service (FNS) program. The largest component of the FNS budget is the Supplementa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
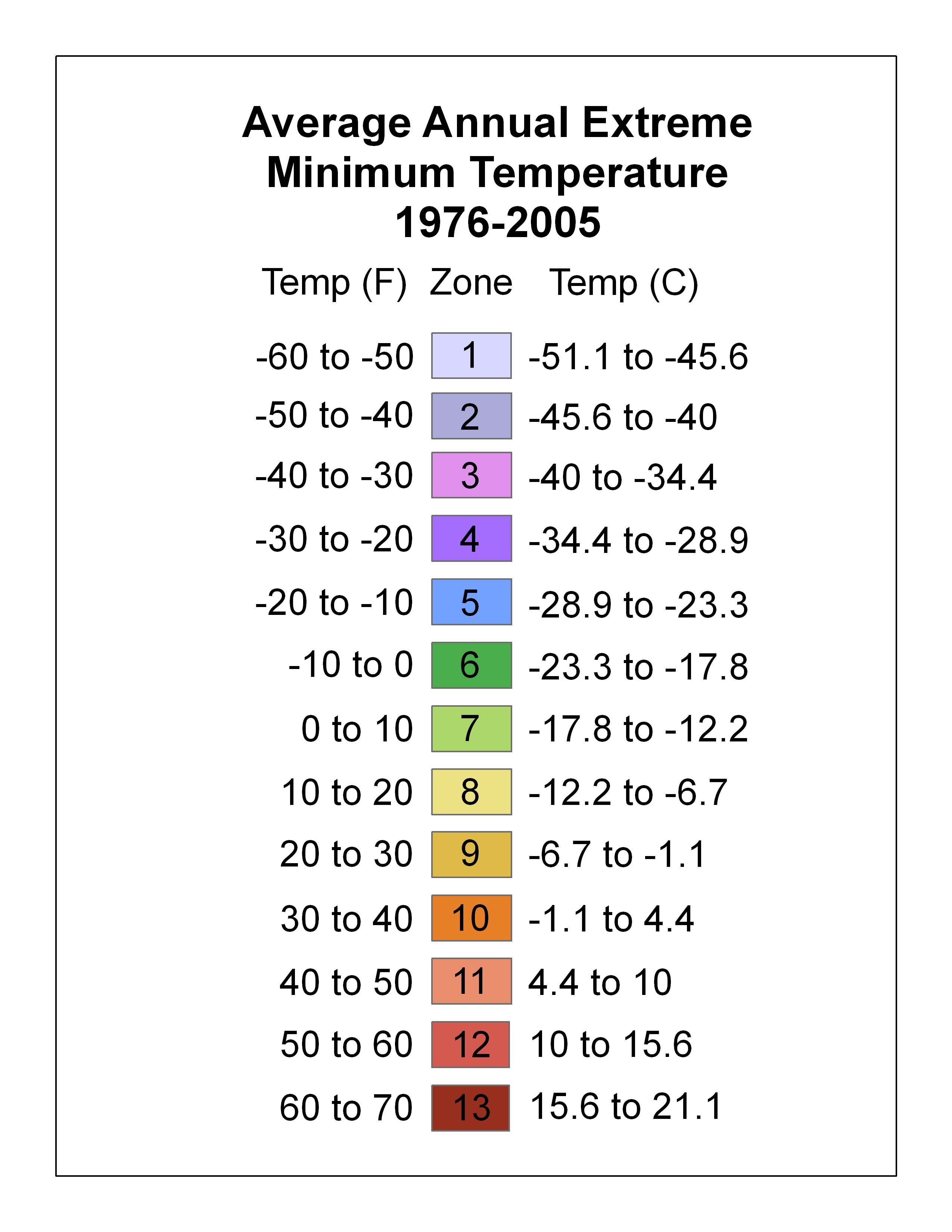
Plant Hardiness Zone
A hardiness zone is a geographic area defined as having a certain average annual minimum temperature, a factor relevant to the survival of many plants. In some systems other statistics are included in the calculations. The original and most widely used system, developed by the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) as a rough guide for landscaping and gardening, defines 13 zones by long-term average annual extreme minimum temperatures. It has been adapted by and to other countries (such as Canada) in various forms. Unless otherwise specified, in American contexts "hardiness zone" or simply "zone" usually refers to the USDA scale. For example, a plant may be described as "hardy to zone 10": this means that the plant can withstand a minimum temperature of 30 ┬░F (ŌłÆ1.1 ┬░C) to 40 ┬░F (4.4 ┬░C). Other hardiness rating schemes have been developed as well, such as the UK Royal Horticultural Society and US Sunset Western Garden Book systems. A heat zone (s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atlantic Hurricane Season
The Atlantic hurricane season is the period in a year from June through November when tropical cyclones form in the Atlantic Ocean, referred to in North American countries as hurricanes, tropical storms, or tropical depressions. In addition, there have been several storms over the years that have not been fully tropical and are categorized as subtropical depressions and subtropical storms. Even though subtropical storms and subtropical depressions are not technically as strong as tropical cyclones, the damages can still be devastating. Worldwide, tropical cyclone activity peaks in late summer, when the difference between temperatures aloft and sea surface temperatures is the greatest. However, each tropical cyclone basin has its own seasonal patterns. On a worldwide scale, May is the least active month, while September is the most active. In the Northern Atlantic Ocean, a distinct hurricane season occurs from June 1 to November 30, sharply peaking from late August through Se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thunderstorm
A thunderstorm, also known as an electrical storm or a lightning storm, is a storm characterized by the presence of lightning and its acoustic effect on the Earth's atmosphere, known as thunder. Relatively weak thunderstorms are sometimes called thundershowers. Thunderstorms occur in a type of cloud known as a cumulonimbus. They are usually accompanied by strong winds and often produce heavy rain and sometimes snow, sleet, or hail, but some thunderstorms produce little precipitation or no precipitation at all. Thunderstorms may line up in a series or become a rainband, known as a squall line. Strong or severe thunderstorms include some of the most dangerous weather phenomena, including large hail, strong winds, and tornadoes. Some of the most persistent severe thunderstorms, known as supercells, rotate as do cyclones. While most thunderstorms move with the mean wind flow through the layer of the troposphere that they occupy, vertical wind shear sometimes causes a de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dew Point
