|
Pravdinsk, Balakhna
Pravdinsk (russian: Пра́вдинск) was an urban locality (an urban-type settlement) in Balakhninsky District of Nizhny Novgorod Oblast, located a few kilometers northwest (upstream along the Volga) from the town of Balakhna. Pravdinsk was annexed by Balakhna in 1993, although the name continues in informal usage. Pravdinsk commuter train station (on the Zavolzhye-Nizhny Novgorod line) maintains its name as well. The settlement was built along with a paper mill, "Pravdinsk Cellulose and Paper Combine" (), now known as OAO Volga, which still produces about one third of Russia's newsprint. The plant and the settlement were named after the ''Pravda ''Pravda'' ( rus, Правда, p=ˈpravdə, a=Ru-правда.ogg, "Truth") is a Russian broadsheet newspaper, and was the official newspaper of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union, when it was one of the most influential papers in the ...'' newspaper, one of the main consumers of the newsprint produced by the mill. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
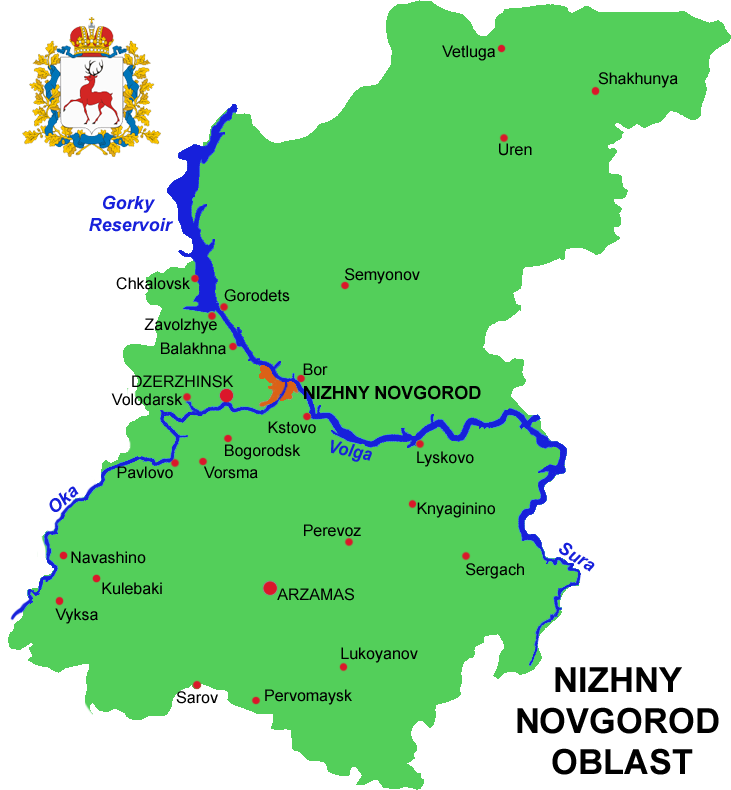
Nizhny Novgorod Oblast
Nizhny Novgorod Oblast (russian: link=no, Нижегородская область, ''Nizhegorodskaya oblast''), is a federal subject of Russia (an oblast). Its administrative center is the city of Nizhny Novgorod. It has a population of 3,310,597 as of the 2010 Census. From 1932 to 1990 it was known as Gorky Oblast. The oblast is crossed by the Volga River. Apart from Nizhny Novgorod's metropolitan area (including Dzerzhinsk, Bor and Kstovo) the biggest city is Arzamas. Near the town of Sarov there is the Serafimo-Diveyevsky Monastery, one of the largest convents in Russia, established by Saint Seraphim of Sarov. The Makaryev Monastery opposite of the town of Lyskovo used to be the location of the largest fair in Eastern Europe. Other historic towns include Gorodets and Balakhna, located on the Volga to the north from Nizhny Novgorod. Geography The oblast covers an area of , which is approximately equal to the entire area of the Benelux countries or Czech Republ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Balakhninsky District
Balakhninsky District (russian: Балахни́нский райо́н) is an administrative district (raion), one of the forty in Nizhny Novgorod Oblast, Russia.Order #3-od Municipally, it is incorporated as Balakhninsky Municipal District.Resolution #670 It is located in the west of the oblast. The area of the district is . Its administrative center is the town of Balakhna Balakhna (russian: Балахна́) is a town and the administrative center of Balakhninsky District in Nizhny Novgorod Oblast, Russia, located on the right bank of the Volga River, north of Nizhny Novgorod, the administrative center of .... Population: 77,598 ( 2010 Census); The population of Balakhna accounts for 66.4% of the district's total population. History The district was established in 1929. References Notes Sources * * {{Use mdy dates, date=September 2012 Districts of Nizhny Novgorod Oblast States and territories established in 1929 __NOTOC__ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Types Of Inhabited Localities In Russia
The classification system of human settlement, inhabited localities in Russia and some other post-Soviet Union, Soviet states has certain peculiarities compared with those in other countries. Classes During the Soviet Union, Soviet time, each of the republics of the Soviet Union, including the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic, Russian SFSR, had its own legislative documents dealing with classification of inhabited localities. After the history of the Soviet Union (1985-1991), dissolution of the Soviet Union, the task of developing and maintaining such classification in Russia was delegated to the federal subjects of Russia, federal subjects.Articles 71 and 72 of the Constitution of Russia do not name issues of the administrative and territorial structure among the tasks handled on the federal level or jointly with the governments of the federal subjects. As such, all federal subjects pass :Subtemplates of Template RussiaAdmMunRef, their own laws establishing the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urban-type Settlement
Urban-type settlementrussian: посёлок городско́го ти́па, translit=posyolok gorodskogo tipa, abbreviated: russian: п.г.т., translit=p.g.t.; ua, селище міського типу, translit=selyshche mis'koho typu, abbreviated: uk, с.м.т., translit=s.m.t.; be, пасёлак гарадскога тыпу, translit=pasiolak haradskoha typu; pl, osiedle typu miejskiego; bg, селище от градски тип, translit=selishte ot gradski tip; ro, așezare de tip orășenesc. is an official designation for a semi-urban settlement (previously called a "town"), used in several Eastern European countries. The term was historically used in Bulgaria, Poland, and the Soviet Union, and remains in use today in 10 of the post-Soviet states. The designation was used in all 15 member republics of the Soviet Union from 1922, when it replaced a number of terms that could have been translated by the English term "town" (Russia – '' posad'', Ukraine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volga River
The Volga (; russian: Во́лга, a=Ru-Волга.ogg, p=ˈvoɫɡə) is the longest river in Europe. Situated in Russia, it flows through Central Russia to Southern Russia and into the Caspian Sea. The Volga has a length of , and a catchment area of «Река Волга» , Russian State Water Registry which is more than twice the size of . It is also Europe's largest river in terms of average at delta – between and – and of |
Balakhna, Balakhninsky District, Nizhny Novgorod Oblast
Balakhna (russian: Балахна́) is a town and the administrative center of Balakhninsky District in Nizhny Novgorod Oblast, Russia, located on the right bank of the Volga River, north of Nizhny Novgorod, the administrative center of the oblast. Population: 33,500 (1968). It was previously known as ''Sol-na-Gorodtse''. Overview It was founded in 1474 as Sol-na-Gorodtse (). After the Khan of Kazan razed it to the ground in 1536, a wooden fort was constructed to protect the settlement against further Tatar incursions. For the following three centuries, Balakhna prospered as a center of saltworks and grain trade. By the Time of Troubles, it was the twelfth largest city in Russia. Adam Olearius visited and described the town in 1636. That year several shipwrights from Holstein built the first Russian ships here, thus establishing Balakhna as a foremost center of national river shipbuilding. The people of Balakhna were also reputed for their skills in knitting and making colo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zavolzhye, Nizhny Novgorod Oblast
Zavolzhye (russian: Заво́лжье) is a town in Gorodetsky District of Nizhny Novgorod Oblast, Russia, located on the right bank of the Volga River, opposite Gorodets, Nizhny Novgorod Oblast, Gorodets, the administrative centre of the district, and northwest of Nizhny Novgorod, the administrative center of the oblast. Population: Etymology The name of the town literally means ''"[the lands] beyond the Volga"'', i.e., on the river's ''left'' bank, since "beyond" here is taken relative to the historically more populated right bank of the river. Thus, Zavolzhye—the region in Nizhny Novgorod Oblast—normally refers to its forested and sparsely populated northeastern half. This makes the name of the town of Zavolzhye somewhat confusing for some people in the region, since the city is located on the ''right'' side of the river—it is only "beyond the river" with respect to much older Gorodets, Nizhny Novgorod Oblast, Gorodets. History It was founded in 1950 as a settlement ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nizhny Novgorod
Nizhny Novgorod ( ; rus, links=no, Нижний Новгород, a=Ru-Nizhny Novgorod.ogg, p=ˈnʲiʐnʲɪj ˈnovɡərət ), colloquially shortened to Nizhny, from the 13th to the 17th century Novgorod of the Lower Land, formerly known as Gorky (, ; 1932–1990), is the administrative centre of Nizhny Novgorod Oblast and the Volga Federal District. The city is located at the confluence of the Oka and the Volga rivers in Central Russia, with a population of over 1.2 million residents, up to roughly 1.7 million residents in the urban agglomeration. Nizhny Novgorod is the sixth-largest city in Russia, the second-most populous city on the Volga, as well as the Volga Federal District. It is an important economic, transportation, scientific, educational and cultural center in Russia and the vast Volga-Vyatka economic region, and is the main center of river tourism in Russia. In the historic part of the city there are many universities, theaters, museums and churches. The city ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paper Mill
A paper mill is a factory devoted to making paper from vegetable fibres such as wood pulp, old rags, and other ingredients. Prior to the invention and adoption of the Fourdrinier machine and other types of paper machine that use an endless belt, all paper in a paper mill was made by hand, one sheet at a time, by specialized laborers. History Historical investigations into the origin of the paper mill are complicated by differing definitions and loose terminology from modern authors: Many modern scholars use the term to refer indiscriminately to all kinds of Mill (grinding), mills, whether powered by humans, Horse mill, by animals or Watermill, by water. Their propensity to refer to any ancient paper manufacturing center as a "mill", without further specifying its exact power source, has increased the difficulty of identifying the particularly efficient and historically important water-powered type. Human and animal-powered mills The use of human and animal powered mills w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Newsprint
Newsprint is a low-cost, non-archival paper consisting mainly of wood pulp and most commonly used to print newspapers and other publications and advertising material. Invented in 1844 by Charles Fenerty of Nova Scotia, Canada, it usually has an off white cast and distinctive feel. It is designed for use in printing presses that employ a long web of paper ( web offset, letterpress and flexographic), rather than individual sheets of paper. Newsprint is favored by publishers and printers as it is relatively low cost (compared with paper grades used for glossy magazines and sales brochures), strong (to run through modern high-speed web printing presses) and can accept four-color printing at qualities that meet the needs of typical newspapers. Invention Charles Fenerty began experimenting with wood pulp around 1838, making his discovery in 1844. On October 26, 1844, Fenerty took a sample of his paper to Halifax's top newspaper, the '' Acadian Recorder'', where he had written a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pravda
''Pravda'' ( rus, Правда, p=ˈpravdə, a=Ru-правда.ogg, "Truth") is a Russian broadsheet newspaper, and was the official newspaper of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union, when it was one of the most influential papers in the country with a circulation of 11 million. The newspaper began publication on 5 May 1912 in the Russian Empire, but was already extant abroad in January 1911. It emerged as a leading newspaper of the Soviet Union after the October Revolution. The newspaper was an organ of the Central Committee of the CPSU between 1912 and 1991. After the dissolution of the Soviet Union ''Pravda'' was sold off by Russian President Boris Yeltsin to a Greek business family in 1996, and the paper came under the control of their private company Pravda International. In 1996, there was an internal dispute between the owners of Pravda International and some of the ''Pravda'' journalists which led to ''Pravda'' splitting into different entities. The Communis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pravdinsk (air Base)
Istomino Airfield is a private general aviation airfield located 5 km northwest of Balakhna and 38 km northwest of Nizhny Novgorod, Nizhny Novgorod Oblast, Russia. The airfield is formerly Pravdinsk Air Base, a military airbase of the Russian Air Force and was named after the nearby town of Pravdinsk. It was a small air base with a few taxiways and tarmac. Units that were stationed at Pravdinsk include 786th Interceptor Aviation Regiment (786 IAP) which had 5 Mikoyan-Gurevich MiG-25 (ASCC: Foxbat) aircraft in the 1970s and upgraded to 31 Mikoyan MiG-31 (ASCC: Foxhound) aircraft in the 1980s. In 2004, after five year of disuse, Pravdinsk Airfield (now more often referred to as Istomino Airfield (Аэродром Истомино), after the nearby village) saw an aircraft again. Now the airfield is used by Nizhny Novgorod parachute sports enthusiasts, who praise it as an excellent drop zone A drop zone (DZ) is a place where parachutists or parachuted supplies la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |