|
PowerBasic
PowerBASIC, formerly Turbo Basic, is the brand of several commercial compilers by PowerBASIC Inc. that compile a dialect of the BASIC programming language. There are both MS-DOS and Microsoft Windows, Windows versions, and two kinds of the latter: Console and Windows. The MS-DOS version has a syntax similar to that of QBasic and QuickBASIC. The Windows versions use a BASIC syntax expanded to include many Windows functions, and the statements can be combined with calls to the Windows API. History The first version of the DOS compiler was published as BASIC/Z, the very first interactive compiler for CP/M and MDOS. Later it was extended to MS-DOS/PC DOS and in 1987 Borland distributed it as ''Turbo Basic''. ''Turbo Basic'' was originally created by Robert "Bob" Zale (1945–2012) and bought from him by Borland. When Borland decided to stop publishing it (1989), Zale bought it back from them, renamed it PowerBASIC and set up PowerBASIC Inc. to continue support and development o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
QuickBASIC
Microsoft QuickBASIC (also QB) is an Integrated Development Environment (or IDE) and compiler for the BASIC programming language that was developed by Microsoft. QuickBASIC runs mainly on DOS, though there was also a short-lived version for the classic Mac OS. It is loosely based on GW-BASIC but adds user-defined types, improved programming structures, better graphics and disk support and a compiler in addition to the BASIC interpreter, interpreter. Microsoft marketed QuickBASIC as the introductory level for their BASIC Professional Development System. Microsoft marketed two other similar IDEs for C and Pascal, viz QuickC and QuickPascal. History Microsoft released the first version of QuickBASIC on August 18, 1985 on a single 5.25-inch 360 KB floppy disk. QuickBASIC version 2.0 and later contained an Integrated Development Environment (IDE), allowing users to edit directly in its on-screen text editor. Although still supported in QuickBASIC, line numbers became optional. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Borland
Borland Software Corporation was a computing technology company founded in 1983 by Niels Jensen, Ole Henriksen, Mogens Glad, and Philippe Kahn. Its main business was developing and selling software development and software deployment products. Borland was first headquartered in Scotts Valley, California, then in Cupertino, California, and then in Austin, Texas. In 2009, the company became a full subsidiary of the British firm Micro Focus International plc. In 2023, Micro Focus (including Borland) was acquired by Canadian firm OpenText, which later absorbed Borland's portfolio into its application delivery management division. History The 1980s: Foundations Borland Ltd. was founded in August 1981 by three Danes, Danish citizens Niels Jensen, Ole Henriksen, and Mogens Glad to develop products like Word Index for the CP/M operating system using an off-the-shelf company. However, the response to the company's products at the CP/M-82 show in San Francisco showed that a U.S. company ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
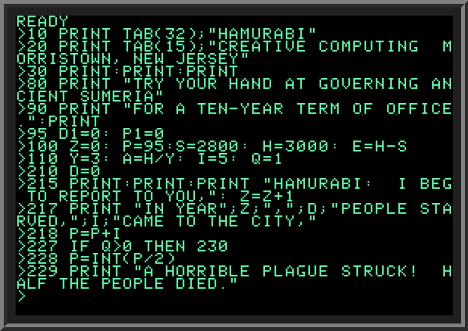
BASIC Interpreter
A BASIC interpreter is an Interpreter (computing), interpreter that enables users to enter and run programs in the BASIC programming language, language and was, for the first part of the microcomputer era, the default Application software, application that computers would launch. Users were expected to use the BASIC interpreter to type-in programs, type in programs or to load programs from storage (initially cassette tapes then floppy disks). BASIC interpreters are of historical importance. Microsoft's first product for sale was a BASIC interpreter (Altair BASIC), which paved the way for the company's success. Before Altair BASIC, microcomputers were sold as kits that needed to be programmed in machine code (for instance, the Apple I). During the Altair period, BASIC interpreters were sold separately, becoming the first software sold to individuals rather than to organizations; Apple BASIC was Apple's first software product. After the Altair 8800, MITS Altair 8800, microcomputers w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MS-DOS
MS-DOS ( ; acronym for Microsoft Disk Operating System, also known as Microsoft DOS) is an operating system for x86-based personal computers mostly developed by Microsoft. Collectively, MS-DOS, its rebranding as IBM PC DOS, and a few operating systems attempting to be compatible with MS-DOS, are sometimes referred to as "DOS" (which is also the generic acronym for disk operating system). MS-DOS was the main operating system for IBM PC compatibles during the 1980s, from which point it was gradually superseded by operating systems offering a graphical user interface (GUI), in various generations of the graphical Microsoft Windows operating system. IBM licensed and re-released it in 1981 as PC DOS 1.0 for use in its PCs. Although MS-DOS and PC DOS were initially developed in parallel by Microsoft and IBM, the two products diverged after twelve years, in 1993, with recognizable differences in compatibility, syntax and capabilities. Beginning in 1988 with DR-DOS, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DOS MZ Executable