The dew point is the temperature to which air must be cooled to become saturated with water vapor, assuming constant air pressure and water content. When cooled below the dew point, moisture capacity is reduced and airborne water vapor will condense to form liquid water known as dew. When this occurs via contact with a colder surface, dew will form on that surface. The dew point is affected by humidity. When there is more moisture in the air, the dew point is higher. When the temperature is below the freezing point of water, the dew point is called the frost point, as frost is formed via deposition rather than condensation. In liquids, the analog to the dew point is the cloud point. Humidity If all the other factors influencing humidity remain constant, at ground level the relative humidity rises as the temperature falls; this is because less vapor is needed to saturate the air. In normal conditions, the dew point temperature will not be greater than the air temperature, sinc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heat Index
The heat index (HI) is an index that combines air temperature and relative humidity, in shaded areas, to posit a human-perceived equivalent temperature, as how hot it would feel if the humidity were some other value in the shade. The result is also known as the "felt air temperature", "apparent temperature", "real feel" or "feels like". For example, when the temperature is with 70% relative humidity, the heat index is . The humidity where the heat index feels like itself is typically left unstated. The heat index example in this case, 41┬░C, feels like 41┬░C only when the humidity is 21%. The human body normally cools itself by perspiration, or sweating. Heat is removed from the body by evaporation of that sweat. However, high relative humidity reduces the evaporation rate. This results in a lower rate of heat removal from the body, hence the sensation of being overheated. This effect is subjective, with different individuals perceiving heat differently for various reasons (such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Continental Climate
Continental climates often have a significant annual variation in temperature (warm summers and cold winters). They tend to occur in the middle latitudes (40 to 55 north), within large landmasses where prevailing winds blow overland bringing some precipitation, and temperatures are not moderated by oceans. Continental climates occur mostly in the Northern Hemisphere due to the large landmasses found there. Most of northern and northeastern China, eastern and southeastern Europe, Western and north western Iran, central and southeastern Canada, and the central and northeastern United States have this type of climate. Continentality is a measure of the degree to which a region experiences this type of climate. In continental climates, precipitation tends to be moderate in amount, concentrated mostly in the warmer months. Only a few areasŌĆöin the mountains of the Pacific Northwest of North America and in Iran, northern Iraq, adjacent Turkey, Afghanistan, Pakistan, and Central AsiaŌĆ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |