|
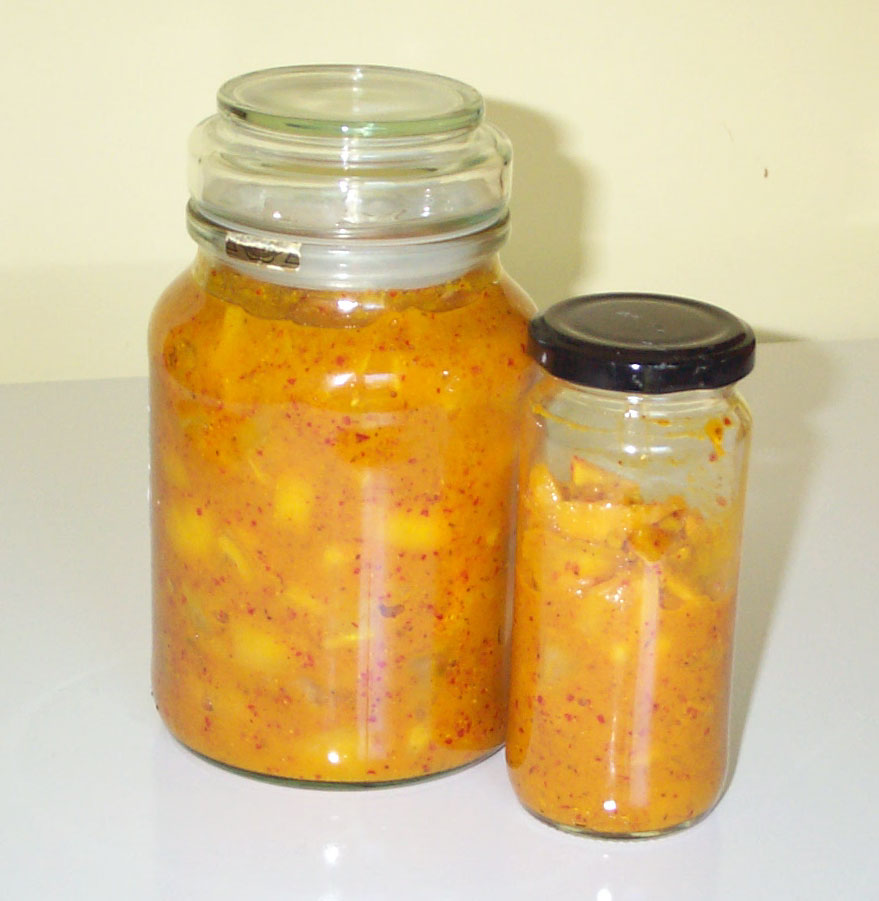
Preserved Lemon
Preserved lemon or lemon pickle is a condiment that is common in the cuisines of Indian subcontinent and Morocco. It's also found in 18th-century English cuisine. It is also known as "country lemon" and ''leems''. Diced, quartered, halved, or whole lemons are pickled in a brine of water, lemon juice, and salt; occasionally spices are included as well.Herbst, Sharon. ''Food Lover's Companion'' (3rd ed), pg 492, Barron's Educational Series Inc. The pickle is allowed to ferment at room temperature for weeks or months before it is used. The pulp of the preserved lemon can be used in stews and sauces, but it is the peel (zest and pith together) that is most valued. The flavor is mildly tart but intensely lemony. Usage Pieces of pickled lemon may be washed before using to remove any surface salt, or blanched to remove more of the salt and bring out the natural mild sweetness. They may then be sliced, chopped, or minced as needed for the texture of the dish. The rind may be use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lemon Pickle
Preserved lemon or lemon pickle is a condiment that is common in the cuisines of Indian subcontinent and Morocco. It's also found in 18th-century English cuisine. It is also known as "country lemon" and ''leems''. Diced, quartered, halved, or whole lemons are pickled in a brine of water, lemon juice, and salt; occasionally spices are included as well.Herbst, Sharon. ''Food Lover's Companion'' (3rd ed), pg 492, Barron's Educational Series Inc. The pickle is allowed to ferment at room temperature for weeks or months before it is used. The pulp of the preserved lemon can be used in stews and sauces, but it is the peel (zest and pith together) that is most valued. The flavor is mildly tart but intensely lemony. Usage Pieces of pickled lemon may be washed before using to remove any surface salt, or blanched to remove more of the salt and bring out the natural mild sweetness. They may then be sliced, chopped, or minced as needed for the texture of the dish. The rind may be used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horseradish
Horseradish (''Armoracia rusticana'', syn. ''Cochlearia armoracia'') is a perennial plant of the family Brassicaceae (which also includes mustard, wasabi, broccoli, cabbage, and radish). It is a root vegetable, cultivated and used worldwide as a spice and as a condiment. The species is probably native to southeastern Europe and western Asia. Description Horseradish grows up to tall, with hairless bright green unlobed leaves up to long that may be mistaken for docks ('' Rumex''). It is cultivated primarily for its large, white, tapered root. The white four-petalled flowers are scented and are borne in dense panicles. Established plants may form extensive patches and may become invasive unless carefully managed. Intact horseradish root has little aroma. When cut or grated, enzymes from within the plant cells digest sinigrin (a glucosinolate) to produce allyl isothiocyanate (mustard oil), which irritates the mucous membranes of the sinuses and eyes. Once exposed to air or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maria Rundell
Maria Eliza Rundell (née Ketelby; 1745 – 16 December 1828) was an English writer. Little is known about most of her life, but in 1805, when she was over 60, she sent an unedited collection of recipes and household advice to John Murray, of whose family—owners of the John Murray publishing house—she was a friend. She asked for, and expected, no payment or royalties. Murray published the work, ''A New System of Domestic Cookery'', in November 1805. It was a huge success and several editions followed; the book sold around half a million copies in Rundell's lifetime. The book was aimed at middle-class housewives. In addition to dealing with food preparation, it offers advice on medical remedies and how to set up a home brewery and includes a section entitled "Directions to Servants". The book contains an early recipe for tomato sauce—possibly the first—and the first recipe in print for Scotch eggs. Rundell also advises readers on being economical with their food and avo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allspice
Allspice, also known as Jamaica pepper, myrtle pepper, pimenta, or pimento, is the dried unripe berry (botany), berry of ''Pimenta dioica'', a Canopy (forest), midcanopy tree native to the Greater Antilles, southern Mexico, and Central America, now cultivated in many warm parts of the world. The name ''allspice'' was coined as early as 1621 by the English, who valued it as a spice that combined the flavours of cinnamon, nutmeg, and clove. Several unrelated fragrant shrubs are called "Carolina allspice" (''Calycanthus floridus''), "Japanese allspice" (''Chimonanthus praecox''), or "wild allspice" (''Lindera benzoin''). Production Allspice is the dried fruit of the ''Pimenta dioica'' plant. The fruits are picked when green and unripe, and are traditionally Drying (food), dried in the sun. When dry, they are brown and resemble large, smooth Black pepper, peppercorns. Fresh leaves are similar in texture to Bay Laurel, bay leaves and similarly used in cooking. Leaves and wood are o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rape-vinegar
Vinegar is an aqueous solution of acetic acid and trace compounds that may include flavorings. Vinegar typically contains 5–8% acetic acid by volume. Usually, the acetic acid is produced by a double fermentation, converting simple sugars to ethanol using yeast, and ethanol to acetic acid by acetic acid bacteria. Many types of vinegar are available, depending on source materials. It is now mainly used in the culinary arts as a flavorful, acidic cooking ingredient, or in pickling. Various types are used as condiments or garnishes, including balsamic vinegar and malt vinegar. As the most easily manufactured mild acid, it has a wide variety of industrial and domestic uses, including use as a household cleaner. Etymology The word "vinegar" arrived in Middle English from Old French (''vyn egre''; sour wine), which in turn derives from Latin: ''vinum'' (wine) + ''acer'' (sour). Chemistry The conversion of ethanol (CH3CH2OH) and oxygen (O2) to acetic acid (CH3COOH) takes place b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
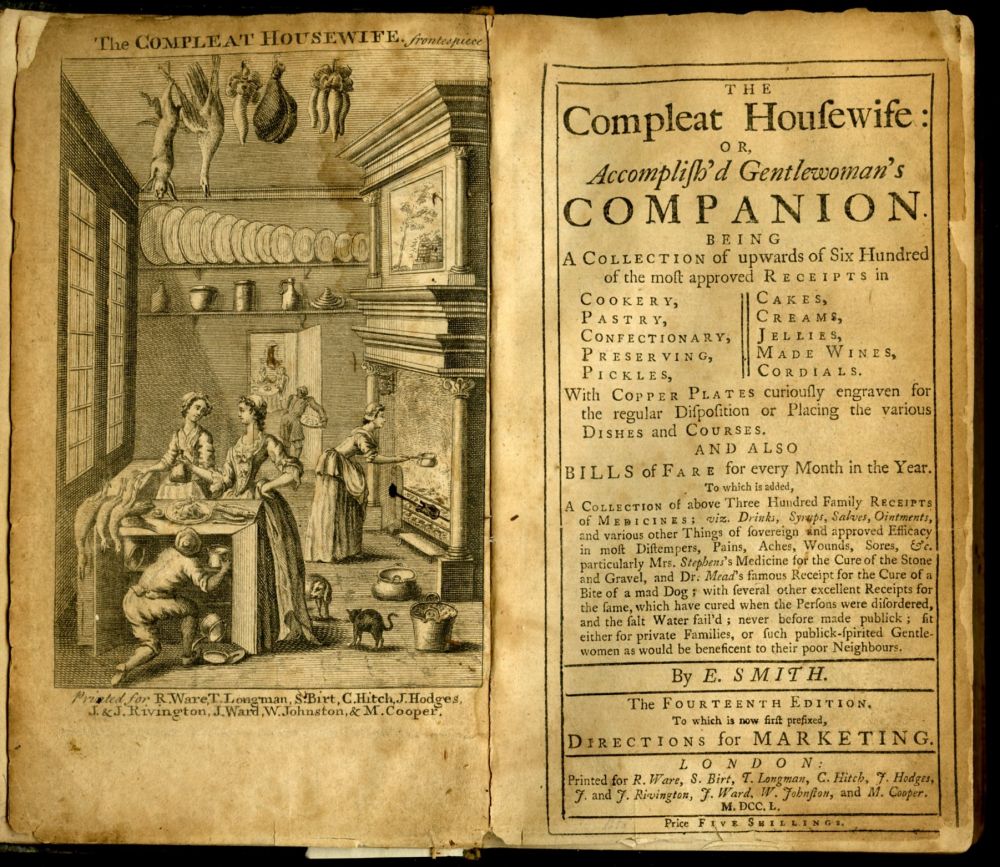
A New System Of Domestic Cookery
''A New System of Domestic Cookery'', first published in 1806 by Maria Rundell (1745 – 16 December 1828), was the most popular English cookbook of the first half of the nineteenth century; it is often referred to simply as "Mrs Rundell", but its full title is ''A New System of Domestic Cookery: Formed Upon Principles of Economy; and Adapted to the Use of Private Families''. Mrs Rundell has been called "the original domestic goddess" and her book "a publishing sensation" and "the most famous cookery book of its time". It ran to over 67 editions; the 1865 edition had grown to 644 pages, and earned two thousand guineas. Book The first edition of 1806 was a short collection of Mrs Rundell's recipes published by John Murray. It went through dozens of editions, both legitimate and pirated, in both Britain and the United States, where the first edition was published in 1807. The frontispiece typically credited the authorship to "A Lady". Later editions continued for some forty y ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Murray (publishing House)
John Murray is a British publisher, known for the authors it has published in its long history including, Jane Austen, Sir Arthur Conan Doyle, Lord Byron, Charles Lyell, Johann Wolfgang von Goethe, Herman Melville, Edward Whymper, Thomas Malthus, David Ricardo, and Charles Darwin. Since 2004, it has been owned by conglomerate Lagardère under the Hachette UK brand. Business publisher Nicholas Brealey became an imprint of John Murray in 2015. History The business was founded in London in 1768 by John Murray (1737–1793), an Edinburgh-born Royal Marines officer, who built up a list of authors including Isaac D'Israeli and published the ''English Review''. John Murray the elder was one of the founding sponsors of the London evening newspaper ''The Star'' in 1788. He was succeeded by his son John Murray II, who made the publishing house important and influential. He was a friend of many leading writers of the day and launched the ''Quarterly Review'' in 1809. He was the pub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Veal
Veal is the meat of calves, in contrast to the beef from older cattle. Veal can be produced from a calf of either sex and any breed, however most veal comes from young male calves of dairy breeds which are not used for breeding. Generally, veal is more expensive by weight than beef from older cattle. Veal production is a way to add value to dairy bull calves and to utilize whey solids, a byproduct from the manufacturing of cheese. Definitions and types There are several types of veal, and terminology varies by country. Similar terms are used in the US, including calf, bob, intermediate, milk-fed, and special-fed. Culinary uses In Italian, French and other Mediterranean cuisines, veal is often in the form of cutlets, such as the Italian ''cotoletta'' or the famous Austrian dish Wiener Schnitzel. Some classic French veal dishes include fried ''escalopes'', fried veal ''Grenadines'' (small, thick fillet steaks), stuffed ''paupiettes'', roast joints, and '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salmon
Salmon () is the common name for several list of commercially important fish species, commercially important species of euryhaline ray-finned fish from the family (biology), family Salmonidae, which are native to tributary, tributaries of the North Atlantic (genus ''Salmo'') and North Pacific (genus ''Oncorhynchus'') basin. Other closely related fish in the same family include trout, Salvelinus, char, Thymallus, grayling, Freshwater whitefish, whitefish, lenok and Hucho, taimen. Salmon are typically fish migration, anadromous: they hatch in the gravel stream bed, beds of shallow fresh water streams, migrate to the ocean as adults and live like sea fish, then return to fresh water to reproduce. However, populations of several species are restricted to fresh water throughout their lives. Folklore has it that the fish return to the exact spot where they hatched to spawn (biology), spawn, and tracking studies have shown this to be mostly true. A portion of a returning salmon run ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cookbook
A cookbook or cookery book is a kitchen reference containing recipes. Cookbooks may be general, or may specialize in a particular cuisine or category of food. Recipes in cookbooks are organized in various ways: by course (appetizer, first course, main course, dessert), by main ingredient, by cooking technique, alphabetically, by region or country, and so on. They may include illustrations of finished dishes and preparation steps; discussions of cooking techniques, advice on kitchen equipment, ingredients, and substitutions; historical and cultural notes; and so on. Cookbooks may be written by individual authors, who may be chefs, cooking teachers, or other food writers; they may be written by collectives; or they may be anonymous. They may be addressed to home cooks, to professional restaurant cooks, to institutional cooks, or to more specialized audiences. Some cookbooks are didactic, with detailed recipes addressed to beginners or people learning to cook particular dishes o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grapefruit
The grapefruit (''Citrus'' × ''paradisi'') is a subtropical citrus tree known for its relatively large, sour to semi-sweet, somewhat bitter fruit. The interior flesh is segmented and varies in color from pale yellow to dark pink. Grapefruit is a citrus hybrid originating in Barbados. It is an accidental cross between the sweet orange (''C. sinensis'') and the pomelo or shaddock (''C. maxima''), both of which were introduced from Asia in the 17th century. It has also been called the ''forbidden fruit''. In the past it was referred to as the ''pomelo'', but that term is now mostly used as the common name for ''Citrus maxima''. In 2019, world production of grapefruits (combined with pomelos) was 9.3 million tonnes, of which 53% was in China. Other significant producers include Vietnam, United States and Mexico. Description The evergreen grapefruit trees usually grow to around tall, although they may reach . The leaves are long (up to ), thin, glossy, and dark green. They produc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
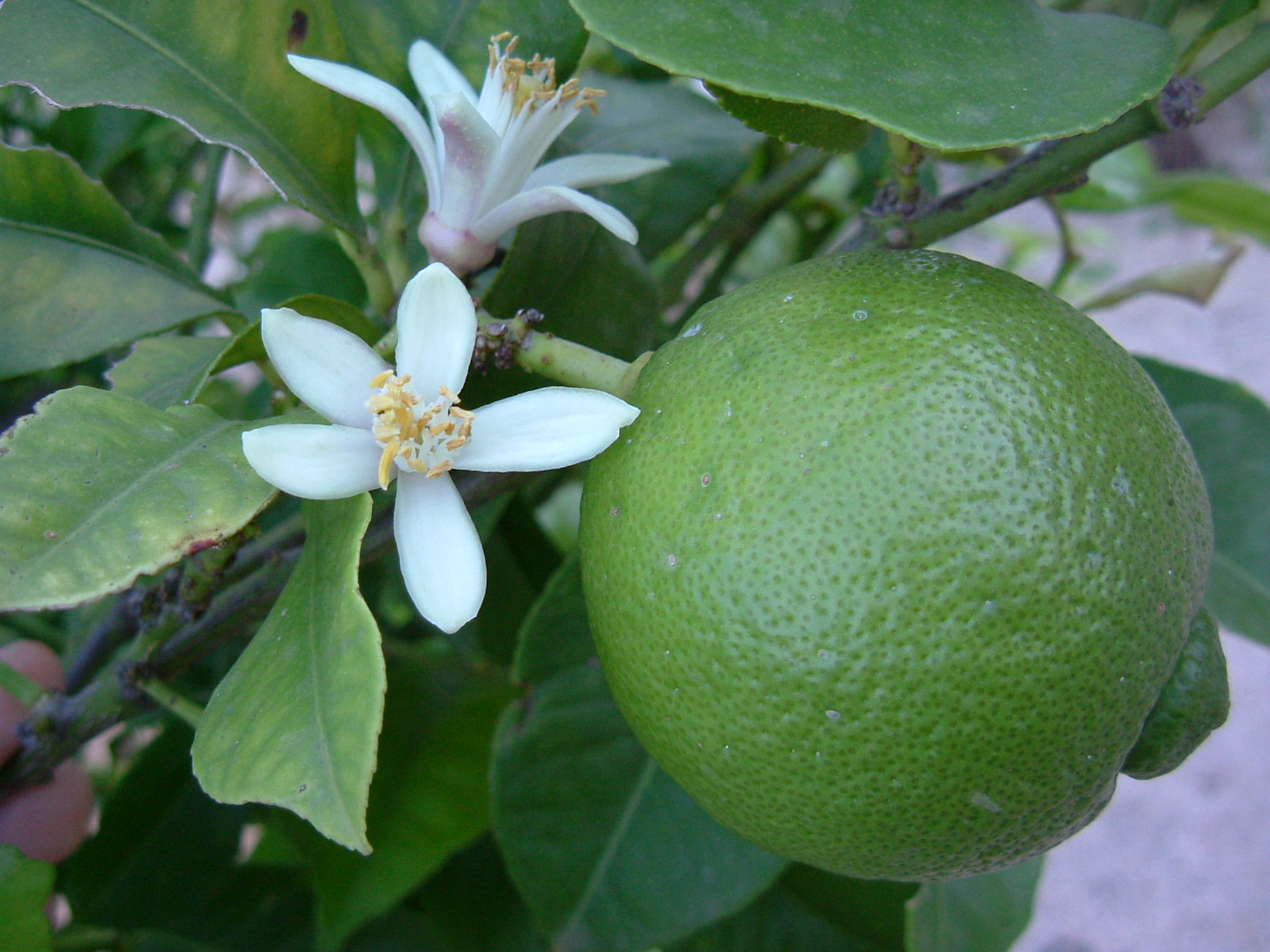
Lime (fruit)
A lime (from French language, French ''lime'', from Arabic ''līma'', from Persian language, Persian ''līmū'', "lemon") is a citrus fruit, which is typically round, lime (color), green in color, in diameter, and contains acidic juice vesicles. There are several species of citrus trees whose fruits are called limes, including the Key lime (''Citrus aurantiifolia''), Persian lime, kaffir lime, Makrut lime, and Citrus glauca, desert lime. Limes are a rich source of vitamin C, are sour, and are often used to accent the flavours of foods and beverages. They are grown year-round. Plants with fruit called "limes" have diverse genetic origins; limes do not form a monophyletic group. Plants known as "lime" The difficulty in identifying exactly which species of fruit are called lime in different parts of the English-speaking world (and the same problem applies to synonyms in other European languages) is increased by the botanical complexity of the citrus genus itself, to which the m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |