|
Prenalterol
Prenalterol is a cardiac stimulant which acts as a β1 adrenoreceptor agonist. Synthesis Stereospecific Prenalterol exhibits adrenergic agonist activity in spite of an interposed oxymethylene group. The stereospecific synthesis devised for this molecule relies on the fact that the side chain is very similar in oxidation state to that of a sugar. Condensation of monobenzone (2) with the epoxide derived from α-D-glucofuranose affords the glycosylated derivative (3). Hydrolytic removal of the acetonide protecting groups followed by cleavage of the sugar with periodate gives aldehyde (4). This is reduced to the glycol by means of NaBH4 and the terminal alcohol is converted to the mesylate (5). Displacement of the leaving group with isopropylamine followed by hydrogenolytic removal of the ''O''-benzyl ether affords the β1-adrenergic selective adrenergic agonist prenalterol (6). Racemic Prepns of the racemic mixture: corresp to H. Köppe et al., (1965, 1972 both to Boehringer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prenalterol Synthesis
Prenalterol is a cardiac stimulant which acts as a β1 adrenoreceptor agonist. Synthesis Stereospecific Prenalterol exhibits adrenergic agonist activity in spite of an interposed oxymethylene group. The stereospecific synthesis devised for this molecule relies on the fact that the side chain is very similar in oxidation state to that of a sugar. Condensation of monobenzone (2) with the epoxide derived from α-D-glucofuranose affords the glycosylated derivative (3). Hydrolytic removal of the acetonide protecting groups followed by cleavage of the sugar with periodate gives aldehyde (4). This is reduced to the glycol by means of NaBH4 and the terminal alcohol is converted to the mesylate (5). Displacement of the leaving group with isopropylamine followed by hydrogenolytic removal of the ''O''-benzyl ether affords the β1-adrenergic selective adrenergic agonist prenalterol (6). Racemic Prepns of the racemic mixture: corresp to H. Köppe et al., (1965, 1972 both to Boehringer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oral Administration
Oral administration is a route of administration where a substance is taken through the mouth. Per os abbreviated to P.O. is sometimes used as a direction for medication to be taken orally. Many medications are taken orally because they are intended to have a systemic effect, reaching different parts of the body via the bloodstream, for example. Oral administration can be easier and less painful than other routes, such as injection. However, the onset of action is relatively low, and the effectiveness is reduced if it is not absorbed properly in the digestive system, or if it is broken down by digestive enzymes before it can reach the bloodstream. Some medications may cause gastrointestinal side effects, such as nausea or vomiting, when taken orally. Oral administration can also only be applied to conscious patients, and patients willing and able to swallow. Terminology ''Per os'' (; ''P.O.'') is an adverbial phrase meaning literally from Latin "through the mouth" or "by mouth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
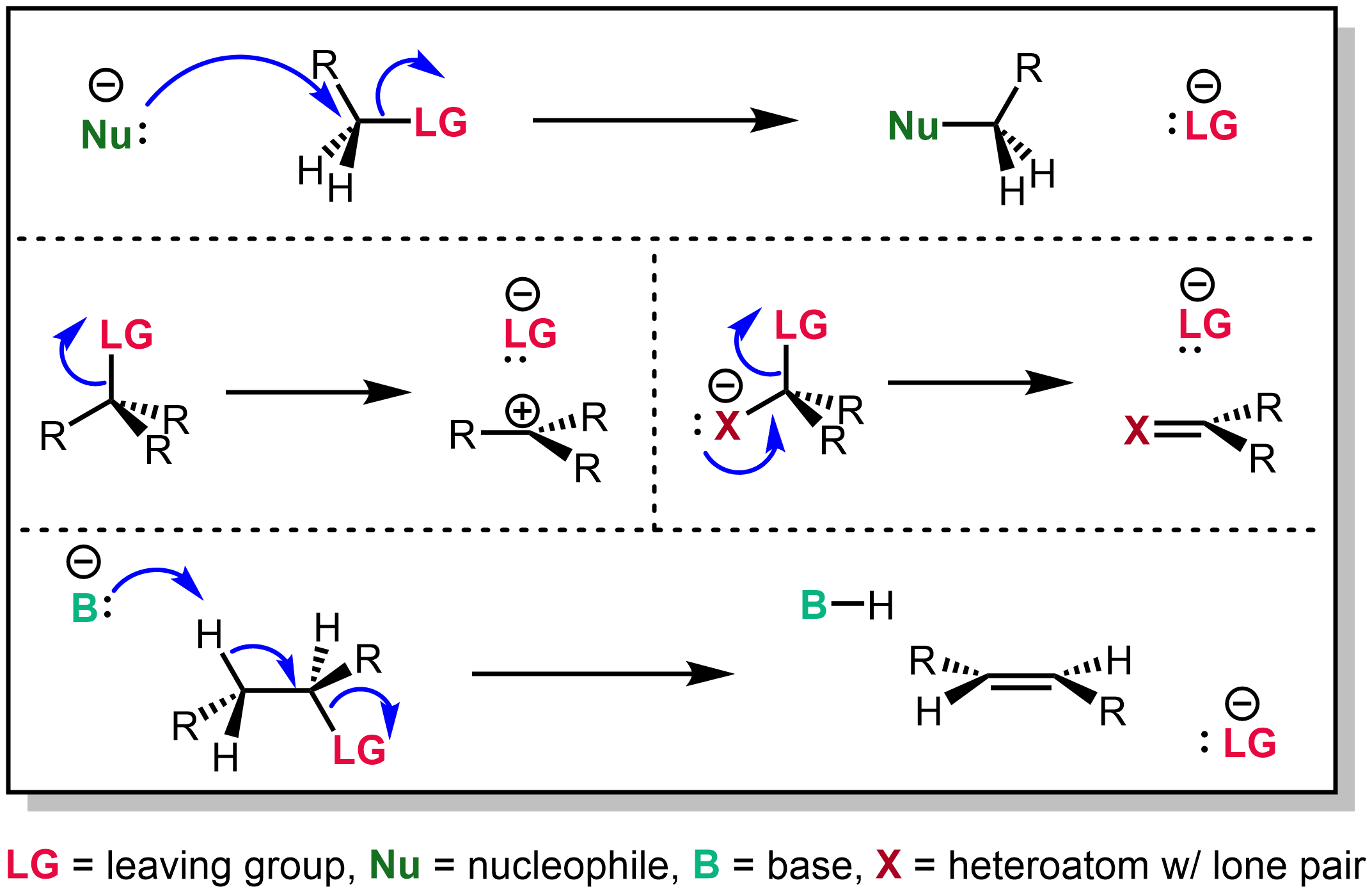
Leaving Group
In chemistry, a leaving group is defined by the IUPAC as an atom or group of atoms that detaches from the main or residual part of a substrate during a reaction or elementary step of a reaction. However, in common usage, the term is often limited to a fragment that departs with a pair of electrons in heterolytic bond cleavage. In this usage, a leaving group is a less formal but more commonly used synonym of the term '' nucleofuge''. In this context, leaving groups are generally anions or neutral species, departing from a neutral or cationic substrates, respectively, though in rare cases, cations leaving from a dicationic substrate are also known. A species' ability to serve as a leaving group depends on its ability to stabilize the additional electron density that results from bond heterolysis. Common anionic leaving groups are halides such as Cl−, Br−, and I−, and sulfonate esters such as tosylate (TsO−), while water (H2O), alcohols (HOR), and amines (R3N) are common neutr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inotropic Agents
An inotrope is an agent that alters the force or energy of muscular contractions. Negatively inotropic agents weaken the force of muscular contractions. Positively inotropic agents increase the strength of muscular contraction. The term ''inotropic state'' is most commonly used in reference to various drugs that affect the strength of contraction of heart muscle. However, it can also refer to pathological conditions. For example, enlarged heart muscle can increase inotropic state, whereas dead heart muscle can decrease it. Medical uses Both positive and negative inotropes are used in the management of various cardiovascular conditions. The choice of agent depends largely on specific pharmacological effects of individual agents with respect to the condition. One of the most important factors affecting inotropic state is the level of calcium in the cytoplasm of the muscle cell. Positive inotropes usually increase this level, while negative inotropes decrease it. However, not al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiac Stimulants
The heart is a muscular organ in most animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels of the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the body, while carrying metabolic waste such as carbon dioxide to the lungs. In humans, the heart is approximately the size of a closed fist and is located between the lungs, in the middle compartment of the chest. In humans, other mammals, and birds, the heart is divided into four chambers: upper left and right atria and lower left and right ventricles. Commonly the right atrium and ventricle are referred together as the right heart and their left counterparts as the left heart. Fish, in contrast, have two chambers, an atrium and a ventricle, while most reptiles have three chambers. In a healthy heart blood flows one way through the heart due to heart valves, which prevent backflow. The heart is enclosed in a protective sac, the pericardium, which also contains a small amount of fluid. The wall of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amines
In chemistry, amines (, ) are compounds and functional groups that contain a basic nitrogen atom with a lone pair. Amines are formally derivatives of ammonia (), wherein one or more hydrogen atoms have been replaced by a substituent such as an alkyl or aryl group (these may respectively be called alkylamines and arylamines; amines in which both types of substituent are attached to one nitrogen atom may be called alkylarylamines). Important amines include amino acids, biogenic amines, trimethylamine, and aniline; Inorganic derivatives of ammonia are also called amines, such as monochloramine (). The substituent is called an amino group. Compounds with a nitrogen atom attached to a carbonyl group, thus having the structure , are called amides and have different chemical properties from amines. Classification of amines Amines can be classified according to the nature and number of substituents on nitrogen. Aliphatic amines contain only H and alkyl substituents. Aromatic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Secondary Alcohols
In chemistry, an alcohol is a type of organic compound that carries at least one hydroxyl () functional group bound to a saturated carbon atom. The term ''alcohol'' originally referred to the primary alcohol ethanol (ethyl alcohol), which is used as a drug and is the main alcohol present in alcoholic drinks. An important class of alcohols, of which methanol and ethanol are the simplest examples, includes all compounds which conform to the general formula . Simple monoalcohols that are the subject of this article include primary (), secondary () and tertiary () alcohols. The suffix ''-ol'' appears in the IUPAC chemical name of all substances where the hydroxyl group is the functional group with the highest priority. When a higher priority group is present in the compound, the prefix ''hydroxy-'' is used in its IUPAC name. The suffix ''-ol'' in non-IUPAC names (such as paracetamol or cholesterol) also typically indicates that the substance is an alcohol. However, some compound ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xamoterol
Xamoterol is a cardiac stimulant. It works by binding to the β1 adrenergic receptor. It is a 3rd generation adrenergic β receptor partial agonist In pharmacology, partial agonists are drugs that bind to and activate a given receptor, but have only partial efficacy at the receptor relative to a full agonist. They may also be considered ligands which display both agonistic and antagonistic e .... It provides cardiac stimulation at rest but it acts as a blocker during exercise. References Beta1-adrenergic agonists Cardiac stimulants Inotropic agents 4-Morpholinyl compunds Phenol ethers Phenols {{cardiovascular-drug-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primidolol
Primidolol is a beta adrenergic receptor antagonist Beta blockers, also spelled β-blockers, are a class of medications that are predominantly used to manage abnormal heart rhythms, and to protect the heart from a second heart attack after a first heart attack (secondary prevention). They are al .... References Beta blockers Pyrimidinediones {{cardiovascular-drug-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imperial Chemical Industries
Imperial Chemical Industries (ICI) was a British chemical company. It was, for much of its history, the largest manufacturer in Britain. It was formed by the merger of four leading British chemical companies in 1926. Its headquarters were at Millbank in London. ICI was a constituent of the FT 30 and later the FTSE 100 indices. ICI made general chemicals, plastics, paints, pharmaceuticals and speciality products, including food ingredients, speciality polymers, electronic materials, fragrances and flavourings. In 2008, it was acquired by AkzoNobel, which immediately sold parts of ICI to Henkel and integrated ICI's remaining operations within its existing organisation. History Development of the business (1926–1944) The company was founded in December 1926 from the merger of four companies: Brunner Mond, Nobel Explosives, the United Alkali Company, and British Dyestuffs Corporation. It established its head office at Millbank in London in 1928. Competing with DuPont a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boehringer Ingelheim
C.H. Boehringer Sohn AG & Co. is the parent company of the Boehringer Ingelheim group, which was founded in 1885 by Albert Boehringer in Ingelheim am Rhein, Germany. As of 2018, Boehringer Ingelheim is one of the world's largest pharmaceutical companies, and the largest private one. Headquartered in Ingelheim, it operates globally with 146 affiliates and more than 47,700 employees. Unlike most large pharmaceutical companies which are listed, the company is private and fully owned by the Boehringer, Liebrecht and von Baumbach families. The company's key areas of interest are: respiratory diseases, metabolism, immunology, oncology and diseases of the central nervous system. Boehringer Ingelheim is a full member of the European Federation of Pharmaceutical Industries and Associations (EFPIA). The corporate logo of Boehringer Ingelheim depicts a stylized rendition of the central section of the imperial palace of Charlemagne. History 1885–1999 *1885: Albert Boehringer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |