|
President Of The Constituent Assembly
This article lists Presidents of the French Parliament or, as the case may be, of its lower chamber. The National Constituent Assembly was created in 1789 out of the Estates-General. It, and the revolutionary legislative assemblies that followed – the Legislative Assembly (1791–1792) and the National Convention (1792–1795), had a quickly rotating Presidency. With the establishment of the Directory in 1795, there were two chambers of the French legislature. The lower, the Council of Five Hundred, also had a quickly rotating chairmanship. Under Napoleon I, the Legislative Corps had all authority to actually enact laws, but was essentially a rubberstamp body, lacking the power to debate legislation. With the restoration of the monarchy, a bicameral system was restored, with a Chamber of Peers and a Chamber of Deputies. The Chamber of Deputies, for the first time, had presidents elected for a substantial period of time. With the revolution of 1848, the monarchical assembli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Parliament
The French Parliament (french: Parlement français) is the bicameral legislature of the French Republic, consisting of the Senate () and the National Assembly (). Each assembly conducts legislative sessions at separate locations in Paris: the Senate meets in the and the National Assembly convenes at . Each house has its own regulations and rules of procedure. However, occasionally they may meet as a single house known as the Congress of the French Parliament (), convened at the Palace of Versailles, to revise and amend the Constitution of France. History and name The French Parliament, as a legislative body, should not be confused with the various parlements of the Ancien Régime in France, which were courts of justice and tribunals with certain political functions varying from province to province and as to whether the local law was written and Roman, or customary common law. The word "Parliament", in the modern meaning of the term, appeared in France in the 19th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
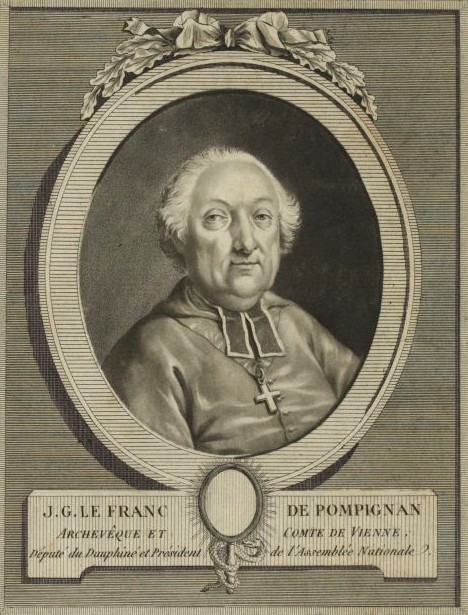
Jean-Georges Lefranc De Pompignan
Jean Georges Lefranc de Pompignan (22 February 1715 in Montauban – 29 December 1790 in Paris) was a French clergyman, younger brother of Jean-Jacques Lefranc, Marquis de Pompignan. Pompignan was the archbishop of Vienne against whose defense of the faith Voltaire launched the good-natured mockery of ''Les Lettres d'un Quaker''. Elected to the Estates General, he passed over to the Liberal side, and led the 149 members of the clergy who united with the third estate to form the National Assembly In politics, a national assembly is either a unicameral legislature, the lower house of a bicameral legislature, or both houses of a bicameral legislature together. In the English language it generally means "an assembly composed of the repre .... He was one of its first presidents, and was minister of public worship when the Civil Constitution of the Clergy was forced upon the clergy. 1715 births 1790 deaths French untitled nobility Bishops of Le Puy-en-Velay Archbishops ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean-Xavier Bureau De Pusy
Jean-Xavier Bureau de Pusy (7 January 1750, at Port-sur-Saône in the department of Haute-Saône – 2 February 1806, in Genoa, Italy) was a French military engineer and politician, during the French Revolution. Political career Deputy of nobility for the bailliage d'Amont in the Estates General of 1789 that became the National Constituent Assembly, Jean-Xavier Bureau de Pusy was three times named president of the National Constituent Assembly: * from 2 to 24 February 1790; * from 11 to 24 September 1790; * from 24 May to 5 June 1791. He contributed actively to the division of France into 83 departments, in 1790, and with the metric system. In 1790, he corresponded with Alexander Hamilton. Military career On 1 January 1771 he entered the School of Engineering at Mézières as a second lieutenant. He was a military engineer at the Fort de Joux in 1786, in 1789 he was captain with the Royal corps of Engineers. After the session of the National Constituent Assembly, he resum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gui-Jean-Baptiste Target
Gui-Jean-Baptiste Target (, 17 December 1733 – 9 September 1806) was a French lawyer and politician. Biography Born in Paris, Target was the son of a lawyer, and was himself a lawyer to the Parlement of Paris. He acquired a great reputation as a lawyer, less by practice in the courts than in a consultative capacity, and served the ancien régime as member of a committee to revise the civil and criminal laws of the kingdom. He strenuously opposed the "''parlement Maupeou''", devised by Chancellor Maupeou to replace the old judiciary bodies in 1771, refusing to plead before it, an act that earned him the sobriquet of the "Virgin of the palace". He was counsel for Louis René Edouard, cardinal de Rohan in the "affair of the diamond necklace". In 1785, he was elected to the Académie française. He contributed to the development of the Edict of Tolerance signed at Versailles by Louis XVI in 1787. French Revolution In 1789, he was returned as one of the deputies of the Third E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
François-Xavier-Marc-Antoine De Montesquiou-Fézensac
Abbé François-Xavier-Marc-Antoine de Montesquiou-Fézensac (château de Marsan, Gers, 3 August 1757 – Chateau de Cirey, Haute-Marne, 4 February 1832) was a French clergyman and politician. Biography He was a member of a very old French nobility family from Gascony. His kinsman Anne-Pierre, marquis de Montesquiou-Fézensac would serve alongside him in the National Assembly. Montesquiou-Fézensac was named (1782) Abbé of Beaulieu, near Langres. The Abbé de Montesquieu attended the Assembly of the French clergy (1785) as Agent-General. French Revolution The Abbé was elected by the First Estate of Paris to the Estates General of 1789. He would stand out alongside the Abbé Maury by his oratory, and was elected president of the National Assembly three times. He presided over the Assembly an impressive three terms (4–18 January 1790; 28 February - 15 March 1790; 14–30 March 1791). He opposed strongly the Civil Constitution of the Clergy and supported the monarchy. He was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean-Nicolas Démeunier
Jean-Nicolas Démeunier (sometimes Desmeuniers) (15 March 1751 – 2 February 1814) was a French author and politician. Biography Démeunier was born in Nozeroy in the department of Jura. He is the author of several historical essays, political and moral, and many translations of English travel books. He attended his studies in his home province before his literary abilities earned him the attention of the royal court. Démeunier was appointed Royal Censor and secretary to "Monsieur", the Louis XVIII, who was the brother of King Louis XVI, and the King of France after the Restoration, an event that occurred only months after Démeunier's death. French Revolution Supporter of the French Revolution, he was elected (16 May 1789) by the Third Estate of the city of Paris to the Estates General with 133 votes. When the conservative members of the Constitutional Committee resigned mid-September 1789, he was one of the deputies selected to replace them. He served a turn as Preside ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raymond De Boisgelin De Cucé
Raymond is a male given name. It was borrowed into English from French (older French spellings were Reimund and Raimund, whereas the modern English and French spellings are identical). It originated as the Germanic ᚱᚨᚷᛁᚾᛗᚢᚾᛞ (''Raginmund'') or ᚱᛖᚷᛁᚾᛗᚢᚾᛞ (''Reginmund''). ''Ragin'' (Gothic) and ''regin'' (Old German) meant "counsel". The Old High German ''mund'' originally meant "hand", but came to mean "protection". This etymology suggests that the name originated in the Early Middle Ages, possibly from Latin. Alternatively, the name can also be derived from Germanic Hraidmund, the first element being ''Hraid'', possibly meaning "fame" (compare ''Hrod'', found in names such as Robert, Roderick, Rudolph, Roland, Rodney and Roger) and ''mund'' meaning "protector". Despite the German and French origins of the English name, some of its early uses in English documents appear in Latinized form. As a surname, its first recorded appearance in Bri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armand Gaston Camus
Armand-Gaston Camus (2 April 17402 November 1804), French revolutionist, was a successful lawyer and advocate before the French Revolution. He was the son of Pierre Camus, a lawyer in the Parlement of Paris. Camus is considered the founder of the Archives Nationales, as in 1789 he was appointed as archivist of its predecessor, the Commission des archives of the Assembly ( Estates-General). He served in this role until his death. French Revolution In 1789 Camus was elected by the Third Estate of Paris to the Estates-General; he attracted attention by his speeches against social inequalities. He was one of the National Assembly's earliest presidents (28 October11 November 1789), and he was the most frequent speaker: no one addressed the Assembly more times than he did (more than 600 times); d'André is second at 497, and le Chapelier third at 447. Camus was so frequently called upon to speak mostly because of his expertise in canon law. Camus was appointed on 14 August 1789 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emmanuel Marie Michel Philippe Fréteau De Saint-Just
Emmanuel Marie Michel Philippe Fréteau de Saint-Just (28 March 1745 – 14 June 1794) was a French nobleman and an elected representative of the Second Estate during the French Revolution. He was a politically liberal deputy to the Estates-General of 1789 and worked for the cause of constitutional monarchy. In 1789, Fréteau de Saint-Just served two terms as President of the National Constituent Assembly. Assemblée nationale de Francebr>"Emmanuel, Marie, Michel, Philippe Fréteau de Saint-Just"Retrieved 15 May 2017 As the Revolution became more radical, Fréteau de Saint-Just became politically marginalized, and by 1792 he had retired from national politics completely. Nonetheless, his aristocratic background drew increasing ire from militant revolutionaries until he was finally arrested and executed at the guillotine in 1794 during the Reign of Terror. Biography Fréteau de Saint-Just was Seigneur of Vaux-le-Pénil and Saint-Liesne, estates located just outside Paris, acq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean-Joseph Mounier
Jean Joseph Mounier (12 November 1758 – 28 January 1806) was a French politician and judge. Biography Mounier was born the son of a cloth merchant in Grenoble in Southeastern France. He studied law, and in 1782 purchased a minor judgeship at Grenoble. He took part in the struggle between the '' parlements'' and the court in 1788, and promoted the meeting of the estates of Dauphiné at Vizille (20 July 1788), on the eve of the French Revolution. He was secretary of the assembly, and drafted the ''cahiers'' ("notebooks") of grievances and remonstrances presented by it to King Louis XVI. Thus brought into prominence, Mounier was unanimously elected deputy of the third estate to the Estates General of 1789; Mounier also founded the Monarchiens party in August 1789. There, and in the Constituent Assembly, he was at first an upholder of the new ideas, pronouncing himself in favor of the union of the Third Estate with the two privileged orders, proposing the famous Tennis Court Oath ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
César Guillaume De La Luzerne
César-Guillaume La Luzerne (7 July 1738 - 21 June 1821) was a Roman Catholic clergyman. He was a minor statesman of the French Revolution, and a cardinal and important figure of the Bourbon Restoration. Family and early life La Luzerne's family was one of the most illustrious of the Normandy. His father Cesar-Antoine, was a Maréchal de camp in the king's army, his mother was Marie-Elisabeth de Lamoignon de Blancmesnil (1716-1758), the daughter of Lord Chancellor Lamoignon (served 1750-1768) and the sister of the extraordinary Secretary of State Malesherbes. His brothers were César Henri, comte de La Luzerne, Naval Minister (1787-1790) and Anne-César, ambassador to the United States and to the court of London. Cesar-Guillaume was the middle son and so intended by his family to go into the church, and so attended the seminary of Saint-Magloire. In 1754, while still a young man, his grandfather arranged his appointment to the position of Canon of Notre Dame Cathedral. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)