The DOS MZ executable format is the executable file format used for .EXE files in DOS. The file can be identified by the ASCII string "MZ" (hexadecimal: 4D 5A) at the beginning of the file (the " magic number"). "MZ" are the initials of Mark Zbikowski, one of the leading developers of MS-DOS. . "Every PE file begins with a small MS-DOS executable. ... The first bytes of a PE file begin with the traditional MS-DOS header, called an IMAGE_DOS_HEADER. The only two values of any importance are e_magic and e_lfanew. ... The e_magic field (a WORD) needs to be set to the value 0x5A4D. ... In ASCII representation, 0x5A4D is MZ, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Integrated Development Environment
An integrated development environment (IDE) is a Application software, software application that provides comprehensive facilities for software development. An IDE normally consists of at least a source-code editor, build automation tools, and a debugger. Some IDEs, such as IntelliJ IDEA, Eclipse (software), Eclipse and Lazarus (software), Lazarus contain the necessary compiler, interpreter (computing), interpreter or both; others, such as SharpDevelop and NetBeans, do not. The boundary between an IDE and other parts of the broader software development environment is not well-defined; sometimes a version control system or various tools to simplify the construction of a graphical user interface (GUI) are integrated. Many modern IDEs also have a class browser, an object browser, and a class diagram, class hierarchy diagram for use in object-oriented programming, object-oriented software development. Overview Integrated development environments are designed to maximize progra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Single-precision Floating-point Format
Single-precision floating-point format (sometimes called FP32 or float32) is a computer number format, usually occupying 32 bits in computer memory; it represents a wide dynamic range of numeric values by using a floating radix point. A floating-point variable can represent a wider range of numbers than a fixed-point variable of the same bit width at the cost of precision. A signed 32-bit integer variable has a maximum value of 231 − 1 = 2,147,483,647, whereas an IEEE 754 32-bit base-2 floating-point variable has a maximum value of (2 − 2−23) × 2127 ≈ 3.4028235 × 1038. All integers with seven or fewer decimal digits, and any 2''n'' for a whole number −149 ≤ ''n'' ≤ 127, can be converted exactly into an IEEE 754 single-precision floating-point value. In the IEEE 754 standard, the 32-bit base-2 format is officially referred to as binary32; it was called single in IEEE 754-1985. IEEE 754 specifies additional floating-point types, such as 64-bit base-2 ''doubl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
String (computer Science)
In computer programming, a string is traditionally a sequence of character (computing), characters, either as a literal (computer programming), literal constant or as some kind of Variable (computer science), variable. The latter may allow its elements to be Immutable object, mutated and the length changed, or it may be fixed (after creation). A string is often implemented as an array data structure of bytes (or word (computer architecture), words) that stores a sequence of elements, typically characters, using some character encoding. More general, ''string'' may also denote a sequence (or List (abstract data type), list) of data other than just characters. Depending on the programming language and precise data type used, a variable (programming), variable declared to be a string may either cause storage in memory to be statically allocated for a predetermined maximum length or employ dynamic allocation to allow it to hold a variable number of elements. When a string appears lit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Structured Programming
Structured programming is a programming paradigm aimed at improving the clarity, quality, and development time of a computer program by making specific disciplined use of the structured control flow constructs of selection ( if/then/else) and repetition ( while and for), block structures, and subroutines. It emerged in the late 1950s with the appearance of the ALGOL 58 and ALGOL 60 programming languages, with the latter including support for block structures. Contributing factors to its popularity and widespread acceptance, at first in academia and later among practitioners, include the discovery of what is now known as the structured program theorem in 1966, and the publication of the influential " Go To Statement Considered Harmful" open letter in 1968 by Dutch computer scientist Edsger W. Dijkstra, who coined the term "structured programming". Structured programming is most frequently used with deviations that allow for clearer programs in some particular cases, such as whe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ALGOL
ALGOL (; short for "Algorithmic Language") is a family of imperative computer programming languages originally developed in 1958. ALGOL heavily influenced many other languages and was the standard method for algorithm description used by the Association for Computing Machinery (ACM) in textbooks and academic sources for more than thirty years. In the sense that the syntax of most modern languages is "Algol-like", it was arguably more influential than three other high-level programming languages among which it was roughly contemporary: FORTRAN, Lisp, and COBOL. It was designed to avoid some of the perceived problems with FORTRAN and eventually gave rise to many other programming languages, including PL/I, Simula, BCPL, B, Pascal, Ada, and C. ALGOL introduced code blocks and the begin...end pairs for delimiting them. It was also the first language implementing nested function definitions with lexical scope. Moreover, it was the first programming language which gave ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |