|
Presidencies Of British India
The provinces of India, earlier presidencies of British India and still earlier, presidency towns, were the administrative divisions of British governance on the Indian subcontinent. Collectively, they have been called British India. In one form or another, they existed between 1612 and 1947, conventionally divided into three historical periods: *Between 1612 and 1757 the East India Company set up factories (trading posts) in several locations, mostly in coastal India, with the consent of the Mughal emperors, Maratha Empire or local rulers. Its rivals were the merchant trading companies of Portugal, Denmark, the Netherlands, and France. By the mid-18th century, three ''presidency towns'': Madras, Bombay and Calcutta, had grown in size. *During the period of Company rule in India (1757ŌĆō1858), the company gradually acquired sovereignty over large parts of India, now called "presidencies". However, it also increasingly came under British government oversight, in effect sharing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort William, Calcutta, 1735
A fortification is a military construction or building designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is also used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from Latin ''fortis'' ("strong") and ''facere'' ("to make"). From very early history to modern times, defensive walls have often been necessary for cities to survive in an ever-changing world of invasion and conquest. Some settlements in the Indus Valley civilization were the first small cities to be fortified. In ancient Greece, large stone walls had been built in Mycenaean Greece, such as the ancient site of Mycenae (famous for the huge stone blocks of its 'cyclopean' walls). A Greek ''Towns of ancient Greece#Military settlements, phrourion'' was a fortified collection of buildings used as a military garrison, and is the equivalent of the ancient Roman, Roman castellum or English language, English fortress. These constructions mainly served the purpose of a watch tower, to guard certa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surat
Surat is a city in the western Indian state of Gujarat. The word Surat literally means ''face'' in Gujarati and Hindi. Located on the banks of the river Tapti near its confluence with the Arabian Sea, it used to be a large seaport. It is now the commercial and economic center in South Gujarat, and one of the largest urban areas of western India. It has well-established diamond and textile industry, and is a major supply centre for apparels and accessories. About 90% of the world's diamonds supply are cut and polished in the city. It is the second largest city in Gujarat after Ahmedabad and the eighth largest city by population and ninth largest urban agglomeration in India. It is the administrative capital of the Surat district. The city is located south of the state capital, Gandhinagar; south of Ahmedabad; and north of Mumbai. The city centre is located on the Tapti River, close to Arabian Sea. Surat will be the world's fastest growing city from 2019 to 2035, acco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Crown
The Crown is the state in all its aspects within the jurisprudence of the Commonwealth realms and their subdivisions (such as the Crown Dependencies, overseas territories, provinces, or states). Legally ill-defined, the term has different meanings depending on context. It is used to designate the monarch in either a personal capacity, as Head of the Commonwealth, or as the king or queen of their realms (whereas the monarchy of the United Kingdom and the monarchy of Canada, for example, are distinct although they are in personal union). It can also refer to the rule of law; however, in common parlance 'The Crown' refers to the functions of government and the civil service. Thus, in the United Kingdom (one of the Commonwealth realms), the government of the United Kingdom can be distinguished from the Crown and the state, in precise usage, although the distinction is not always relevant in broad or casual usage. A corporation sole, the Crown is the legal embodiment of execut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trust Law
A trust is a legal relationship in which the holder of a right gives it to another person or entity who must keep and use it solely for another's benefit. In the Anglo-American common law, the party who entrusts the right is known as the "settlor", the party to whom the right is entrusted is known as the "trustee", the party for whose benefit the property is entrusted is known as the " beneficiary", and the entrusted property itself is known as the "corpus" or "trust property". A ''testamentary trust'' is created by a will and arises after the death of the settlor. An ''inter vivos trust'' is created during the settlor's lifetime by a trust instrument. A trust may be revocable or irrevocable; an irrevocable trust can be "broken" (revoked) only by a judicial proceeding. The trustee is the legal owner of the property in trust, as fiduciary for the beneficiary or beneficiaries who is/are the equitable owner(s) of the trust property. Trustees thus have a fiduciary duty to manage th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the south, the Arabian Sea on the southwest, and the Bay of Bengal on the southeast, it shares land borders with Pakistan to the west; China, Nepal, and Bhutan to the north; and Bangladesh and Myanmar to the east. In the Indian Ocean, India is in the vicinity of Sri Lanka and the Maldives; its Andaman and Nicobar Islands share a maritime border with Thailand, Myanmar, and Indonesia. Modern humans arrived on the Indian subcontinent from Africa no later than 55,000 years ago., "Y-Chromosome and Mt-DNA data support the colonization of South Asia by modern humans originating in Africa. ... Coalescence dates for most non-European populations average to between 73ŌĆō55 ka.", "Modern human beingsŌĆö''Homo sapiens''ŌĆöoriginated in Africa. Then, int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bengal Presidency
The Bengal Presidency, officially the Presidency of Fort William and later Bengal Province, was a subdivision of the British Empire in India. At the height of its territorial jurisdiction, it covered large parts of what is now South Asia and Southeast Asia. Bengal proper covered the ethno-linguistic region of Bengal (present-day Bangladesh and the Indian state of West Bengal). Calcutta, the city which grew around Fort William, was the capital of the Bengal Presidency. For many years, the Governor of Bengal was concurrently the Viceroy of India and Calcutta was the de facto capital of India until 1911. The Bengal Presidency emerged from trading posts established in Mughal Bengal during the reign of Emperor Jahangir in 1612. The East India Company (HEIC), a British monopoly with a Royal Charter, competed with other European companies to gain influence in Bengal. After the decisive overthrow of the Nawab of Bengal in 1757 and the Battle of Buxar in 1764, the HEIC expanded ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Buxar
The Battle of Buxar was fought between 22 and 23 October 1764, between the forces under the command of the British East India Company, led by Hector Munro, and the combined armies of Mir Qasim, Nawab of Bengal till 1764; the Nawab of Awadh, Shuja-ud-Daula; and the Mughal Emperor, Shah Alam II. The battle was fought at Buxar, a "strong fortified town" within the territory of Bihar, located on the banks of the Ganga river about west of Patna; it was a challenging victory for the British East India Company. The war was brought to an end by the Treaty of Allahabad in 1765. Battle The British army engaged in the fighting numbered 17,072 comprising 1,859 British regulars, 5,297 Indian sepoys and 9,189 Indian cavalry. The alliance army's numbers were estimated to be over 40,000. According to other sources, the combined army of the Mughals, Awadh and Mir Qasim consisting of 10 ,000 men was defeated by a British army comprising 10,000 men. The Nawabs had gained their military power aft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Plassey
The Battle of Plassey was a decisive victory of the British East India Company over the Nawab of Bengal and his French allies on 23 June 1757, under the leadership of Robert Clive. The victory was made possible by the defection of Mir Jafar, who was Nawab Siraj-ud-Daulah's commander in chief. The battle helped the British East India Company take control of Bengal. Over the next hundred years, they seized control of most of the rest of the Indian subcontinent, including Burma. The battle took place at Palashi (Anglicised version: ''Plassey'') on the banks of the Hooghly River, about north of Calcutta (now Kolkata) and south of Murshidabad in West Bengal, then capital of Bengal Subah (now in Nadia district in West Bengal). The belligerents were the Nawab Siraj-ud-Daulah, the last independent Nawab of Bengal , and the British East India Company. He succeeded Alivardi Khan (his maternal grandfather). Siraj-ud-Daulah had become the Nawab of Bengal the year before, and he had order ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bengal
Bengal ( ; bn, Ó”¼Ó”ŠÓ”éÓ”▓Ó”Š/Ó”¼Ó”ÖÓ¦ŹÓ”Ś, translit=B─üngl─ü/B├┤ng├┤, ) is a geopolitical, cultural and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the eastern part of the Indian subcontinent at the apex of the Bay of Bengal, predominantly covering present-day Bangladesh and the Indian state of West Bengal. Geographically, it consists of the Ganges-Brahmaputra delta system, the largest river delta in the world and a section of the Himalayas up to Nepal and Bhutan. Dense woodlands, including hilly rainforests, cover Bengal's northern and eastern areas, while an elevated forested plateau covers its central area; the highest point is at Sandakphu. In the littoral southwest are the Sundarbans, the world's largest mangrove forest. The region has a monsoon climate, which the Bengali calendar divides into six seasons. Bengal, then known as Gangaridai, was a leading power in ancient South Asia, with extensive trade networks forming connections to as far away as Roman Egypt. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East India Company (other)
East India Company is a general term, referring to a number of European trading companies established in the early modern era to establish trade relations and subsequently political control over the Indian subcontinent, the Indonesian archipelago and the neighboring lands. They would include: * British East India Company (1600ŌĆō1874) * Dutch East India Company (1602ŌĆō1799) * Danish East India Company (1616ŌĆō1650), re-established (1670ŌĆō1729) * Portuguese East India Company (1628ŌĆō1633) * Genoese East India Company (1649ŌĆō1650) * French East India Company (1664ŌĆō1769), re-established (1785ŌĆō1794) * Swedish East India Company (1731ŌĆō1813) * Austrian East India Company (1776ŌĆō1781) Other uses * ''East India Company'' (video game) * The East India Company, a retail business founded by Sanjiv Mehta in 2010 See also * West India Company (other) * East India Company College * East India (other) * Colonial India * Christianity in India * Christianity in Indo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
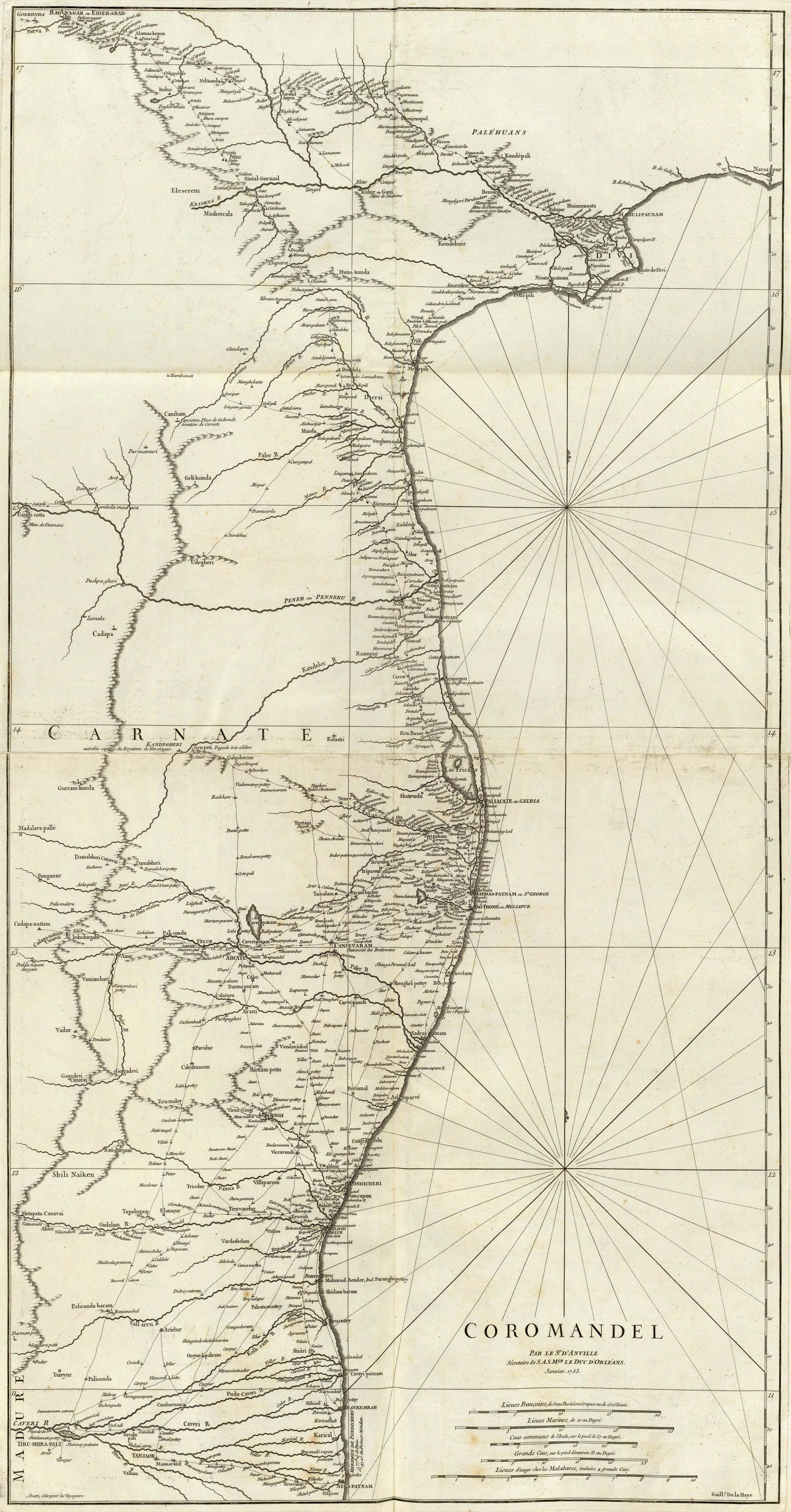
Coromandel Coast
The Coromandel Coast is the southeastern coastal region of the Indian subcontinent, bounded by the Utkal Plains to the north, the Bay of Bengal to the east, the Kaveri delta to the south, and the Eastern Ghats to the west, extending over an area of about 22,800 square kilometres. The coast has an average elevation of 80 metres and is backed by the Eastern Ghats, a chain of low lying and flat-topped hills. In historical Muslim sources from the 12th century onward, the Coromandel Coast was called Ma╩┐bar. Etymology The land of the Chola dynasty was called ''Cholamandalam'' (Ó«ÜÓ»ŗÓ«┤ Ó««Ó«ŻÓ»ŹÓ«¤Ó«▓Ó««Ó»Ź) in Tamil, translated as ''The realm of the Cholas'', from which the Portuguese derived the name ''Coromandel''.''The Land of the Tamulians and Its Missions'', by Eduard Raimund Baierlein, James Dunning BakerSouth Indian Coins ŌĆō Page 61 by T. Desikachari ŌĆō Coins, Indic ŌĆō 1984Indian History ŌĆō Page 112''Annals of Oriental Research'' ŌĆō Page 1 by University of Madras ŌĆ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)